Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Can you test 100% of your application? Or can you cover every possible testing scenario? And how much time and resources should you allocate to make the software bug-free? There are multiple questions, and all their answers lie in Test coverage techniques.
Table Of Contents
What Are Test Coverage Techniques?
Test coverage helps QA teams:
- Identify untested or risky areas of the product
- Measure testing effectiveness
- Improve confidence in product quality
- Optimize testing efforts by focusing on critical areas
It ensures no significant functionality is overlooked before release.
Formula to Calculate Test Coverage:

Why Are Test Coverage Techniques Important for Test Automation?
Automated testing makes use of tools and test scripts to validate the application. The only manual intervention in automated testing is when testers write and run the scripts. Translating the manual cases to automation covers many scenarios to test the application in lesser time.
Thus, better test coverage can be achieved sooner. With test automation, you can also focus on areas that are easily missed or difficult to test manually. For instance, checking UI changes manually might seem easy, but pixel-by-pixel comparison and the right font and size can be accurately validated using visual test automation. You can use test coverage techniques and automation to analyze the priority of the test case and run them to get results.
One example of this could be an application that consists of multiple research papers, but only users with valid credentials can access them. In that case, identifying the correct logins and sessions per user is a critical task that is difficult to check with manual testing approach. Combining test coverage techniques with automation will clearly determine the areas that need attention and also provide quick testing of the complete scenario.
For automated testing, choose tools that support the implementation of test coverage techniques we are about to discuss in this blog. Testsigma is an AI-based test automation tool that automates your test cases using these techniques, which we will discuss in later sections.
Read here – Test Coverage Metrics
Test Coverage Techniques You Should Know
Test coverage is a metric to determine how much of your software application has been tested. It helps QA teams identify untested areas, measure testing effectiveness, and ensure better product quality. A higher test coverage percentage generally indicates that more parts of the code, features, or requirements have been verified through tests. However, 100% coverage doesn’t always mean the software is defect-free; tests have exercised all defined parts.
Product Coverage
A Product coverage measures the extent to which all product features, modules, and user flows have been tested. It ensures that every critical part of the application, whether it’s a login page, shopping cart, or dashboard, is validated. Teams can track this using feature-based test matrices or by automating repetitive tests across functionalities.
Risk Coverage
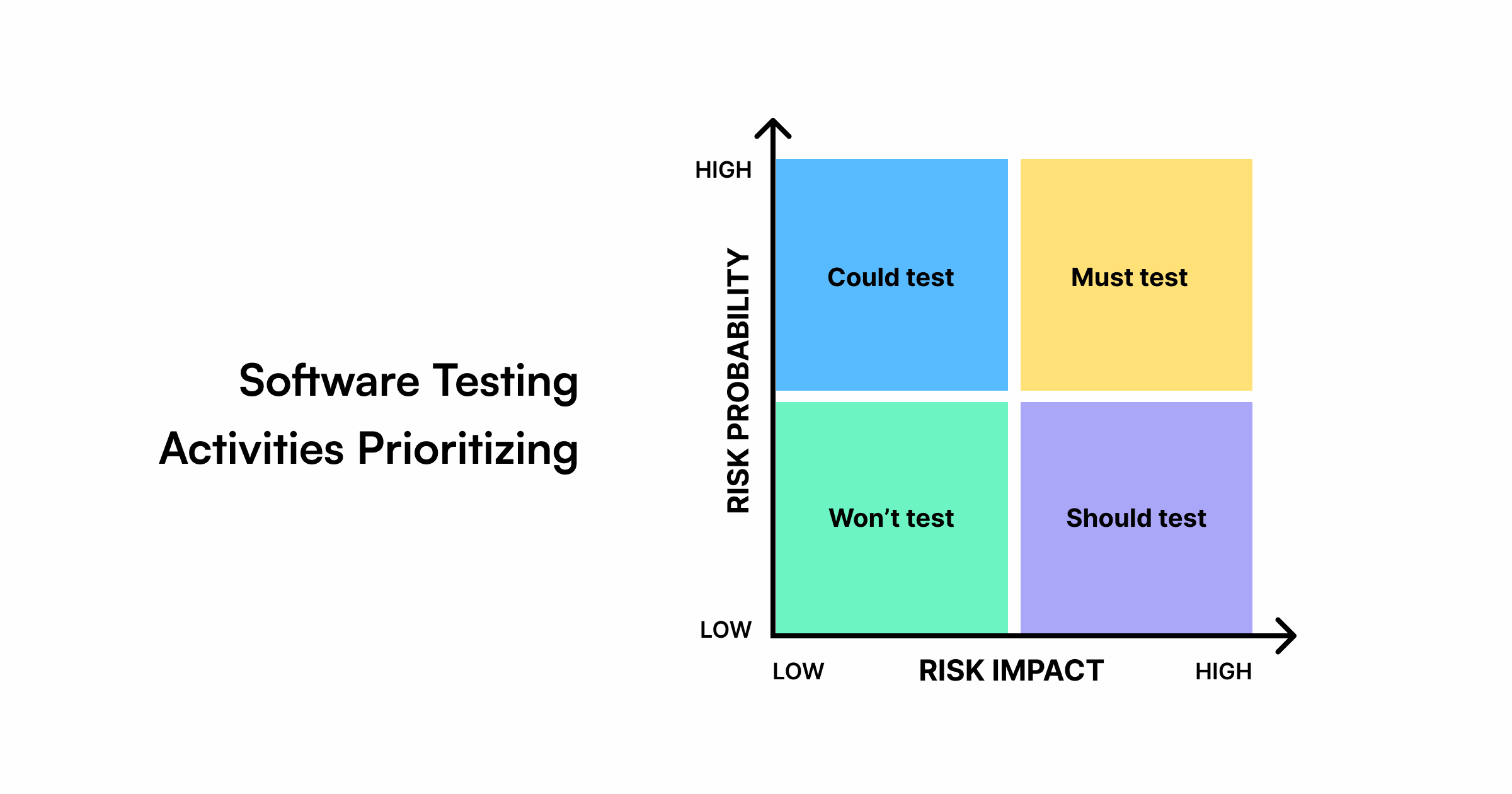
Risk coverage focuses on testing areas with the highest potential for failure or business impact. Instead of testing everything equally, QA teams identify high-risk features (e.g., payment processing, authentication) and prioritize them. This technique helps maximize the testing ROI by ensuring the product’s critical parts are thoroughly verified.
Requirements Coverage
Requirements coverage measures how many of the software’s defined requirements both functional and non-functional have been validated by at least one test case. It ensures that all customer and business needs outlined during the requirements phase are tested and met before release.
How It Works
QA teams map each requirement to one or more test cases, typically using a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM). This mapping helps ensure there are no missing tests for any requirement and that all features behave as intended.
If your application has 50 documented requirements and 45 of them have corresponding test cases executed successfully, your requirements coverage is 90%.
Why It Matters:
- Ensures full traceability from requirements to tests
- Reduces risk of missing critical functionality
- Helps validate that the software aligns with stakeholder expectations.
Regularly update your RTM when new requirements are added or changed to keep your coverage metric accurate.
Boundary Value Coverage
Boundary value coverage focuses on testing at the edges of input ranges values just inside, on, and just outside defined boundaries.
It helps uncover defects that often occur at boundary conditions, where systems are more likely to behave unexpectedly. For each input field or parameter, define the valid input range and test around its limits.
For example, if a system accepts values from 1 to 100, the test cases should include 0, 1, 100, and 101. Suppose there are 20 boundary value test cases planned, and 18 have been executed. Your boundary value coverage = (18 ÷ 20) × 100 = 90%.
Why It Matters:
- Detects off-by-one and edge-related defects
- Improves the robustness and reliability of the software
- Helps ensure input validation and error-handling logic are correctly implemented.
Pair boundary testing with equivalence partitioning to optimize test effort, this way, you cover both typical and edge scenarios effectively.
Compatibility Coverage
Compatibility coverage measures how well your application performs across different environments such as browsers, operating systems, devices, and screen resolutions. It ensures users have a consistent and functional experience regardless of the platform they use.
Identify all environment combinations relevant to your users for instance, Chrome on Windows, Safari on macOS, or Android vs iOS devices.
Then track how many of these have been tested successfully.
If your target matrix includes 10 browser OS combinations and you’ve tested 8 of them, your compatibility coverage is 80%.
Why It Matters:
- Prevents environment-specific bugs that can affect user experience
- Ensures cross-platform consistency and accessibility
- Crucial for responsive web and mobile apps with diverse user bases.
AI-Aided Test Automation
AI-aided test automation leverages artificial intelligence to optimize and expand test coverage automatically. AI can identify untested areas, generate missing test cases, self-heal broken tests, and continuously update test suites.
Benefits of Test Coverage Techniques
Implementing test coverage techniques helps QA teams measure, optimize, and communicate the effectiveness of their testing efforts.
- Detect Untested or Risky Areas – Highlights parts of the application that haven’t been tested, helping QA teams focus on high-risk or high-impact modules before release.
- Improve Product Quality and Reliability – Ensures every feature, requirement, and edge case is validated, reducing the chance of defects slipping into production.
- Ensure Requirement Traceability – Links each requirement to test cases, confirming that all business goals and user expectations are thoroughly tested.
- Optimize Testing Efforts – Prevents redundant testing and directs QA focus toward areas with low coverage or higher risk, improving efficiency and test ROI.
- Build Stakeholder Confidence – Provides measurable QA metrics that increase transparency and trust between development, QA, and management teams.
- Enable Data-Driven QA Decisions – Offers factual insights to guide prioritization, resource allocation, and release readiness decisions instead of relying on intuition.
How Test Management by Testsigma Improves Test Coverage?
Test Management by Testsigma is an agentic test management platform designed for speed, scale, and simplicity. It empowers teams to manage the entire testing lifecycle in one unified platform while significantly improving test coverage.
What sets Testsigma apart is its intelligent AI core, Atto, your dedicated QA coworker. Atto uses specialized agents to enhance coverage across all phases of testing from planning to execution and bug reporting adding speed, intelligence, and agility to your QA processes.
Here’s how each agent boosts test coverage
- Sprint Planner Agent – Automatically plans tests as Jira sprints begin, ensuring that all planned features and requirements have corresponding tests from the start.
- Generator Agent – Generates test cases from Jira, Figma, Xray, documentation, images, and videos. It intelligently suggests edge cases, helping teams achieve near-complete test coverage quickly and efficiently.
- Runner Agent – Enables instant execution of manual test cases in the browser without scripting. Perfect for sanity checks and rapid validation, it ensures key functionalities are consistently tested.
- Bug Reporter Agent – Captures detailed bug reports with reproduction steps, logs, and screenshots, and files them directly into tools like Jira. This reduces the chance of missed defects, indirectly improving coverage by ensuring every failing scenario is logged and addressed.
Key Takeaway
Testing is important, but how much testing is important? What parameters exist to help you understand if you are testing the application enough? It’s test coverage. It measures the lines of code that have been tested against the total lines of code. The idea is to ensure that you know how much testing is over and how much is still left. And for that, you follow several test coverage techniques that we have mentioned in this blog.
From risk coverage and product coverage to automation and boundary-level evaluation, all these techniques will help you assess your testing efforts. And for everything automation, you already have Testsigma to assist you in no-code testing with all the benefits of test coverage. Explore our website for more information, and sign up for the free demo.
Frequently Asked Questions
Test coverage metrics are measurements that quantify how much of an application or code has been tested. They help QA teams track testing effectiveness, identify untested areas, and ensure critical parts of the system are verified.
Common metrics include,
Code Coverage – Percentage of code lines or statements executed by tests.
Requirements Coverage – Percentage of functional/non-functional requirements covered by tests.
Test Case Coverage – Percentage of planned test cases executed.
Test coverage in software testing measures the extent to which software has been tested. It shows which parts of the system code, requirements, features, or user flows have been verified by test cases.
Here are four widely used tools for measuring and improving test coverage:
Testsigma – AI-driven test management platform that ensures near-complete test coverage across features, requirements, and edge cases.
JaCoCo – A Java code coverage tool that integrates with build tools and IDEs.
Cobertura – Tracks Java code coverage and generates detailed reports.
Selenium + Reporting Tools – When combined with frameworks like TestNG or JUnit, Selenium helps track test execution and coverage for web applications.


