Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Research reveals a troubling reality: 58% of software bugs stem from testing process and infrastructure failures, not actual design flaws. These preventable defects slip into production where they cost up to 30 times more to fix, creating a cycle of emergency hotfixes, customer churn, and mounting technical debt that slows future releases. The solution lies in strategic test automation, and not just automating more tests, but automating the right tests at the right time with measurable business impact.
This guide will show you how to build a test automation strategy that prevents process-driven bugs, accelerates delivery cycles, and transforms testing from a bottleneck into a competitive advantage.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is a Test Automation Strategy?
- 2 Why Do You Need a Test Automation Strategy?
- 3 Key Components of a Strong Test Automation Strategy
- 3.1 Setting Clear Objectives & KPIs
- 3.2 Selecting the Right Test Cases to Automate
- 3.3 Choosing the Right Automation Tools & Frameworks
- 3.4 Designing Scalable Test Architecture
- 3.5 Building a Test Data Management Approach
- 3.6 Integrating Automation with CI/CD Pipelines
- 3.7 Reporting, Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
- 4 How to Create a Test Automation Strategy
- 5 Best Practices for Test Automation Strategy
- 6 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Test Automation Strategy
- 7 Test Automation Strategy Example
- 8 How Testsigma Helps Build a Winning Test Automation Strategy?
- 9 Conclusion
What is a Test Automation Strategy?
A test automation strategy is a structured roadmap that defines what should be automated, why it matters, and how it will be executed. Instead of treating automation as an ad-hoc activity, a strategy ensures it is purposeful, measurable, and aligned with business priorities.
It’s important to distinguish a framework from a strategy. The two terms that are often mistakenly used interchangeably:
- A framework is the technical foundation: the set of tools, libraries, and coding practices that enable automation.
- A strategy is the broader plan: identifying high-value test cases, choosing the right tools and environments, and setting KPIs that track impact.
Every QA team needs a defined automation strategy. Without one, automation often results in fragile scripts, high maintenance costs, and coverage gaps in critical workflows. With one, teams can scale automation consistently, tie it to business goals, and realize tangible outcomes like faster release cycles, reduced risk, and higher product quality.
Why Do You Need a Test Automation Strategy?
A test automation strategy is essentially the difference between automation that accelerates delivery and automation that drains resources. Without a plan, teams often end up with fragile tests, mounting maintenance costs, and little to show in terms of business impact. When done right, a strategy creates measurable value across the software lifecycle:
- Automated regression testing and integration testing provide quick feedback, helping teams deliver features sooner.
- A strategy defines how automation grows with new apps, platforms, and teams, making it sustainable over time.
- By focusing on high-value test cases and minimizing rework, teams lower the overall cost of quality.
- Consistent, repeatable tests expand coverage, reduce defects, and improve customer experience.
Risks Without a Strategy
- Unplanned automation often leads to brittle scripts that fail for the wrong reasons.
- Low-value scenarios get automated while critical gaps remain.
- Disorganized test suites quickly become a burden instead of a benefit.
- Without alignment to goals and KPIs, stakeholders struggle to see the value.
Key Components of a Strong Test Automation Strategy
A test automation strategy is only as effective as the components it’s built on. Many teams fail not because they lack tools or skills, but because they miss one or more of these building blocks. Clear objectives, smart test selection, solid architecture, reliable data, and pipeline integration are the difference between automation that accelerates delivery and automation that collapses under its own weight.
Setting Clear Objectives & KPIs
Start here, always. Without KPIs, teams end up celebrating “we automated 500 tests” without knowing if that improved quality or delivery. Strong objectives tie directly to business impact:
- Execution time cut from 6 hours to 40 minutes.
- Regression coverage up from 40% to 85%.
- Defect leakage rate dropping by half over two quarters.
The numbers tell you whether automation is working or just keeping people busy.
Selecting the Right Test Cases to Automate
Many teams make the mistake of automating everything they can click on. The result? A bloated test suite full of low-value scripts that are brittle, slow, and expensive to maintain. A strong automation strategy takes the opposite approach: it focuses on the critical user journeys that carry business risk and occur frequently, like login, checkout, or payments. By concentrating effort where failures hurt most, teams keep their test suites lean, stable, and impactful.
Choosing the Right Automation Tools & Frameworks
There’s no single best tool, only the right fit. If you are confused as to what tool and framework to pick from, ask three questions:
- Does it support your tech stack and platforms?
- Can your team actually maintain it?
- Does it scale when your app scales?
Selenium/Appium/Cypress: ultimate flexibility, but higher maintenance.
Testsigma/TestComplete/BrowserStack Automate: quicker onboarding, built-in device clouds.
CI/CD-native tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps integrations.
The wrong tool forces you to bend your strategy around it. The right tool bends to your needs.
Designing Scalable Test Architecture
Care for a cautionary tale? One financial services firm built 2,000 tests in under a year. None were reusable, naming conventions were random, and running the suite took 10+ hours. Result? They scrapped it all. Architecture is what prevents this collapse.
- Page Object Model keeps locators clean.
- BDD ensures business-readable tests.
- Parallel execution on cloud grids keeps speed in check.
- Version control makes automation part of the dev lifecycle.
Building a Test DATA Management Approach
This is where many strategies quietly fail. Tests pass one day and fail the next because data was missing, duplicated, or already consumed. To fix this:
- Use synthetic test data where possible.
- Mask production data to stay compliant but realistic.
- Reset data states between runs to avoid flaky failures.
Integrating Automation with CI/CD Pipelines
This isn’t optional anymore. Automation must live inside the pipeline, not outside it. Think of a pull request that automatically kicks off smoke tests in GitHub Actions, blocks a merge if login or payment flows fail, and pushes results straight into Slack. That’s how you turn testing from a phase into a heartbeat that runs with every commit.
Reporting, Monitoring & Continuous Improvement
Here’s the trap: teams showcase ‘number of automated tests’ as if volume equals value. Stakeholders don’t care about raw counts. What they actually care about is impact. Reporting should highlight:
- Where failures are happening.
- Which tests are flaky.
- Whether defect escape rates are going down.
Dashboards, alerts, and regular pruning of flaky tests keep automation alive. A strategy isn’t carved in stone. It is more like a feedback loop that sharpens over time.
How to Create a Test Automation Strategy
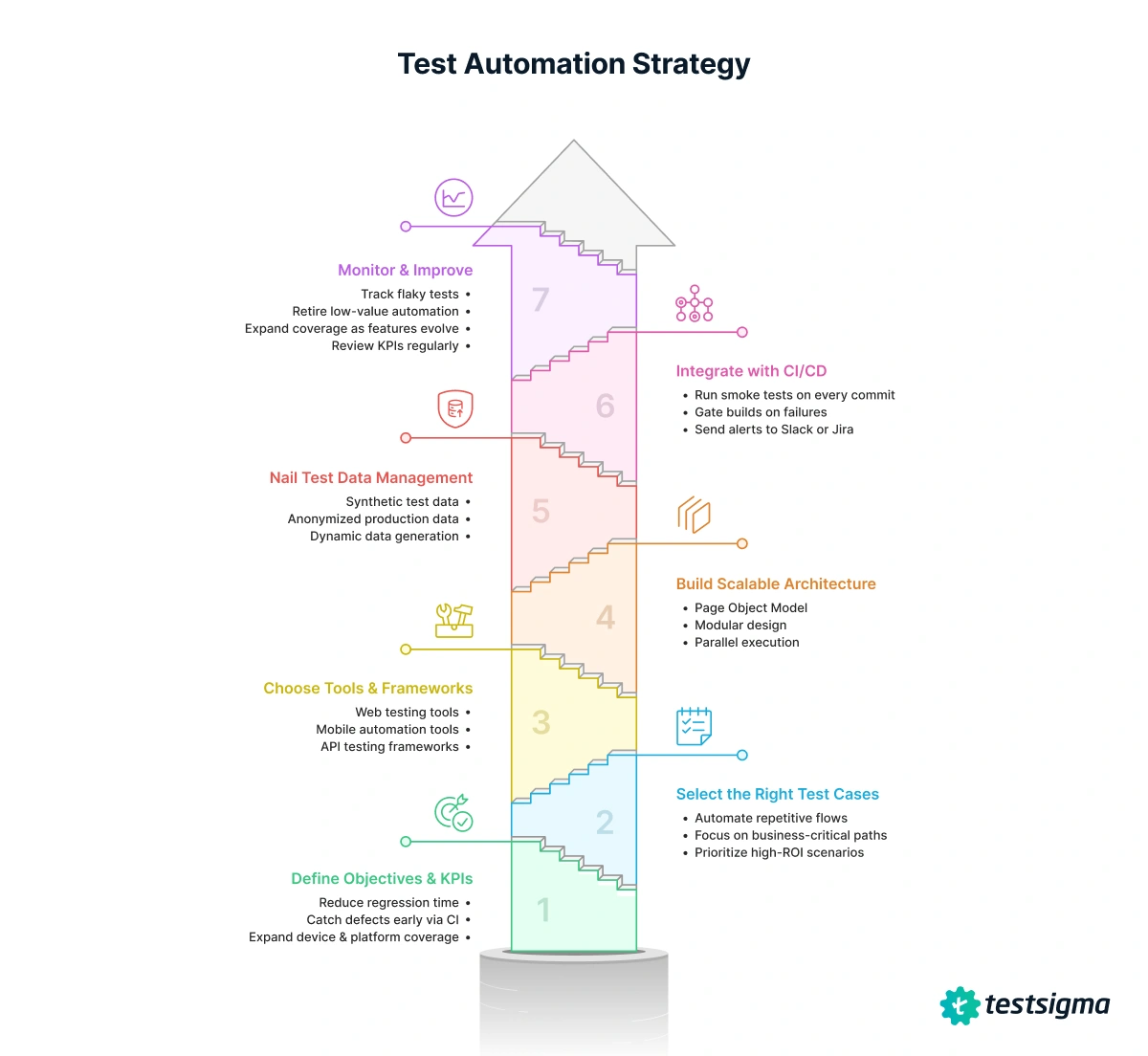
1. Define Objectives & KPIs: Think of this step as setting your north star. Without a destination, every tool demo feels shiny. With one, you filter ruthlessly.
Some examples of KPIs and objectives are:
Cut regression time by 50%: If your current regression takes 10 days, target 5 days by automating the top 200 repetitive tests.
Catch 90% of defects before release: Integrate automated smoke and sanity suites into your CI pipeline.
Expand coverage across 10 devices: Use device farms like BrowserStack or Sauce Labs to ensure multi-device coverage.
2. Select the Right Test Cases: Don’t automate everything. Automate what repeats, what’s business-critical, and what’s impossible to scale manually. Skipping this step is like paving every back alley when all you need is the highway.
Example: In an eCommerce app, automating ‘Add to Cart’ and ‘Payment Checkout’ provides higher ROI than automating ‘Change Profile Picture.’
3. Choose Tools & Frameworks: The tools and frameworks you select will determine whether your automation effort scales smoothly or stalls early. The key is to balance flexibility with maintainability.
Some examples include:
- Web apps: Testsigma, Selenium, Playwright, or Cypress.
- Mobile apps: Appium or Testsigma’s no-code mobile testing.
- API tests: Postman, REST Assured, or Testsigma’s API module.
4. Build Scalable Architecture
This isn’t about tests. It’s about the engineering discipline.
- Page Object Model helps less duplication.
- Modular design can increase reusability.
- Parallel execution increases speed.
5. Nail Test Data Management
If you skip this, automation breaks. That’s a guarantee. Bad data means flaky tests, and flaky tests mean zero trust. Synthetic data, anonymized prod data, and dynamic datasets are your biggest strengths. Test data isn’t a side task. It’s the actual backbone of the process.
Examples of solid test data practices:
- Synthetic Data: Create realistic mock data using tools like Mockaroo or Faker.
- Anonymized Production Data: Safe and representative, great for staging environments.
- Dynamic Data Generation: Use scripts or APIs to refresh data before each run.
6. Integrate with CI/CD
What’s the point of automation if it runs once a week? Embed it into pipelines:
- Smoke on every commit.
- Gate builds on failures.
- Push alerts into Slack/Jira.
7. Monitor & Improve
Automation is not a one-time setup. Over time, applications change, and so must the tests. A mature strategy includes ongoing monitoring and continuous improvement:
- Track flakiness to identify whether failures come from unstable scripts or real product issues.
- Retire outdated tests that no longer add value, so the suite stays lean and relevant.
- Add new coverage as features evolve, ensuring automation reflects the current state of the product.
- Review KPIs regularly (execution speed, defect leakage, coverage) to align with business goals.
Example: A Jenkins pipeline runs smoke tests automatically after each code push, posting a Slack message if any test fails. This keeps the feedback loop under 10 minutes.
Best Practices for Test Automation Strategy
A practical test automation strategy requires a clear, stepwise approach. Follow these steps to ensure your automation efforts are efficient, scalable, and aligned with business goals:
Start Small, Scale Gradually
The urge to automate everything is real, but resist it. Begin with high-value, repetitive flows in login, checkout, and payment processing. Quick wins build confidence, justify investment, and prove ROI to stakeholders. Scale in phases. Add modules, expand coverage, but never rush. A massive, untested suite collapses faster than you realize.
Balance between Manual & Automated Testing
Exploratory testing, usability checks, and edge-case validations still require human judgment. Skipping manual testing can leave blind spots in critical workflows. The secret is balance. Let automation handle repetition and scale while humans focus on nuance and judgment.
Ensure Cross-Platform & Cross-Browser Coverage
Coverage is only valuable if it mirrors reality. Look at your analytics. Which browsers and devices actually matter? A mobile-first app may demand intense iOS and Android testing. Legacy desktop browsers might need minimal attention. Prioritize wisely. Too much breadth spreads your suite thin.
Invest in Maintenance & Self-Healing Tests
Update scripts regularly. Remove outdated cases. Adopt self-healing tools to handle minor UI and backend changes automatically. Neglect this, and every build becomes a guessing game where you end up asking questions like ‘did the test fail’, or ‘did the product break’?
Maintain Collaboration between Dev, QA & Ops
Automation succeeds when it’s not siloed. Share your strategy, define joint KPIs, integrate tests into CI/CD pipelines. Early collaboration accelerates feedback loops, reduces bottlenecks, and ensures automation aligns with business goals. When Dev, QA, and Ops are in sync, release cycles smooth out.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Test Automation Strategy
Even well-intentioned automation can fail if common pitfalls are ignored. Teams often encounter predictable challenges that slow delivery, increase maintenance, and reduce confidence in tests.

Over-Automation
Attempting to automate every scenario, including low-impact UI changes or rarely used flows, increases maintenance overhead. Teams end up fixing failing tests instead of building features. Focus on automating high-frequency, high-risk workflows first.
Inconsistent Test DATA and Environments
Tests fail when data or environments do not reflect production conditions. Using dynamic datasets without proper control or skipping the staging setup leads to unreliable results and flaky tests. Maintain consistent, environment-specific datasets and synthetic or anonymized production data.
Lack of Maintainability
Rigid or tightly coupled scripts break with minor product changes, creating a constant maintenance burden. Adopt modular, reusable test design and, where possible, self-healing tools to reduce manual updates.
Missing Metrics and Reporting
Automation without KPIs or dashboards provides limited insight into effectiveness. Teams may run hundreds of tests without knowing if they improve quality. Track coverage, execution time, defect leakage, and flaky tests to ensure automation delivers measurable value.
Isolation From Development and Operations
Automation disconnected from CI/CD pipelines and cross-team collaboration risks delayed feedback and missed defects. Integrate automation into workflows and maintain clear communication between Dev, QA, and Ops teams.
Test Automation Strategy Example
A well-structured framework ensures your automation efforts are aligned, maintainable, and capable of delivering measurable results. Here’s how to structure it effectively for any QA team:
1. Planning & Requirement Analysis
Begin by defining clear objectives for automation. Identify critical workflows, high-risk areas, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success. Decide which features truly require automation and which are better left for manual testing. This step ensures your efforts target areas with maximum business impact.
2. Test Case Design & Prioritization
Design test cases to be modular and reusable. Prioritize scenarios based on business importance, frequency of execution, and potential risk. By focusing on high-value workflows, you minimize maintenance overhead and improve long-term stability.
3. Tool Selection & Environment Setup
Select tools and frameworks that integrate seamlessly with your technology stack and CI/CD pipelines. Ensure environments are configured consistently and test data is reliable, representative, and secure. Tool choice should be driven by team skillset, scalability requirements, and maintainability, not trendiness.
4. Automation Execution
Integrate your automated tests into the CI/CD process to provide rapid, repeatable feedback. Schedule parallel execution where possible to accelerate test cycles across platforms and browsers. The goal is not just automation for coverage, but automation that prevents regressions and accelerates delivery.
5. Reporting & Monitoring
Establish clear reporting mechanisms. Track pass/fail rates, defect trends, and coverage metrics in dashboards accessible to both QA and business stakeholders. Continuous monitoring identifies flaky tests early, ensuring automation remains reliable and actionable.
6. Continuous Improvement
Automation is never finished. Regularly review and update test scripts, remove outdated tests, and incorporate lessons from production issues. Adjust priorities as new features are introduced to keep the strategy aligned with business goals and application changes.
How Testsigma Helps Build a Winning Test Automation Strategy?
Implementing a robust test automation strategy is easier with the right tools. Testsigma offers a comprehensive platform that aligns with modern QA needs, making automation faster, smarter, and more reliable.
1. No-Code & AI-Powered Automation
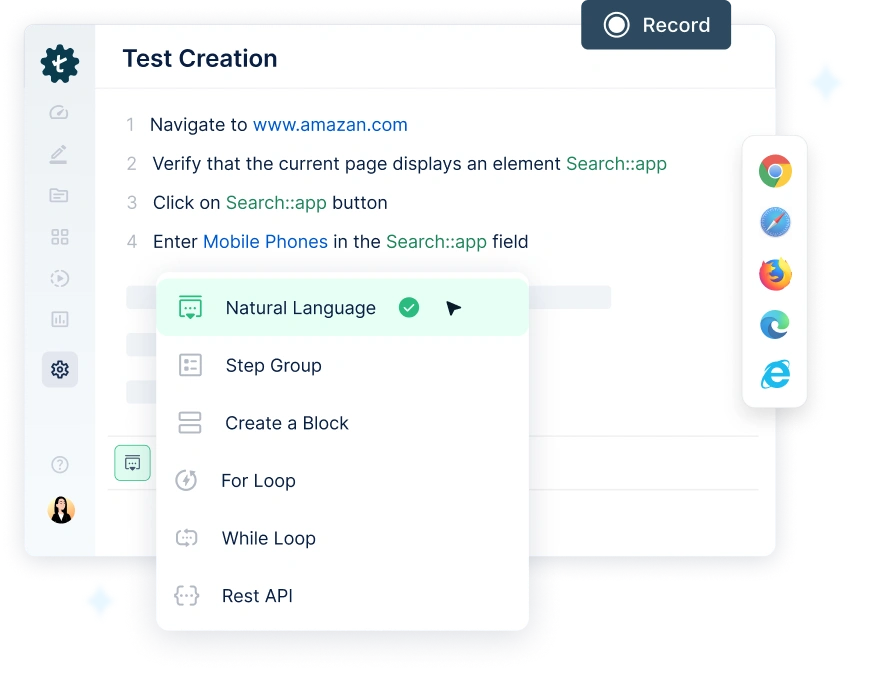
Testsigma’s no-code interface enables teams to create and maintain automated tests without extensive programming knowledge. AI-powered features assist in generating test scripts, predicting failures, and optimizing workflows, accelerating test creation while reducing human error.
2. Self-Healing Tests That Reduce Maintenance
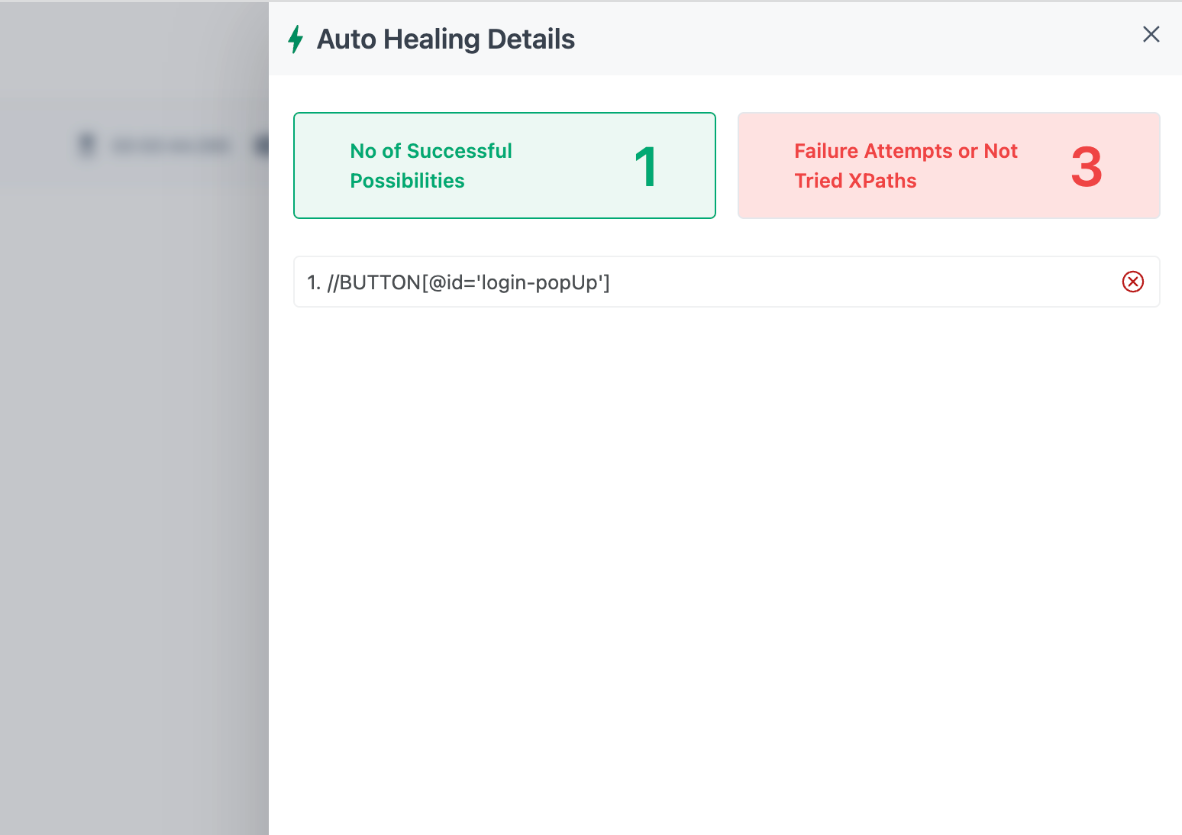
Test scripts often fail due to minor UI or backend changes. Testsigma’s self-healing capabilities automatically detect and update affected tests, drastically reducing maintenance effort and keeping regression cycles smooth and uninterrupted.
3. End-to-end Cross-Platform Coverage (web, Mobile, API, Desktop)
Whether your application runs on multiple browsers, mobile devices, APIs, or desktop platforms, Testsigma supports it all. Unified coverage ensures consistent testing quality across all environments, saving time and resources.
4. Seamless CI/CD Integrations & Real-Time Reporting
Integrate Testsigma effortlessly into your CI/CD pipelines to enable continuous testing. Real-time reporting dashboards provide actionable insights for QA teams and stakeholders, helping prioritize defects and track automation ROI effectively.
Conclusion
A well-defined test automation strategy is the backbone of efficient, scalable, and high-quality software testing. From setting clear objectives to selecting the right tools, automating the right test cases, and maintaining continuous improvement, a solid strategy minimizes risks, reduces costs, and accelerates release cycles. By implementing best practices and avoiding common pitfalls, such as over-automation, neglecting test data, or overlooking maintainability, QA teams can maximize the ROI of their automation efforts. Visualizing your strategy with frameworks and examples ensures clarity, alignment, and repeatable success across teams.
Build your automation strategy today with Testsigma and leverage low-code, AI-powered automation, self-healing tests, and seamless CI/CD integrations to take your QA process to the next level.



