Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What is a Test Environment?
- 3 Why Do You Need a Test Environment in Software Testing?
- 4 Key Components of a Test Environment
- 5 Types of Test Environments
- 6 Test Environment vs. Staging Environment
- 7 How to Set Up a Test Environment?
- 8 Test Environment Management: 6 Best Practices
- 9 Test Environment Checklist
- 10 Common Challenges in Test Environments (and How to Solve Them)
- 11 Best Practices for Setting Up and Managing Test Environments
- 12 Implementing Test Environments with Testsigma
- 13 What Every Tester Should Remember
- 14 FAQs on Test Environments
Overview
What is a Test Environment?
A test environment is a dedicated setup where software is deployed to simulate real-world conditions before release. It’s like a practice field for your application, a safe space to catch bugs, test performance, and ensure everything works as expected before going live.
Why is Test Environment Management Important?
Managing test environments ensures testing runs smoothly and efficiently. It involves:
- Setting clear configuration standards
- Automating environment setup to save time
- Controlling access to maintain security and consistency
- Promoting collaboration between teams
Best Practices for Managing Test Environments
- Start testing early in the development cycle
- Use containers like Docker for consistent setups
- Automate provisioning to reduce manual errors
- Monitor performance and issues continuously
- Leverage cloud platforms for scalability and flexibility
Ever faced the nightmare of deploying a new feature only to find it crashes on users’ devices or doesn’t work as expected? It’s a frustrating experience that can damage reputation and cost both time and money.
The root cause often lies in not testing in an environment that accurately reflects real-world conditions, leading to surprises after launch.
That’s where a test environment becomes your best friend. It’s a dedicated space, complete with the right hardware, software, and network settings, that mirrors your production setup.
Using a test environment allows you to catch bugs early, ensure everything works perfectly, and deliver a seamless experience to users.
What is a Test Environment?
A test environment is a dedicated setup where software testing occurs, replicating the production environment as closely as possible. It includes all necessary hardware, software, network configurations, and data needed to validate an application before it reaches users.
Unlike the production environment, where real users interact with software, the test environment provides a safe space to find and fix bugs.
Why Do You Need a Test Environment in Software Testing?
Development teams cannot release software without ensuring it delivers the best user experience. As with many alternatives available, users quickly abandon buggy or glitchy apps.
Effective software testing requires a controlled environment that replicates the conditions in which the software will operate post-deployment.
This environment is essential for systematically assessing software behavior, identifying issues, and verifying functionality before release.
Ensures High-Quality Releases
A test environment lets you thoroughly check your software in a controlled, consistent space, so you can catch and fix problems early. The result? Cleaner releases that users can depend on.
Reduces Bugs in Production
Nobody wants bugs to surprise them after launch. Testing in a setup that mimics real-world conditions uncovers issues you might miss otherwise. This reduces the risk of disruptions, cranky customers, and emergency fixes that slow your team down.
Supports Agile and Continuous Testing
Speed and quality must go hand in hand in agile workflows. Having a reliable test environment supports frequent automated tests and quick feedback, enabling your team to continuously deliver improvements.
Improves Collaboration across Teams
When every team member works within the same environment, miscommunication drops dramatically. Shared test environments break down silos between developers, testers, and operations, fostering smoother collaboration and faster problem-solving.
Key Components of a Test Environment
Building a reliable test environment is about carefully assembling the essential pieces that work together to create a testing space that feels like the real thing.
Let’s dive into what makes up a strong test environment.
Hardware and Infrastructure
The backbone of your test environment is the physical and virtual hardware: servers, devices, and networks that duplicate the production setup. Without this solid foundation, it’s like trying to test a car on a roller coaster.
Software and Tools
Operating systems, applications, and testing tools make up the software layer of your environment. These are the instruments your testers and automation run on.
Test DATA
Having realistic, well-prepared test data fuels your tests with relevant scenarios and edge cases. It makes sure your software behaves correctly across a variety of conditions without exposing sensitive information.
Network and Security Settings
Your network configuration needs to mirror what happens “out there” in the real world, including firewalls, VPNs, and access controls. This ensures your app’s security and connectivity are tested under realistic conditions.
Access Control and Permissions
Role-based access management keeps your environment safe and stable by ensuring only authorized teams can make changes, preventing accidental disruptions.
Types of Test Environments
A software goes through several stages, each requiring a unique setup to validate specific aspects of quality and functionality.
Differentiating these environments helps teams target the right conditions for testing, ensuring thorough validation and smoother releases.
| Environment | Purpose | Focus Area | Typical Users | Example Scenario |
| Unit Testing Environment | Test individual units of code | Functionality of smallest modules | Developers | Validating a new function or method |
| Integration Testing Environment | Interaction of test combined components | Data flow and communication between modules | Developers, testers | Ensuring payment modules talks to inventory |
| Performance Testing Environment | Measure system responsiveness and stability | Speed, load handling, scalability | Performance engineers | Simulating 1000 concurrent users |
| Security Testing Environment | Identify vulnerabilities and risks | Application security | Security analysts | Penetration testing for data leaks |
| UAT (User Acceptance Testing) Environment | Validate software meets business needs | User workflows and acceptance | End users, business teams | Final approval before production release |
| Beta Testing Environment | Real-world testing with limited user base | Usability and unexpected bugs | Selected users | Releasing new app features to a subset of users |
| Chaos Testing Environment | Test system resilience to failures | Fault tolerance and recovery | SREs, DevOps teams | Simulating server outages to test fallback |
| End-to-End Testing Environment | Validate entire application flow | Complete workflows and integrations | QA teams | Verifying checkout process from login to payment |
Test Environment Vs. Staging Environment
While both play vital roles in quality assurance, they serve different purposes and occur at different stages of the release cycle.
Here’s a brief look at the test environment vs. staging environment:
Test Environment
A test environment is a controlled setup of hardware, software, and configurations where testing teams run tests to identify issues and validate features. It is used throughout development for continuous testing and debugging to improve software quality.
When to Use:
Use the test environment during development cycles for unit, integration, and functional testing to ensure code changes work as expected before moving closer to release.
Idea:
A test environment is a controlled setup focused on testing specific components or features.
Staging Environment
A staging environment is a near-exact duplicate of the production system used for final validation. It replicates production conditions, data, and configurations to test the complete system end-to-end.
When to Use:
Use the staging environment just before release to perform final acceptance testing, verify integrations, and confirm readiness for production deployment.
Idea:
The staging environment mirrors production entirely to validate the complete application.
How to Set up a Test Environment?
Setting up a test environment is a systematic process that ensures your testing space replicates the conditions your software will face.
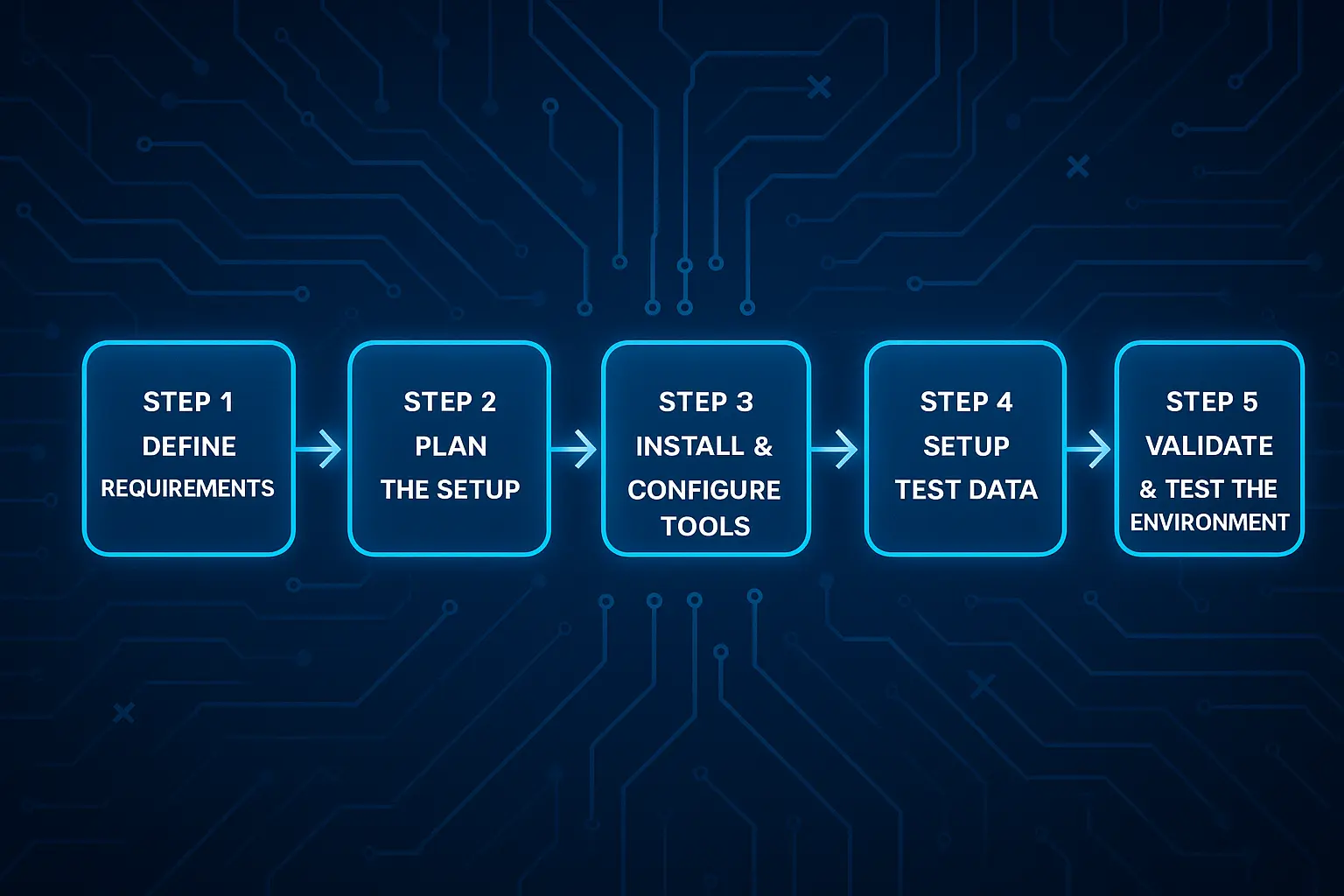
Here’s how to approach it step-by-step:
Step 1: Define Requirements
Outline hardware, software, testing goals, and any regulatory or compliance standards.
Step 2: Plan the Setup
Design your infrastructure, select necessary tools, and identify or create relevant test data.
Step 3: Install and Configure Tools
Deploy operating systems, browsers, testing frameworks, and monitoring utilities tailored to your needs.
Step 4: Set up Test DATA
Populate environments with realistic and privacy-compliant data sets to simulate real user scenarios.
Step 5: Validate and Test the Environment
Run preliminary tests (smoke tests) to confirm all systems are functioning properly before full-scale testing.
Test Environment Management: 6 Best Practices
By following structured processes and best practices, organizations can reduce downtime, optimize resources, and enhance collaboration across teams.
- Establish Standards and Guidelines
Define clear policies and documentation to ensure a consistent environment setup and usage.
- Centralized Environment Management
Use unified tools and dashboards to monitor and coordinate multiple test environments.
- Implement Version Control for Environments
Track infrastructure and configuration changes for reproducibility and rollback.
- Automate Provisioning and Maintenance
Leverage automation to quickly create, update, and tear down test setups.
- Monitor and Control Access
Enforce role-based permissions to secure the environments and prevent accidental changes.
- Collaborate Across QA, DevOps, and Security Teams
Encourage cross-functional communication for a smoother environment planning and problem resolution.
Test Environment Checklist
A test environment checklist helps ensure all critical components are functioning before beginning testing. It reduces risks and prevents delays by confirming readiness at every essential step.
Hardware Setup Verified
Confirm servers and devices meet required specifications.
Software Installed and Licensed
Ensure all necessary software is installed and properly licensed.
Test DATA Prepared
Verify test data is accurate, relevant, and secured.
Security Measures in Place
Check firewalls, encryption, and access controls for protection.
Backup and Rollback Plans Ready
Prepare backups and recovery plans for unexpected failures.
Ready to streamline your testing?
Download our Test Environment Checklist and ensure nothing slips through the cracks!
Common Challenges in Test Environments (and How to Solve Them)
Imagine a testing team trying to verify software on dozens of device types but only having access to a handful of outdated models. Or worse, scrambling to find valid test data due to privacy restrictions. These real-world limitations can slow down testing, reduce coverage, and increase the risks of bugs slipping through.
Acquiring Required Browsers, Devices, and Licenses
Solution: Leverage cloud testing platforms and device farms to access a wide array of devices and browsers on demand.
Handling Test DATA Privacy and Security
Solution: Apply data masking and anonymization to safeguard sensitive information during tests.
High Maintenance Costs
Solution: Reduce operational expenses with automation and scalable cloud infrastructures.
Environment Instability and Configuration Drift
Solution: Use regular audits and version control tools to maintain environment consistency.
Limited Scalability
Solution: Adopt containerization and cloud resources for flexible, scalable test environments.
Best Practices for Setting up and Managing Test Environments
Embracing modern strategies and automation streamlines the process for more reliable testing.
- Begin testing early using shift-left methods to find issues sooner.
- Use containerization (Docker, Kubernetes) to create consistent, reproducible environments.
- Automate environment provisioning with CI/CD to speed up setup and updates.
- Continuously monitor environments to catch and resolve problems quickly.
- Leverage cloud-based environments for scalable, cost-effective testing resources.
Real-World Example of a Test Environment
Teams ensure software reliability before production by creating test environments that closely resemble real-world conditions. This approach helps identify potential issues early and improves overall software quality.
Example:
Consider a web application that must work seamlessly on various browsers and devices: Chrome, Firefox, Safari, desktops, and mobiles. For this, the test environment should include databases replicating the production schema but filled with test data.
APIs connect to mock or sandboxed services to simulate interactions without affecting live data. Through collaboration between developers, testers, and operations, this setup helps catch bugs and performance issues before release.
Implementing Test Environments with Testsigma
Setting up and managing test environments can be complex, but Testsigma simplifies the process with its cloud-first, low-code platform. It offers quick environment setup, cross-browser and device testing, and seamless integrations, reducing maintenance overhead and accelerating testing cycles.
Teams benefit from scalable infrastructure and collaborative features, ensuring reliable and efficient test execution.
Testsigma supports a wide range of testing needs, from functional to API testing, and enables tests to run in parallel across multiple environments, saving valuable time. Its AI-powered capabilities help maintain and update tests automatically as applications evolve, reducing manual effort significantly.
Success story: Many teams have improved their QA efficiency by switching to Testsigma, experiencing faster releases and higher product quality.
Start your free trial now and revolutionize testing with Testsigma’s power!
What Every Tester Should Remember
A reliable test environment is key to delivering high-quality software. It helps detect bugs early, supports agile workflows, and enhances team collaboration.
By combining careful planning, automation, and best practices like containerization and cloud usage, teams can maintain stable, production-like environments.
Use the checklist and automation platforms like Testsigma to simplify setup and management, ensuring efficient, effective testing that boosts overall software quality.
FAQs on Test Environments
Test environments focus on various testing stages and configurations, while staging is the final pre-production replica for validation.
Tools include container platforms (Docker), CI/CD tools (Jenkins), test automation frameworks, and monitoring solutions.
Through version control, regular audits, automated provisioning, and controlled access.
Yes, cloud platforms offer scalable, on-demand environments, reducing hardware costs.



