Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
It is 2025, and the field of software testing is constantly evolving. From automation to artificial intelligence, the future of software testing looks very different from what it has been in the past. However, software testing has become increasingly challenging as software becomes more complex and user expectations rise.
In this blog, we will explore the various trends and developments shaping the future of software testing and how these changes will impact how we approach quality assurance in the software industry.
Table Of Contents
- 1 The Evolution of Software Testing Trends
- 1.1 1. Shift-Left Testing
- 1.2 2. AI and Machine Learning (AI/ML) in Testing
- 1.3 3. The Increasing Popularity of IoT
- 1.4 4. Expanding Test Coverage
- 1.5 5. Large Language Models (LLMs)
- 1.6 6. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
- 1.7 7. DevOps and Agile Testing
- 1.8 8. Microservices Testing
- 1.9 9. API-Centric Testing
- 1.10 10. Increased focus on security testing
- 1.11 11. Improving Web Accessibility
- 1.12 12. Mobile App Testing Evolution
- 1.13 13. Test DATA Management
- 1.14 14. Shift-Right Testing
- 1.15 15. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
- 1.16 16. Agentic testing
- 1.17 17. In-Sprint Test Automation
- 1.18 18. Shift From Function to Non-Function
- 1.19 19. Blockchain Testing
- 1.20 20. Chaos Engineering
- 1.21 21. Cybersecurity with DevSecOps
- 1.22 22. Crowdsourced Testing
- 1.23 23. Compliance Testing
- 1.24 24. More Agile Testing practices
- 1.25 25. Automated Test Case Generation
- 2 What to Do & How to Go with the Trend?
- 3 Software Testing Trends to Overcome Challenges
- 4 Let’s Catch up!
The Evolution of Software Testing Trends
The following 25 radical waves will thus sweep the shores of software testing come 2025:
1. Shift-Left Testing
Shift-left testing means moving testing activities earlier in the software development lifecycle, often starting from the requirements and design phases.
Benefits of Shift-left testing
- As development progresses, the complexity and interconnectedness of code increase, making late-stage bug fixes more intricate, time-consuming, and expensive to resolve.
- Developers receive faster feedback on their code, getting immediate insights into issues as they write. This allows them to understand and correct mistakes, preventing errors from propagating and becoming deeply embedded.
- Early bug detection naturally encourages practices like Test-Driven Development (TDD). When developers are constantly validating their code, it promotes writing cleaner, more robust, and more maintainable code from the outset. This proactive approach leads to a higher overall standard of code quality.
- By identifying and resolving issues early, you drastically reduce the number of blockers that typically arise during Quality Assurance (QA). This smooths out the testing phase, minimizes delays, and ultimately leads to shorter, more predictable release cycles, getting your product to market faster.
2. AI and Machine Learning (Ai/ml) in Testing
The start of AI and ML has permanently altered the realm of testing; they can automate boring tasks, study large volumes of test data intelligently during testing, and catch failure-prone areas without any manual guidance.
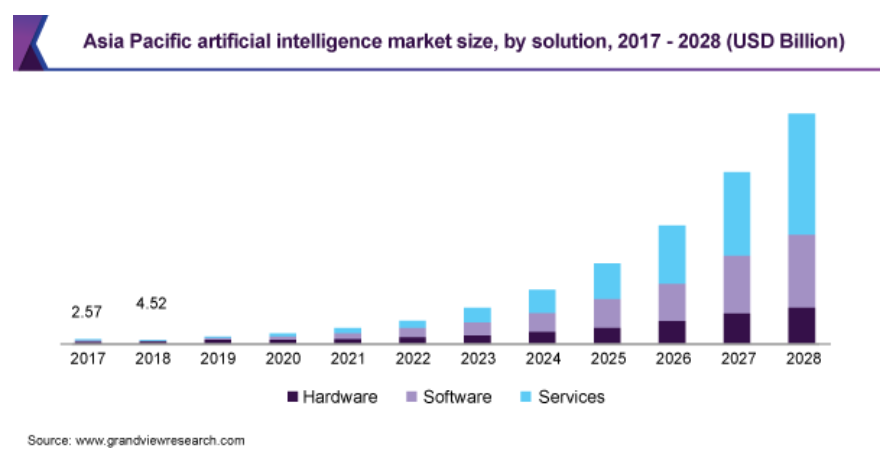
AI can also be used in analyzing any leaks in testing, defaults, and predicting the test coverage, even before running the test cases to save time. If you have something in mind, feel free to comment below.
AI is coming to the deeper scenarios of software testing, but one tool has been quick to pick up the trend and implement it in its DNA. Testsigma, completely cloud-based test automation tool uses AI technology in software testing to save time, and costs and smoothen out the learning curve of the testers.
With AI technology, the tester can write the test cases in the English language that can be translated into a programming language by the tool. Testsigma also comes with self-healing technologies that can detect changes in the user interface and change the test script corresponding to that element automatically. Artificial intelligence practices can improve the quality of processes and save time.
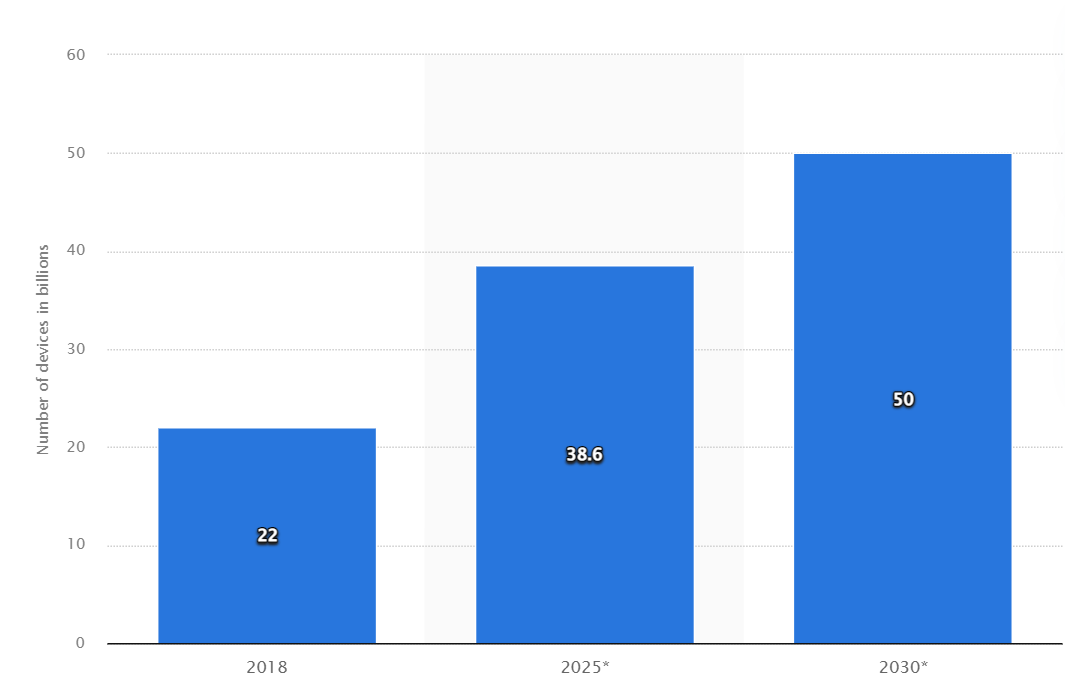
3. The Increasing Popularity of IoT
IoT is gaining increasing traction. This indicates that we are on the threshold of an interesting future when smart devices and IoT solutions will become ubiquitous and grow.
IT expansion suffered a setback in early 2020 due to low investment, yet it later gained momentum and is expected by IDC to reach more than $437 billion in Asia Pacific by 2025.
Introducing the future prospects for IoT: what could be expected by 2025.
- Organizations are benefiting from the growth of IoT in parallel with Machine Learning and coming up with smart ways to analyze data without manual efforts; this can simplify the workflow.
- Smart cities are adopting IoT widely: innovation in urban living has revolutionized traffic management and enabled smart surveillance making it safer for the city residents. With these smart IoT solutions, city governments can re-engineer their infrastructural needs to quality technology at the best level which is more innovative and user-friendly.
- The use of automation by manufacturers is a trend growing throughout the industry, strong not only this year but well into 2025 and beyond.
- Healthcare IoT devices’ innovation changes the way diseases can be detected and treated: which makes it possible to detect diseases at an early stage. This ensures better chances of recovery for those affected by the disease.
4. Expanding Test Coverage
Testing all potential inputs and outputs is increasingly difficult as software applications become more complex. Testers must prioritize their work to focus on the most critical test cases. One popular approach is risk-based testing, which prioritizes tests based on the risks associated with a particular feature or functionality.
Benefits of Enhanced Test Coverage
- A popular approach in improving test coverage is exploratory testing, which allows testers to quickly gather data about the application under test without following a set of predetermined test cases. This approach can be beneficial when testing new features or unfamiliar applications.
- In some cases, automated tests may be used to expand test coverage. Computerized tests are especially well-suited for repetitive tasks or those requiring many test cases.
- However, it is essential to remember that automated tests can only partially replace manual testing. This is because computerized tests can only check for the specific conditions they are programmed for.
5. Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs with their ability to process and understand vast amounts of text data, are transforming the way we write and execute automated tests. LLMs can understand the natural language used in test case descriptions and specifications, allowing testers to create more human-readable and maintainable tests. Also, LLMs can be used to analyze test results and generate clear, concise reports, saving testers valuable time and effort.
For example, an LLM can analyze a test case written in plain English like “Verify user login fails with an invalid password” and automatically translate it into the appropriate code for the testing framework. This not only simplifies test creation but also reduces the risk of errors due to manual coding.
6. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic process automation has already been involved in the software testing process and we believe that it will continue to be in the trend for 2023 with an increased acceptance.
Research and market surveys project RPA revenue to be around 3.4 billion US dollars by 2027. With 28.2% year-on-year growth, RPA is always preferred as the first choice for automating mundane tasks.
RPA, also called robotic process automation, is a process of automating repetitive tasks and require no manual intervention as such. RPA takes down the actions of the tester for the first time to make note of what has to be done.
Using artificial intelligence and machine learning, RPA then executes multiple scenarios using the same actions on the screen. Since it is automatic, it saves time and costs for the company.
From the above definition, you might think it resembles automating tests since it also talks about performing repetitive tasks as it does. It is a genuine confusion, and therefore we have written a dedicated post on how RPA differs from test automation with various use cases and examples.
7. Devops and Agile Testing
The testing process is integrated into the DevOps process, which implies a close partnership between developers and testers. This allows for the creation of high-quality software and the speeding up of delivery cycles to address user requirements.
8. Microservices Testing
Every part is tested to ensure it works well alone and together with other components. Test individual microservices or containerized applications (e.g., Docker) with ease. Testsigma ensures seamless integration and functionality within your microservices architecture.
9. API-Centric Testing
API is vital for any modern application; therefore, its functionality, reliability, performance, and most importantly security need to be scrutinized thoroughly. In Testsigma you can create and execute automated tests for your application’s APIs, guaranteeing their functionality, performance, and security.
10. Increased Focus on Security Testing
As the number of cyberattacks continues to increase, it is becoming increasingly important for software testers to focus on security testing. Security testing is a process of assessing the security of a software application and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
Several approaches can be used for security testing, and multiple techniques are often necessary to assess an application’s security comprehensively.
- One approach is penetration testing, which involves using various tools and techniques to attempt to break into an application and identify technical and non-technical vulnerabilities.
- Another popular approach is code review, which involves manually reviewing source code to identify potential security issues. Code review can be beneficial for identifying vulnerabilities that may be obscure when testing the application itself.
In addition to these specific approaches, security must be considered throughout the software development process. This includes ensuring that secure coding practices are used and that all team members are aware of potential security risks.
11. Improving Web Accessibility
Software testing is about finding bugs and ensuring the software is accessible to all users. This includes users with disabilities, who may use assistive technologies such as screen readers to interact with web applications. To accommodate these users, testers must pay close attention to accessibility issues during the testing process.
Benefits of Web Accessibility
- Web accessibility refers to making websites usable by people with disabilities. This includes people who are blind or have low vision, deaf or hard of hearing, and those with physical or cognitive impairments.
- In WebAIM’s report on digital accessibility, 96.8% of the top 1 million websites had detectable accessibility errors. Although this number is slightly improved from the 97.4% seen in the 2021 report, it still leaves many websites with potential barriers for users with disabilities.
- The WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines) provides a set of standards that can be used to make websites more accessible. Some guidelines include providing text alternatives for non-text content, ensuring that content is readable and understandable, and ensuring that web pages are navigable using keyboard-only input.
- One crucial step is to ensure that all content is available in multiple formats so that users can choose the format that best suits their needs. For example, the text should be both HTML and PDF; images should be available in standard and high-contrast formats; video should be captioned or transcribed.
- Another critical step is checking colour contrast ratios to ensure that text is legible for low-vision users. The WCAG recommends a contrast ratio of at least 4.5:1 for standard text and 3:1 for large text.
Note – It is essential to test websites using various assistive technologies, such as screen readers, to ensure that users with disabilities can access all content.
12. Mobile App Testing Evolution
Testing mobile applications is critical because of the variations that exist with different devices, operating systems, and network conditions to ensure compatibility and usability across all platforms. Perform thorough testing of your mobile applications on a variety of real devices and emulators directly within Testsigma. This eliminates the need for complex device management setups.
13. Test DATA Management
While conducting a test for data management, managing and deploying test data to support various testing activities should be valuable. It is also important to pay attention to compliance or data protection regulations without failing tests.
14. Shift-Right Testing
Shift-right testing refers to testing after deployment, focusing on real user behavior, performance, and reliability in production.
Benefits of Shift-Right Testing
- Gain an authentic understanding of user behavior. By observing how real users navigate, interact with features, and encounter friction points, you get better user insights than any simulated environment can provide. This helps you identify what’s working, what’s confusing, and what’s missing directly from your target audience.
- By monitoring live usage, you uncover issues that only appear under these real-world conditions, leading to a more robust and resilient application.
- Embrace a paradigm of continuous quality by enabling “Testing in Production” (TiP). This doesn’t mean skipping pre-production testing; rather, it’s about setting up robust monitoring and feedback loops in your live environment.
- This testing allows for immediate detection of anomalies and validation of new features, ensuring ongoing quality without disruption.
- Instead of guessing which issues are most critical, you can focus on resolving problems that frequently affect users or improve features that are heavily utilized. This direct, data-driven approach leads to a significantly improved Customer Experience, as you’re addressing what matters most to your users.
15. Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
Collaboration through BDD allows developers, testers, and stakeholders to define and test application behavior using natural language, fostering a shared understanding of requirements.
16. Agentic Testing
One of the groundbreaking trends in the QA industry is Agentic testing. In agentic testing, different AI agents perform various testing tasks. This helps the testers focus on more important tasks and spend less time on redundant tasks. These AI agents are more like QA coworkers.
Benefits of Agentic Testing
- AI agents can generate test cases automatically by analyzing requirements, user flows, or app changes.
- Agentic systems detect UI or code changes and auto-update broken test steps, aiding in self-healing.
- Agents learn from test history, risk areas, and code changes to prioritize critical tests as tests are executed based on real-time app context, usage data, or production feedback.
- AI agents evolve by learning from past test results, user behavior, and defect patterns.
- Specialized agents handle different tasks, such as test creation, data generation, defect detection, etc.
- Agentic testing tools integrate deeply with CI/CD and deliver near-instant insights.
Reduce test authoring time from hours to seconds with Agentic test automation – Try Testsigma now
17. In-Sprint Test Automation
In-sprint test automation is a software testing methodology that picked up as a trend in 2021 and will still continue to do so in 2025. Agile methodology forces organizations to work speedily and release new versions quickly.
As a result, one sprint consists of 2 – 4 weeks after which there is no time left for testing the software. So testers are often found testing a previous version which has a major drawback. If your version is released with just regression and DDT methods, a few of the bugs might seep into the production which can cost even 100 times more.
In-sprint changes this process by allowing the testers to work in the same sprint step by step. So a testing team need not wait till the complete development is over and can start during the development process. This keeps the quality of software on the better side while allowing testers to test the same version to be in sync.
18. Shift From Function to Non-Function
A significant shift in QA is the move from purely functional testing to giving equal importance to non-functional aspects such as usability, accessibility, performance, and reliability. These areas now have dedicated testing methodologies to ensure applications not only work but also provide a seamless and resilient user experience.
Benefits of Non-Functional Testing
- Ensures applications are accessible to diverse users, including those with disabilities.
- Improves user experience through usability testing, validating design and workflows.
- Strengthens system reliability and performance under varying loads and conditions.
- Helps meet compliance standards like WCAG (Accessibility) or ISO (Reliability).
- Reduces business risk by validating how applications behave in real-world environments.
19. Blockchain Testing
With the rise of decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts, blockchain testing has emerged as a critical QA focus. Blockchain testing ensures the security, performance, and protocol adherence of distributed systems.
Benefits of Blockchain Testing
- Validates smart contract functionality to avoid vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Ensures transaction integrity and consistency across nodes in the blockchain network.
- Measures performance and scalability under real-world transaction loads.
- Verifies compliance with blockchain protocols for interoperability.
- Strengthens overall security posture in decentralized ecosystems.
20. Chaos Engineering
Chaos engineering is a proactive QA approach where teams intentionally introduce controlled failures to uncover hidden weaknesses in systems. By breaking things in a safe and measurable way, organizations build more resilient and fault-tolerant systems.
Benefits of Chaos Engineering
- Identifies system vulnerabilities before they occur in production.
- Enhances resilience by preparing systems to recover quickly from unexpected failures.
- Improves observability and monitoring by validating system behavior under stress.
- Builds confidence in system stability during disasters or high-load events.
- Fosters a culture of reliability by shifting the mindset from “avoiding failure” to “embracing failure as a learning tool.”
21. Cybersecurity with Devsecops
Development + Security + Operations = DevSecOps
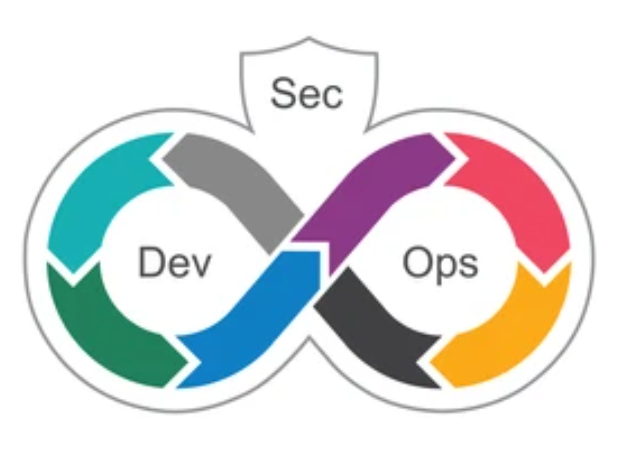
DevSecOps is a method consisting of automation, platform design, and culture that treats security as a shared responsibility across all IT processes. It is more about security ingrained within the system than one that surrounds data and applications like a fortress.
With DevSecOps, identifying possible security threats at their nascent stage becomes viable; upon discovery of such a security risk, it rectifies those loopholes very early on.
Cybersecurity through DevSecOps:
In this regard, DevSecOps has the potential to be a significant step in the establishment of strong security standards, as it involves security at every commit and pull request level. This allows organizations that implement security across the entire lifecycle of products and applications to easily discover any threats that may exist and promptly address them.
Benefits of implementing DevSecOps:
The major advantage that comes with implementing DevSecOps is breaking down silos between different teams.
It helps you catch code vulnerabilities early. DevSecOps specialists ensure that compliance takes priority position by weaving compliance and security checks into the DevOps pipeline.
22. Crowdsourced Testing
Involving the wider audience of users for Testing in a realistic situation whereby the application is used across different settings and situations leads to understanding user behavior and how the application performs under various conditions.
23. Compliance Testing
Testing compliance is one of the most important stages that software undergoes. The purpose is to see if it matches up to the rules set by certain regulators, those established by law, and also those followed within the industry. This validation exercise is very thorough because it needs to ensure that all requirements are met whether they relate to data privacy, other security protocols, or even accessibility standards.
As such, this test guarantees organizations’ adherence to laws and regulations in place; this would prevent them from facing legal risks and fines which might be a result of not complying with what they ought to do. Moreover, it instills trust among users since it shows commitment towards high standards of quality and safety in their software products.
24. More Agile Testing Practices
As the software development industry continues to move towards agile methodology, it is becoming increasingly important for testers to adopt agile testing practices. Agile testing is a process of testing software in short, iterative cycles. This type of testing is well-suited for projects using an agile development methodology.
Benefits of Agile Test Practices
- One of the benefits of agile testing is that it allows testers to adapt to changes in the software quickly. This is because agile testing is typically done in short cycles, so new features can be tested as soon as they are implemented.
- In addition, agile testing also allows for more frequent feedback from testers. This is because agile testing cycles are typically shorter than traditional waterfall cycles. As a result, testers can provide immediate feedback to developers, which can help improve the final product’s quality.
- Another benefit of agile testing is that it can reduce the overall cost of testing. This is because agile testing cycles are typically shorter than traditional waterfall cycles. Agile testing can reduce the overall testing costs while providing high-quality results.
25. Automated Test Case Generation
The use of generative AI allows the production of brand-new test cases and user situations modeled on actual situations. It can produce realistic test data, often capturing peculiar cases or user interactions that normal testing might not have caught as they exist in reality. This assists in revealing latent bugs and problems that could precipitate software failure at later stages where they could have been easily fixed.
Think about Generative AI in software testing, mimicking a user drowning in an online shopping cart with hundreds of items or a mobile app death owing to an abrupt fluctuation in the network. These situations may seem improbable, but they can unveil vulnerabilities within the software, hence giving rise to stronger applications.
What to Do & How to Go with the Trend?
Do not fear! Adapting to these changes should be as easy as breathing. Follow these simple points:
- Determine what you lack: Take a close look at your existing testing methods and find the weak links. Tailor the trends to suit your testing aspirations.
- Take baby steps: Evaluate your current testing practices and pinpoint areas for improvement. Align the trends with your specific testing goals.
- Help your team grow: Rather than offering training or resources for your testers to easily comprehend and utilize the new tools and methodologies, feed them to fish.
- Welcome trial and error: Instead of being afraid to experiment with different approaches, just get started. Learn from what doesn’t work and tweak your approach accordingly.
With these actions, you’ll be able to keep abreast with emerging trends in software testing which will propel you to greater heights!
Software Testing Trends to Overcome Challenges
Software testing is tricky!
New trends are here to help. Imagine catching bugs early (Shift-Left Testing) and using robots to test faster (RPA). We can write tests without tons of coding (Low-Code) and make sure software works on everything from phones to laptops (Mobile Testing). Security is super important, so there are new tests for that, too.
By following the above-mentioned trends, we can release better software faster!
Let’s Catch up!
The software testing domain is a dynamic and ever-changing field. However, the awareness of these new trends can help testers work better and faster. Techniques like catching bugs early, automation, and using new tools all make it easier for teams to ensure that the software they deliver is high-quality and developed quickly. In light of these innovative testing practices surfacing with the advancement of technology, there will be more yet to come pledging the future of software development to be secure, reliable, and user-centric.



