Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Frontend Testing?
- 2 Why is Frontend Testing Important?
- 3 Frontend Testing Examples
- 4 Types of Frontend Testing
- 5 Benefits of Frontend Testing
- 6 Step by Step Frontend Testing Process:
- 7 Best Frontend Testing Frameworks
- 8 Common Challenges in Frontend Testing
- 9 Frontend Testing Best Practices
- 10 Tips to Improve Frontend Testing
- 11 How to Perform Frontend Testing with Testsigma
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Frontend Testing?
Frontend testing is the process of checking whether the user interface (UI) of a website or application works as expected. It ensures that everything a user sees and interacts with like buttons, forms, menus, and layouts looks right, functions properly, and responds smoothly across different devices and browsers. In simple terms, it’s about testing what the user experiences directly.
Why is Frontend Testing Important?
- A flawless frontend builds trust, keeps users engaged, and reflects the overall quality of the product.
- It verifies that all visual elements like buttons, menus, images, and forms appear correctly and work as intended.
- By testing the frontend during development, teams can catch UI issues, broken links, layout problems, and functionality errors before they reach production.
- Frontend testing helps identify performance bottlenecks such as slow-loading pages, unresponsive buttons, or lagging animations.
- Accessibility testing ensures that everyone including users with disabilities can navigate and use the application effectively.
- Frontend testing checks elements like color contrast, keyboard navigation, and screen reader compatibility to make the app more inclusive. It also improves overall usability by ensuring intuitive interactions and clear layouts.
Frontend Testing Examples
Example 1: Form Validation Error Handling
When a user fills out a form like a signup or login page frontend testing checks if the form behaves correctly. For example, if someone submits the form without entering an email, the app should display an error message like “Please enter a valid email address.” Testing ensures that these validations appear properly, the messages are clear, and the form doesn’t break when users make mistakes.
Example 2: Cross-Browser UI Consistency
Web applications must look and function the same across different browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Frontend testing verifies that layouts, fonts, buttons, and animations render correctly everywhere. For instance, a button that looks perfect on Chrome shouldn’t appear misaligned or cut off on Safari. Testing across browsers helps maintain a consistent user experience.
Example 3: Mobile Responsiveness
Since users access websites from various devices like smartphones, tablets, laptops; frontend testing ensures the UI adapts seamlessly to different screen sizes and resolutions. For example, on mobile, navigation menus should collapse into a hamburger icon, and images should resize without distortion. Responsive testing helps confirm that users can interact comfortably, no matter what device they’re using.
Types of Frontend Testing
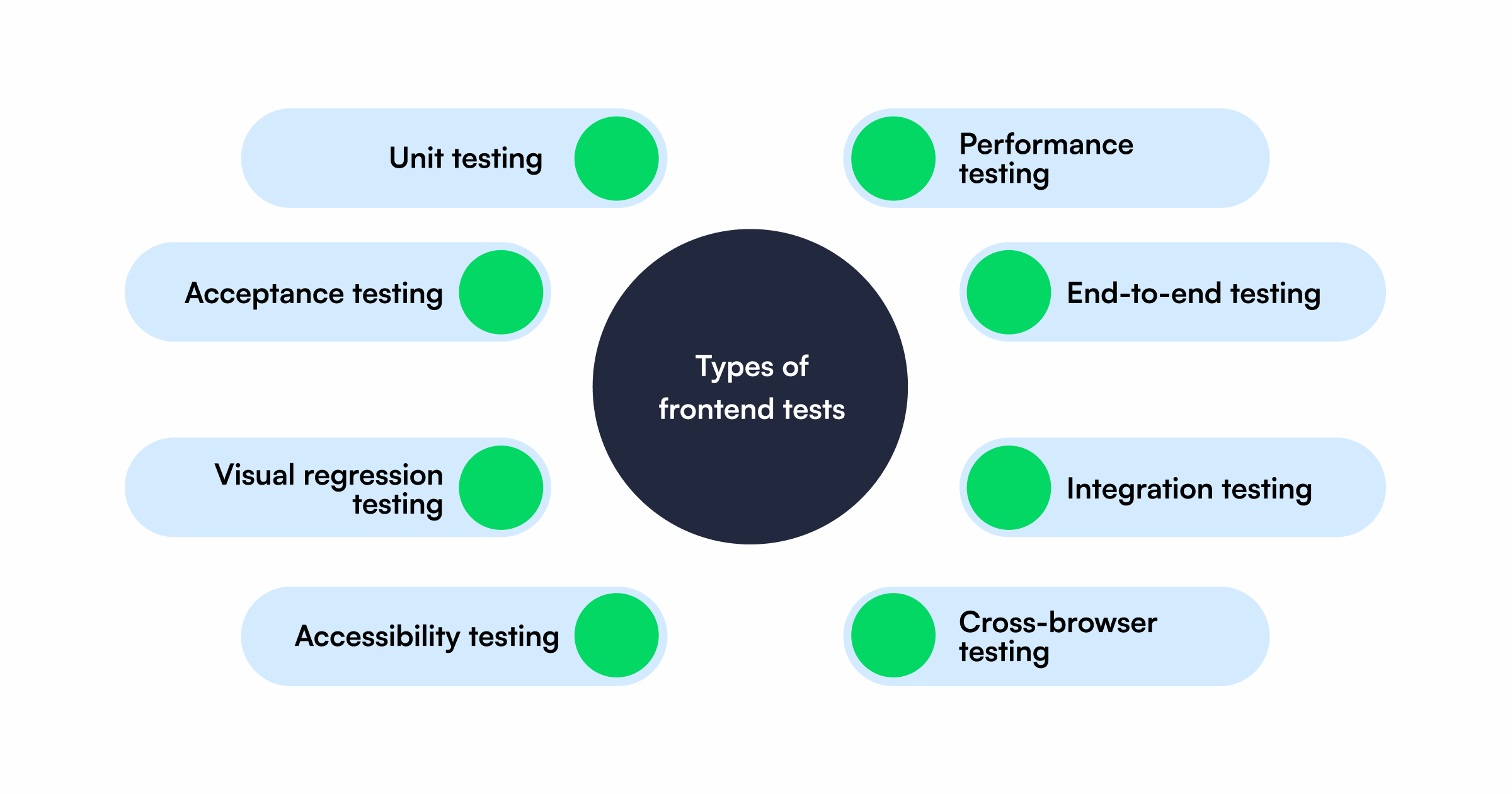
1) Unit Testing
Unit testing checks the smallest parts of the frontend such as individual functions, buttons, or components to make sure they work correctly on their own. For example, you might test if a “Submit” button calls the right function when clicked. It helps developers catch errors early before combining different parts of the app.
2) Integration Testing
Once individual components work properly, integration testing checks how they interact with each other. For instance, it verifies that when a user enters data into a form and clicks “Submit,” the input is correctly passed to the next part of the application. It ensures smooth communication between connected UI elements and modules.
3) End-to-end (E2e) Testing
E2E testing simulates real user actions to test the entire application flow from start to finish. For example, logging in, adding an item to the cart, and completing checkout. It ensures that all components, from frontend to backend, work together as expected in a real-world scenario.
4) Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing checks whether the application meets business requirements and delivers what users expect. It’s usually done from the end user’s perspective to confirm that the overall experience is correct before release. For example, ensuring that a user can successfully register, log in, and view their profile as intended.
5) Visual Regression Testing
This type of testing compares new versions of the UI with previous ones to spot unintended visual changes like misplaced buttons, broken layouts, or shifted elements. It’s especially helpful after code updates or design changes to make sure the app still looks the same visually.
6) Cross-Browser & Cross-Device Testing
This testing ensures that the application looks and behaves consistently across different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari and devices like mobile, tablet, desktop. It helps detect browser-specific bugs and ensures a uniform experience for all users.
7) Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates how fast and responsive the frontend is. It checks things like page load times, image rendering, and how the app behaves under heavy traffic. The goal is to deliver a smooth, fast, and optimized user experience.
8) Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing ensures that everyone including users with disabilities can use the application easily. It checks color contrast, font sizes, keyboard navigation, and screen reader support. This makes the app more inclusive and compliant with accessibility standards like WCAG.
Benefits of Frontend Testing
- Faster Release Cycles – Automated frontend testing helps teams detect and fix UI issues early, reducing the time spent on manual testing. When tests run automatically with every code change, developers can release updates more quickly and confidently, speeding up the entire development and deployment cycle.
- Reduced Production Bugs – Thorough frontend testing catches visual, functional, and usability issues before they reach end users. By preventing broken layouts, unresponsive buttons, or browser-specific errors from going live, teams can deliver a more stable and reliable product.
- Better Customer Satisfaction – A well-tested frontend ensures a smooth, consistent, and bug-free experience for users. When pages load quickly, buttons work properly, and forms behave as expected, users are more likely to stay engaged and trust the product, leading to higher satisfaction and retention.
- Cost Savings in QA – Fixing issues early in development is much cheaper than addressing them after release. By automating frontend tests and catching problems sooner, companies save time, reduce rework, and lower overall testing and maintenance costs.
Step by Step Frontend Testing Process:
Step 1: Define Test Requirements
The first step is to identify what needs to be tested on the frontend. This includes UI elements (buttons, forms, navigation), user flows (login, checkout), and compatibility factors (browsers, devices, screen sizes). Clear test requirements help ensure that every important part of the user interface is covered.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tools and Frameworks
Selecting the right testing tools is key to efficient frontend testing. The right combination depends on your app’s complexity, team skills, and automation goals.
Step 3: Create Test DATA Environments
Next, set up the test environment similar to how the application runs in production and prepare any data needed for testing. For example, create sample user accounts, form inputs, or dummy product data to simulate real-world usage. This helps make test scenarios realistic and reliable.
Step 4: Write and Execute Tests
Now it’s time to create and run the tests.
- Manual testing is great for exploratory checks, visual reviews, and usability testing.
- Automated testing is used for repetitive checks like regression, UI functionality, and cross-browser validation.
Running both types ensures comprehensive coverage and faster results.
Step 5: Analyze Reports & Fix Bugs
After tests are executed, review the test reports to identify failed cases, bugs, or performance issues. Developers then fix these issues, and the tests are rerun to confirm everything works as expected. This feedback loop ensures a stable, high-quality frontend.
Step 6: Continuous Testing in CI/CD
In modern development, frontend tests are integrated into CI/CD pipelines. This means tests run automatically every time new code is pushed, ensuring that new updates don’t break existing functionality. It enables faster, safer, and more reliable software releases.
Best Frontend Testing Frameworks
- Testsigma – No-code,agentic AI-powered test automation for web, mobile, and API testing.
- Selenium – Open-source framework for browser automation in multiple languages.
- Cypress – Fast, reliable end-to-end testing built for modern web apps.
- Puppeteer – Headless Chrome automation for UI and performance testing.
- Jest – JavaScript framework for unit and snapshot testing, ideal for React apps.
Also Read: Top 12 Front-End Automation Testing Tools
Common Challenges in Frontend Testing
- Handling Dynamic Elements – Dynamic pop-ups, animations, and changing IDs can cause tests to fail unexpectedly. Use stable locators, smart waits, or AI-driven element detection to handle changes reliably.
- Cross-Browser and Device Fragmentation – Apps may look or behave differently across browsers and devices. Test on real devices or cloud platforms to ensure consistent UI and functionality everywhere.
- Test Maintenance & Flaky Tests – Frequent UI updates can break test scripts or cause random (flaky) failures. Regularly review and update test cases to keep them stable and reliable.
- Performance Bottlenecks – Slow page loads, large images, or heavy scripts affect user experience. Use performance tools like Lighthouse or GTmetrix to identify and fix speed issues early.
Frontend Testing Best Practices
- Begin with the Testing Pyramid – Follow the testing pyramid approach start with a strong base of unit tests, then add integration and end-to-end (E2E) tests on top.
- Automate Repetitive UI Tests – Automate frequent and repetitive checks like form submissions, navigation flows, and visual validations.
- Use Real Devices and Browsers – Test your application on real devices and browsers instead of relying only on emulators or simulators.
- Prioritize Critical User Journeys – Focus first on testing the most important user flows such as login, signup, checkout, or payment.
- Integrate Testing with CI/CD – Embed automated frontend tests into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment pipelines.
Tips to Improve Frontend Testing
- Collaborate Between Devs and QA Early – Involve developers and QA testers from the beginning of the development cycle. Early collaboration helps identify potential UI issues, define better test scenarios, and avoid rework later in the process.
- Mock APIs to Test Faster – Use mock APIs to simulate backend responses when the real API isn’t ready or is unstable. This allows testers to validate the frontend’s behavior independently and continue testing without waiting for backend updates.
- Regularly Update Test Cases – Keep test cases up to date as the application evolves. Remove outdated tests, add new ones for recent features, and refine existing cases to reflect UI or workflow changes, ensuring accuracy and coverage.
How to Perform Frontend Testing with Testsigma
Step 1 – Create an account on Testsigma and login with your credentials.

Step 2 – In Testsigma, you can write test cases using natural language commands like:
‘Click on the “Login” button
Enter “username” in the “Email” field’
No coding required, the built-in NLP engine automatically converts these into executable automated tests.
Step 3 – Create reusable test steps for common actions like logging in or navigating to a specific page. Reuse them across multiple test cases to save time and reduce maintenance.
Step 4 – Execute your frontend tests instantly across 3,000+ real browsers, devices, and OS combinations. Choose between parallel execution for speed or sequential execution for detailed debugging.

Step 5 – View real-time test reports and dashboards with detailed logs, screenshots, and video recordings. Quickly identify failed steps, error causes, and performance issues.

Conclusion
Frontend testing plays a crucial role in ensuring that every interaction on your application delivers a seamless and reliable user experience. With modern tools like Testsigma, teams can move beyond complex scripting and manual validation to achieve smarter, faster, and scalable test automation. By combining AI-driven test creation, cloud execution, and continuous integration, Testsigma empowers QA and development teams to catch issues early, maintain high-quality releases, and keep users happy. In short effective frontend testing isn’t just about finding bugs; it’s about building confidence in every release and delivering exceptional digital experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frontend testing focuses on what users see and interact with the user interface, visuals, and functionality in browsers or devices. Backend testing, on the other hand, checks what happens behind the scenes like databases, servers, and APIs, to ensure data is processed and stored correctly.
In short:
Frontend = User experience (UI/UX)
Backend = Data and logic (Server-side)
Most frontend testing can be automated, especially repetitive tasks like regression, form validation, and UI flow testing. However, some areas like visual design reviews or usability testing, still benefit from manual checks, as they rely on human judgment and user experience insights.
Misaligned or broken layouts, buttons or links not responding, form validation errors and browser or device compatibility issues
Frontend testing supports Agile by enabling continuous testing and faster feedback loops. Automated tests run with every sprint or code change, helping teams detect UI issues early, maintain quality, and release features quickly. It ensures that frequent updates don’t break existing functionality, keeping pace with rapid Agile iterations.



