Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Overview
- 3 How are API called?
- 4 What is API Testing?
- 5 Why is API Testing Important?
- 6 What is API Test Automation and How Does it Work?
- 7 Types of API Testing (With Examples)
- 8 What Exactly Do We Check During API Testing?
- 9 What is the Relationship Between API Testing And API Monitoring?
- 10 What are API Methods?
- 11 What is Meant by Testing API Methods?
- 12 Why Test API Methods?
- 13 How to Test Different API Methods?
- 14 Challenges in Testing Different API Methods.
- 15 Setting Up an API Test Environment:
- 16 How to Test API?
- 17 Types of Output of an API:
- 18 Types of Bugs that API Testing Detects
- 19 Examples of API Tests
- 20 Advantages of API testing
- 21 Best Practices of API Testing
- 22 Challenges of API Testing:
- 23 API Test Automation Strategies & Techniques for Optimizing Quality
- 24 API Testing Tips for Beginners:
- 25 How to Do API Test Automation with Ease in Testsigma?
- 26 What is the Future Of API Testing?
- 27 Closing Thoughts:
Introduction
Welcome to the world of API testing. If you’re reading this, you’re probably looking to learn the basics of testing APIs or wondering how and where to start. This article will help you understand more about APIs, what types of tests you need to perform, and how to execute them and what to validate as part of the testing process.
Overview
What Is API Testing?
API testing ensures that an API works according to specifications, ensuring smooth communication among various software systems.
Types of API Testing
- Functional Testing: Verifying that API is providing appropriate responses for specific requests.
- Performance Evaluation: Analyses an API's capacity to handle high traffic volumes and large data sets.
- Security Testing: Testing an API's protection from unintended access is crucial to its viability.
- Testing API Documentation: Testing to make sure the API reflects what's described in its documentation.
- Regression Testing: Regression testing ensures that changes do not create new errors.
- Fault Tolerance Testing: Assesses how well an API handles unexpected failures or issues.
How Are API Called?
Each user interaction on UI is associated with an API that will be accessed through a URL. Let us say a user fills up a form and clicks on “Send” button, on trigger of this event respective API will be invoked. In the below picture we can see the Request URL is pointing to the endpoint ‘Signup’.
What is API Testing?
Application Program Interface testing is a type of software testing that validates the behavior and performance of an application program interface.
API testing is integral to software development to provide optimal application performance. API, a specialized application programming interface, is a collection of protocols, tools, and functions that facilitate seamless communication between software applications.
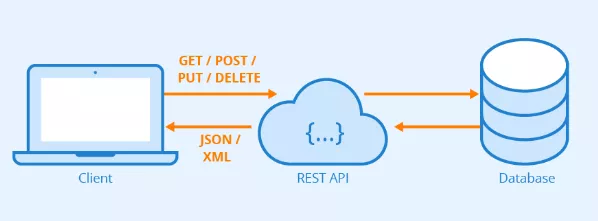
While many software testers perceive working with API as a frightening experience, APIs are the simplest and most non-complicated way of dealing with applications. This article unveils the basic concepts of API testing, intending to make one feel confident and comfortable interacting with APIs.Let us take the first step towards understanding Web APIs with the bird’s view of the client-server diagram. Web application designers use this infamous client-server setup to create a comprehensive picture.
Client/ client-side- includes all the devices used to interact with the application.
The Internet is an enabler; it assists in transporting client requests to the Web server along with relevant details filled in by the user on the client side.
Web-server/server-side is the holy place where all processing takes place. Once the processing is complete, the server pushes the data back to the client.
Why is API Testing Important?
It is important because APIs are the backbone of modern applications and ensure that the different components of the application communicate with each other correctly.
It ensures that the application programming interface (API) performs as expected and fulfills user needs. Through this testing, testers can detect defects and issues in the API, such as incorrect data formats, erroneous responses, or security flaws. Seeing such problems early in the development process allows developers to address them before they become more complex and take longer to resolve.
What is API Test Automation and How Does it Work?
API Test Automation is the process of automating the testing of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). It is a method of ensuring that APIs perform as intended and are secure from potential risks. Using a tool, you can rapidly and efficiently test the APIs to uncover any bugs or vulnerabilities before they become problems. This will help us guarantee that the APIs are dependable and secure while also saving time and money in the long term.
Check here – API Testing Tools
Types of API Testing (with Examples)
When it comes to this testing, the main focus is on verifying the functionality and performance of the API. Basic assertions start from validating the response body, schema, and response codes.
However, other tests need to be performed, such as security testing and performance testing of APIs.
Here are some of the common API testing examples with different types of tests based on which test cases can be created:
- Functional Testing: Functional testing for APIs involves verifying that expected responses and data formats are returned given a specific request. This is done by sending requests to an API and validating that the correct responses are returned. This testing should be done to check that new and existing functionality behaves in the expected manner. For example validating the status code and the response body. Read more on API Functional Testing.
- Performance Testing: This type of testing is used to verify that the API can handle large volumes of data and high traffic. Performance testing is used to measure the speed and responsiveness of the API. This is done by monitoring the API’s uptime, response times, and throughput. For instance, verifying the response time and the response size when the API is under load. When we test for multiple users and multiple requests, we are loading the APIs and trying to analyze the performance of the APIs. Read more on API Performance Testing.
- Security Testing: This type of testing verifies that the API is secure and can protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Security tests are executed to identify security vulnerabilities in an API system, such as cross-site scripting, SQL injection, as well as authentication and authorization controls. The security tests must also identify any security flaws in the infrastructure, such as unencrypted data being transferred or stored, weak passwords, default credentials, and network architecture.
- API Documentation Testing: This type of testing is used to verify that the API is easy to use and understand and it is performing as mentioned in the API documentation. It ensures that the documentation accurately reflects the APIs capabilities and that all of the features are being properly integrated into the product. With API document testing, testers make sure that the API returns the right data, that the parameters and values are properly set, and that the returned data is in the expected format. This is similar to the functional requirement document/specification document validation against the application behavior.
- Regression Testing: This type of testing is used to verify that changes made to the API do not cause unexpected errors or regressions. Testing typically involves sending requests to an API using a variety of test parameters, ensuring that the appropriate response is sent back and any application or database logic is behaving as expected. The Regression Test suite is built and the API automation is implemented. For instance, the bug related to status code is fixed, then the functional validation is also done for that API endpoint.
- Fault Tolerance Testing: This type of testing verifies the system’s ability to respond accurately and promptly when unexpected failures occur. This is done as part of error-handling scenario validation and how the API responds to inputs or requests that could potentially cause harm, such as a denial-of-service attack, input that is too large or complex to process, or logic errors. It is important to test these potential risks, as it will provide insight into the robustness of the API, ensuring that it can handle unpredictable or malicious inputs without crashing.
Other than this we can add the test types based on the project needs and requirements specific to the project.
What Exactly Do We Check During API Testing?
QA testers will evaluate the following parameters during API testing,
- Data Accuracy
- Missing or duplicate functionality
- Authorization checks
- Response time
- Reliability issues
- performance and security issues
- Multithreaded issues
- Error codes if API returns
What is the Relationship between API Testing and API Monitoring?
API testing and API monitoring both aim to maintain API reliability and performance. But, they are performed at different stages of the API lifecycle. API testing is performed during development to identify any issues before it moves to production. On the contrary, API monitoring is done after the API is deployed.
API Monitoring is the process of monitoring APIs, most commonly in the production stage, to track their performance, availability, and functional accuracy.
What Are API Methods?
When we speak of API methods, the Web APIs use HTTP protocol for communication. As we know it follows the client server model, where the client sends the request and the server responds. There are many ways in which HTTP sends requests,which are the HTTP verbs and referred to by the value of their request method property. The important and most commonly used API methods are:
GET request
- This is most common request and it is used to request data from the server
- It retrieves and represents the exact data present and does not modify or perform task
- Even if multiple identical requests are made, it returns the same result, this is called Idempotent
- The Get request follows the read method from the CRUD operations
Example:
- Get API used to load a website or navigate to a landing page
- To get the popular items in a particular category, say latest filter applied for new products under home decor section on a ecommerce website
POST request
- It is used to send the data to the server to create or update a resource, therefore data mutation happens.
- When same request is sent twice, it leads to duplication, it is called Non-Idempotent
- The Post request follows the create method from the CRUD operations
Example:
- When creating a new user account in gmail, it sends a Post request.
- While registering for a webinar on a site, the Post API is used. All the data entered in the field are put in the response body of the request and sent to the server
PUT request
- It is used to send data to the API for creating or updating an existing resource.
- The difference between Put and Post is that the Put API is Idempotent.
- Put will replace the resource in its entirety
Example:
- Editing an existing students record in the student’s portal
DELETE request
- It is used to delete a single or list of resources, more commonly found in RESTful API. It has to be used with caution.
- Multiple identical requests for deleting the same resource will return a 404.
Example:
- Delete API is used to remove the irrelevant user data from the records.
What is Meant by Testing API Methods?
Once the API set up is ready, it is tested based on the API testing methods. There are several ways to test the APIs and that can be done both manually and automated. From developer to testers to the DevOps engineers all create API testing strategy to conduct crucial tests in order to check and validate the API setup and its integration from end to end. Testing individual services or endpoint can be easy, but what is more important is to test the framework completely and eliminate errors in the setup at the earliest
Why Test API Methods?
With a huge number of API requests churned out each day, API testing is needed because it helps in validating if the API setup performs as expected and returns output as intended. The tests will cover API functionality, reliability, performance and security.
The reason why API testing is important is because of the following reasons:
- API testing process is done before UI testing and it helps identify and eliminate most of the server level errors. Also, API testing consumes less testing time and testing cost than GUI testing
- Since the API testing process helps in code-level functionality validation, it helps in identifying the small bugs before it turns into a critical one.
- It helps in securing and optimizing the communication between servers and systems. It also focuses on checking if the business logic laid down is correct at the API level. Since it also includes dealing with sensitive data, checking for API security is crucial. It checks the APIs for compliance and security.
- By ensuring the APIs perform as expected it helps to safeguard the business reputation for quality assurance in the minds of the customer and help them develop trust.
- Checking and aligning the API testing strategy with CI/CD pipeline is important as it provides room for faster release cycle with reduced number of errors.
How to Test Different API Methods?
Manual Ways to Test Apis
In Manual testing, the testing is done manually without the use of test scripts.
Exploratory testing: Just like the name suggests the testers explore the application to identify bugs. Testers could do black box testing by sending the requests to API and check if the desired output is received. In case of white box API testing, the testers usually try to find out and validate the API functions using the source code.
Usability testing: This type of testing depends on the API structure, usability goal and user segment. The API structure has to be reliable and usable. This testing is majorly user-centric, and the testing is carried out mimicking how the target user group would use the software. It helps validate the product’s functionality from the end users perspective.
Ad.hoc testing: It is usually carried out after the formal testing is done. The testers randomly test the product to check for any loopholes. It is done to check the stability of the overall APIs integration. It is mostly done when minor tweaks or new features are added to the product, the testers will right away check the specific update without any pre-defined planning or documentation of test cases.
Automated Ways to Test Apis
In automation testing the tests are automated using automation frameworks or tools.
Functional testing: It is performed to validate if the API performs as expected. The functionality of the API is tested using both positive and negative test scenarios to see if it returns the intended output. The API has to be well built to identify the valid and invalid requests Functional API testing can be a little challenging because of the lack of GUI. So the functional testing testing of API starts with verification of authentication process
Load testing: This is mainly to see how the API functions under heavy traffic. Based on the requirements, it involves stimulating a large amount of request volume and checking the response output and response time (ranging from per second or per minute to per hour) and looking out for errors. It is to check how the API operates under load. Load testing is carried out in regular intervals to record the performance benchmarks and breaking point of the APIs.
Security testing: The APIs along with its basic functionality also have security requirements listed down, such as authentication and access control. It is to protect the data and application from hacker attacks.
Regression testing: Testers prefer regression testing when their application is updated at frequent intervals, for example if new features are added during every sprint, and when there is a need for repeated testing. It helps to save time and efforts in re-running the test scenarios multiple times.
Searching and selecting the right tool and forming an API testing strategy is a crucial step. Testsigma is a low-code test automation platform, where tests are created using NLPs . Since it is low-code it does not require any prior coding knowledge and also helps non-coders to perform testing with ease.
Testsigma also provides Integrated Automated API testing. Testsigma’s API testing capabilities helps automate API testing for web, mobile and desktop applications using Natural Language Programming. It becomes a one stop solution for test management, test authoring, test execution and reporting without expertise in coding languages.
It enables the creation of tests for REST API methods – GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, thereby providing complete all inclusive test coverage for APIs. It also supports data driven API tests and validates expected vs actual responses in real time and reflects the errors in the test status and test reports.
Challenges in Testing Different API Methods.
Aligning the Initial setup of APIs with the requirements and sequencing the API calls is a mandatory step and it takes time and effort. In order to reduce manual intervention in API testing, identifying, automating and validating the tests can be initially challenging.
- Checking the system integration for APIs is a major task performed focusing more on the API design to evaluate its performance and validate each and every response to check if all the API calls are working properly.
- Every time there are changes such as a new feature update or enhancements, it is necessary to keep track of the API tests and the impact on the API test automation process setup.
- Validating the API parameters correctly and setting up required checkpoints is an important step to avoid security or stability issues.
- Updating schema of API tests is a significant step, since schema provides the API syntax and grammar of the test documents, it is important to update the schema accordingly on every update and maintain it through the testing process.
- It is a critical decision making process on choosing the right tool that fits the budget and also meets the API testing requirements.
Setting up an API Test Environment:
It is critical for engineers to set up an API test environment to build and test their applications. It is also critical for organizations to ensure that their APIs are safe and function properly. A local environment ensures confidentiality and anonymity while allowing developers to simply set up, configure, and debug their programs.
Some significant aspects of an API test environment are:
- Setting up a server
- Establishing the APIs
- Creating local accounts for testing
- Configuring the database
- Building a virtual environment for the development
- Integrating other services
Users may easily conduct tests on numerous situations in a well-structured environment before deploying their apps into production.
How to Test API?
A few steps are required to test an API.
Establish a Test Strategy /Plan: The first step is to draft a test plan outlining the tests that will be run. Some projects will require both Test Strategy and Test Plan. Understand more about the API capabilities.
Test Design: The following step is to write test cases for each test in the test plan. Assertions that validate the API’s anticipated output should be included in the test cases. A few example test cases are:
Validate and check the request parameter values, Validate the response parameters, Validate the response schema
Test Environment: The next step is to prepare the testing environment. This includes configuring the API as well as any tools or libraries required for testing.
Test Execution: The next step is to run the test cases and validate the API result.
Test Reporting: The final step is to report the test findings. Generate reports detailing the results of the executed test cases, including the findings and any issues encountered
Test Maintenance: Conduct regular updates on test data in the designated environment and monitor the APIs for any changes.
Types of Output of an API:
When an API is used, the client application can expect a response in one or multiple formats such as JSON, XML, HTML, etc. The different types of response formats provide developers with flexibility when it comes to integrating the data into their projects. Let’s discuss the different types of output formats that an API can provide.
1. XML: Extensible Markup Language is a data format used to create hierarchical structures.
2. JSON: JavaScript Object Notation is a lightweight and human-readable data interchange format used to store and transmit data.
3. HTML: HyperText Markup Language is the primary language used to create web pages and applications.
4. Text: Used to return output in a human-readable string format. Mostly the JSON format will be returned as “Text”.
5. Binary: Used to transmit data in a binary format.
6. Images: Formats such as JPEG, GIF, and PNG can be returned via an API.
Every format has its advantages and disadvantages. Based on the project need and the expected usage of the API, the format should be selected.
Types of Bugs That API Testing Detects
Here are some types of bugs API testing can detect:
1. Syntax and Validation Errors – These errors arise due to the incorrect formation of the request body, endpoint URL, etc.
2. Security-relating Bugs – These relate to bugs that may arise due to unauthorized access to the API and the data sent or received.
3. Content Issue – Content issues arise due to the wrong representation of response data, such as data transformation issues, and as a result of incorrect header parameters for the request.
4. Performance-relating Issues – These are issues that may arise due to the API’s slow response time for the requests sent or due to the API crashing or time-out errors.
5. Interoperability Issues – These errors arise when the API communication fails between two different services due to compatibility issues between the two services.
Examples of API Tests
Here are some real-time examples of API tests:
- A bank might test its API to ensure it can correctly process a customer’s request to transfer money from one account to another.
- A social media platform might test its API to ensure it can correctly return a user’s profile information, such as their name, email address, etc.
- An e-commerce website might test its API to ensure it can correctly process a customer’s order, such as shipping the product to the correct address and charging the correct amount.
This testing is an important part of ensuring the quality and reliability of APIs. By performing many tests, testers can help identify and fix problems before they cause issues for users.
Advantages of API Testing
Finally, we can check out some advantages.
1. Improved Test Coverage: It helps ensure that all functionality and data associated with the application are accurately connected and integrated. It can cover areas of the application that UI tests may need to reach.
2. Faster Results: API tests are faster to run and provide results quicker than UI tests.
3. Cross-Platform Testing: API tests can be used to perform integration tests across different platforms.
4. Multi-Environment Testing: API tests can test the system in different environments and accommodate data and system state changes.
5. Reduced Costs: It can be cheaper and faster than traditional UI tests.
Read about API VS UI Testing
Best Practices of API Testing
It is an important part of the software development process. Here are some best practices.
- Test Early and Often: Testing should be done early and frequently to discover any possible faults before they turn into a crisis. Once we have the sample responses or endpoints from the developers we can start playing around and try to understand the response and how it’s related to the UI value/fields.
- Use Automation: Don’t stop with testing the endpoints individually. Automation should be utilized to decrease the amount of time and effort necessary to test APIs. So try to automate and build your test suite.
- Write Assertions: Assertions should be used to verify the expected output of the API. Starting from the API’s response time to various requests by analyzing the structure of the response data.
- Test All Endpoints: All endpoints should be tested to make sure that they are working properly. Also, try chaining the requests and testing the data flow.
- Test for Security: Security should be tested to make sure that the API is secure and is protecting sensitive data. For example, when you use the invalid credentials you should be getting 401 Unauthorized response code and the response body should not contain any sensitive information.
- Measure the API Performance: Performance should be examined to make sure that the API can handle big amounts of data and significant traffic.
- Test for Usability: Usability testing validates the design and user-friendliness of an API. It determines whether the API can be used easily by its user. Only when it’s easy to read and implement can the APIs be adopted for Integration purposes.
- Test for Compatibility: Compatibility should be tested to make sure that the API is compatible with different platforms, browsers, and devices.
- Regression Testing: APIs should be tested to make sure that changes made to the API (due to defect fixes or new features) do not cause unexpected errors or regressions.
- Monitoring: Once you’ve set up your test suite, you should be monitoring test results and updating tests as necessary. Monitoring will help us to track the performance and usage of APIs as traffic and usage grow, allowing them to evaluate prior performance to discover anomalies or patterns, and providing capability for alerting and recording API data.
Challenges of API Testing:
Anyone new to this Testing will have some difficulties getting started. Don’t be concerned. Let’s see in detail the challenges you and your teams face.
1. Lack of Proper API Documentation – The testing team needs to be aware of all the parameters of the API, their types, and the range of valid values. This information is available in the proper documentation, which should be complete and up to date.
2. Lack of Specialized Skills: It requires specific knowledge and experience in API design, development, and testing. The tester must have an advanced understanding of the technology and the language it is written in.
3. Addressing edge cases: Tools often struggle to find unexpected or edge cases, which could potentially lead to unexpected behavior in production.
4. Interoperability of Systems: This testing necessitates a detailed grasp of system compatibility. The tester must ensure that diverse systems communicate successfully and that data is transmitted in the desired manner.
5. Versatility Issues – One of the most difficult challenges in this Testing is cross-platform testing, since an API needs to be tested on different platforms, browsers, and devices.
6. Complex Request and response body/formats: When testing APIs, it might be challenging to simulate all message data types. The tester must understand the data formats as well as the various methodologies for testing message formats. It might be challenging to test all possible requests, responses, and combinations.
7. Test Data and API Parameter Combinations: API testing must be done properly and reliably by using appropriate test data. The process of maintaining a trustworthy collection of test data for API testing is known as test data management, and it necessitates careful administration and organization. API testing entails evaluating practically all potential parameter and value combinations, which makes it tough and time intensive.
8. Data Security Issues: This testing should also focus on the security of the data being exchanged. Controlling access and ensuring data integrity is critical. The tester must be aware of authentication, encryption, and authorization processes.
9. Selection of tools: This testing requires testers to have a good understanding of tools and techniques. This can be challenging when testers are not familiar with scripting languages. And that’s where tools like Testsigma could really help. Testsigma makes it easier for testers. Testsigma lets you automate your tests for web, mobile, desktop and APIs from the same place and is also available as an open-source version.
10. Performance Challenges: Performance is an important element in this testing. The tester must be skilled in understanding the appropriate performance criteria for each API. APIs must be tested for response time using various data sets, configurations, and user load. And proper reporting to the stakeholders.
11. Setting up the Test Environments: Configuring an effective and balanced test environment that allows for the stable and accurate testing of APIs can be a challenging task. The test environment must replicate the environment that the API will experience in production, and must provide a stable testing platform with all the necessary resources.
12. Unstable APIs: Newly developed APIs might not be stable. This will require testers to spend more time on the testing and validation process. We must interact often with API developers and comprehend the API’s behavioral pattern.
13. Error handling scenarios: This testing includes verifying the error codes for different scenarios. Getting to know all the error codes is really challenging. Also covering all the scenarios is a complex task.
API Test Automation Strategies & Techniques for Optimizing Quality
1. Implement End-to-End Tests:
End-to-end testing entails mimicking user journeys and the API calls that go with them through your release candidate. This helps to verify that all functionality is functioning and tested before going live.
2. Utilize Automation Tools:
Don’t stop testing the API endpoints manually. Automation ensures that tests are done at scale and can speed up the API testing process.
3. Monitor Your API Performance:
Automated monitoring aids in the detection of regressions and the identification of performance bottlenecks. You can monitor API performance down to the request and response level with tools like Elastic APM. You may configure alerts to be triggered in the case of severe swings in performance, allowing you to take remedial action swiftly.
4. Leverage Post-Deployment Testing:
This enables you to understand how an API is employed in reality and detect any bugs with its implementation or new features that have been added. Initially, this should be done manually, but as the platform evolves, it may be automated.
5. Utilize Endpoint Coverage Analysis:
This allows you to ensure that your API tests cover the whole endpoint and test all potential states and scenarios. Read more about it here: Test Coverage Criteria for RESTful Web APIs.pdf
API Testing Tips for Beginners:
If you’re new to this testing, here are some tips to help you get started:
- Understand the Basics: It’s important to understand the basics of API testing, API-related jargon, such as the different types of tests that need to be performed and the different types of output that can be expected.
- Start small and simple. If you are new to API testing, start by testing a few basic API calls before moving on to more complex ones. Pick tools like Testsigma and play around the public APIs. Any API is a good repository of public APIs.
- Understand API requirements/capabilities: Ensure you have a clear understanding of the API, its inputs, its outputs, and any underlying protocols or technologies involved.
- Use the Right Tools: The right tools are essential for API testing. Make sure to use the right tools for the job Testsigma is easy to use and feel free to try the tool.
- Create a Test Plan: Create a test plan that outlines the tests that will be performed and the expected output. You can think about the dependencies and risks and detail them.
- Utilize API debugging tools – API debugging tools can help you simulate API requests for API testing. If you are running into any issues with API requests, use API debugging tools to quickly identify and troubleshoot the problem.
- Do your research: Maintain your curiosity for learning new technologies and stay up to date on API developments.
How to Do API Test Automation with Ease in Testsigma?
Automating your API test cases is very easy with Testsigma. Read about – Announcement of Testsigma API Test.
Step 1: Set up the test
- Testsigma defaults to GET for new requests (used to retrieve data).
- Example: Test the expected response code for the user’s data using a GET request.

Step 2: Add Request Details:
- To begin with, we will have to make the following entries in Testsigma: URL: https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users
- The Request Details would be added in an API test case in Testsigma. It would look like the screenshot below:

Step 3: Verify the Response:
- Under “Verify Response,” define what you want to check in the response.
- With this, your automated test is ready to run! It will pass if the response code matches your expectations.

Step 4: Execution
And with just this much effort, the automated test case is ready for execution. When the test case will be executed, if the response code matches the expected status code, the test will pass.

And, if it does not, the test will fail.

________________________________________________________________________________________________________
You can use other methods to send data to your APIs by clicking the drop-down menu, including the following options:
Step 1- Provide Details:
- Title: Name your test step (e.g., Get User Details).
- API Endpoints: Enter the API URL you want to interact with (e.g., https://reqres.in/).

Step 2 – Choose HTTP Method:
- Select the appropriate method for your request:
- GET: Retrieve data.
- POST: Create new data or perform actions.
- PUT: Update existing data.
- PATCH: Update specific data fields.
- DELETE: Remove data.

Step 3 – Configure-Request Details (if applicable):
- Parameters: Add query parameters if needed (e.g., https://reqres.in/api/users?page=2).
- Request Body: Specify data for POST or PUT requests.
- Headers: Include necessary headers (e.g., authentication tokens, content type).
- Authorization: If required, establish authentication (e.g., Basic Auth, OAuth tokens).
- Settings: Adjust any specific settings for your request.

Step 4 – Define Verification Criteria:
- Response Body: Validate the structure and content (e.g., JSON or XML).
- Headers: Verify specific response headers.
- Status: Define the expected HTTP status code (e.g., 200 OK).

Step 5- Capture and Utilize Data (optional):
- Stored Variables: Store parts of the response for later use in your test case.

Step 6 – Attach Files (optional):
- Attachments: Include relevant files or documents for testing.
Step 7 – Link Reusable Objects (optional):
- Global Objects: Utilize predefined global objects in your project for consistency.

Step 8 – Create and Run the Test:
- Click “Create” to save your configuration.

- Run the test to test the RESTful API.

Read more here: Get Started with Testing REST API
What is the Future of API Testing?
API testing is rapidly growing, with the increase in demand for APIs all over the digital world. This growth is driven from cloud computing, complex systems, and small services where API testing is crucial to ensure smooth interaction and speed.
According to statistics, 90% of developers use APIs in some form. A detailed breakdown,
- 69% of them use third-party APIs
- 20% of them use internal or private APIs
93.4% of developers use REST API, and GraphQL is used by 22.5% of them.
Automated testing tools, like Testsigma, help streamline the testing process and improve efficiency.
Closing Thoughts:
We are about to conclude. Yes, it’s pretty long and informative, right? Let’s have a recap.
- For API testing, pick a tool.
- Create the necessary resources for the test environment, such as test databases, mock services, and testing accounts.
- Identify the test cases that must be automated and establish input parameters such as headers and queries, as well as test cases.
- Write short and extensive scripts that include assertions to test various API endpoints.
- Create test cases to put the API through its tests with the supplied parameters.
- Write a test report and save it in your project’s repository.
- Run the test cases and analyze the results to validate the API.
- Have the API tests automated.
- Review the test findings and monitor the API on a regular basis.
We hope you found our API Testing tutorial informative. API testing may be challenging, but with the correct tools and best practices, it can be done easily. So, if you follow the pointers mentioned in this article, you’ll be well on your way to being an API testing pro!

