When it comes to monetary transactions, no amount of verification and security is sufficient. Re-running the tests on either the transfer instances or the system handling the transactions makes the entire process bug-free.
In a similar manner, trading applications that control a huge amount of data, not just in terms of cash flow but also customers, require a heightened level of testing, including security, functionality, and UI. And all of this starts with formulating test cases for the trading application.
Let’s see how you can do it.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Trading Application Testing
- 2 Why is Testing Trading Software Important?
- 3 Types of Software Testing for Trading Software
- 4 What to Focus on while Testing Trading Apps?
- 5 Aspects to Check when Testing Trading Applications
- 6 Test Cases for Testing a Trading Application
- 7 Challenges in Testing Trading Platforms
- 8 How to Create Test Cases for Trading Application Testing Using Test Management by Testsigma
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
Trading Application Testing
A trading application refers to an online platform that deals with buying and selling of financial instruments, such as public company shares, forex, bonds, mutual funds, cryptocurrencies, and stocks. Naturally, the system captures and stores confidential customer data, monetary transactions, and company information that need protection and thorough testing. Any internal delay in placing buying/selling orders or external breach of the system can result in huge data and financial loss.
Not just that, but with a number of traders increasing worldwide, the performance of the system should not waver. The application should provide high volume and low latency throughput to function smoothly.
Moreover, many trading applications are coming up with automated trading, timely reminders, and predictive stock prices, further cementing the need to scrub the application off of bugs using automation testing practices.
Why is Testing Trading Software Important?
In the world of trading, money is money. But time and data are money too!
Every trading software is concerned with handling a vast amount of data in real-time. Clearly, data accuracy is a top priority for these systems to prevent loss of money and recognition. Simultaneously, with such a large data collection comes the possibility of theft, which needs attention as well.
Next, the back-and-forth of selling, buying, and parking stocks demands a fairly complex business flow where software testing comes into the picture to eliminate gaps between the functioning modules of the system.
That’s why, when it comes to testing trading applications, automation tools encompassing functional, performance, UI, security, and data accuracy features are the best choice for any business.
Types of Software Testing for Trading Software
A trading software runs across the board; mainly, it takes care of stock buying/selling options, but most of them also have the feature to check your credit score, invest in mutual funds, file taxes, and just apply for loans including options such as bad credit loans for users with lower credit ratings.
With these many use cases under one roof, it makes sense to cover a wide range of testing types for such applications. Here is a list:
- Functional Testing: Verify all functionalities of the trading application, including account creation, login, order placement, order execution, portfolio management, and transaction history. Also, check for loan applications, investment options, and payment features if applicable.
- Regression Testing: Ensure that recent changes or updates to the trading application have not introduced any unintended side effects or regressions in existing functionalities.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the trading application’s response times, throughput, and scalability under various load conditions to ensure optimal performance during peak trading periods.
- Security Testing: Probably one of the most important testing types, security testing identifies and addresses potential security vulnerabilities in the trading application, such as unauthorized access, data breaches, or manipulation of trading data.
- Compatibility Testing: Test the trading application across different devices, operating systems, browsers, and network configurations to ensure compatibility and consistent user experience.
- Usability Testing: Assess the trading application’s user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) to ensure it is intuitive, easy to navigate, and meets the needs of traders.
- Integration Testing: Verify the integration of the trading application with external systems, such as market data feeds, trading platforms, payment gateways, and regulatory compliance systems.
- Stress Testing: Determine the trading application’s stability and reliability under high load conditions, such as a surge in trading volume or simultaneous user interactions.
- Risk Management Testing: Test the application’s risk management features, such as position limits, margin requirements, risk analytics, and trade reconciliation processes.
- Disaster Recovery Testing: Evaluate the system’s resilience and ability to recover from unexpected events, such as server failures, network outages, or data center disruptions.
- Data Accuracy Testing: Verify the accuracy of financial data displayed and processed by the trading application, including real-time market data, historical price data, account balances, transaction records, and performance metrics.
What to Focus on While Testing Trading Apps?
Testing a trading application requires meticulous attention to various aspects to ensure its reliability, accuracy, security, and performance. Some of the key focus areas should be:
- The complex trading scenario that shows information in real time.
- Handling multiple APIs that run the application.
- Various gateways that manage transactions and security.
- The integration abilities with third-party systems should not negatively affect the trading software.
- Checking the performance and accuracy of the application to avoid monetary mishaps.
Aspects to Check When Testing Trading Applications
When you are creating test cases for a trading application, look at the below aspects and develop the tests accordingly.
- Trading Windows: Verify the functionality and performance of trading windows, including order entry, order modification, order cancellation, and trade execution.
- Order Management System (OMS): Test the OMS functionality, which includes order routing, order matching, order prioritization, and order tracking. Validate that the OMS accurately processes orders according to specified criteria and efficiently manages order flow across different trading venues.
- Portfolio Analysis: Evaluate the portfolio analysis tools and reports available within the trading application. Verify that traders can assess their portfolio performance, analyze asset allocation, track investment returns, and generate custom reports to support decision-making.
- Value at Risk (VaR): Validate the VaR calculation functionality within the trading application, which helps traders assess the potential risk exposure of their investment portfolio. Ensure that VaR calculations are accurate, reliable, and provide traders with meaningful insights into portfolio risk.
- Execution Management System (EMS): Evaluate the EMS functionality, which facilitates the execution of trades across different asset classes and trading venues. Verify that traders can access real-time market data, execute orders quickly and efficiently, and monitor trade execution performance.
- Market Data Feeds: Validate the reliability and accuracy of market data feeds integrated into the trading application. Ensure that real-time market data, including stock lists, quotes, market depth, news, and analytics, is delivered promptly and reflects current market conditions.
- Risk Management Tools: Test the risk management tools and features available to traders within the application. Verify that traders can set risk parameters, monitor risk exposure in real time, and receive alerts or notifications for risk events or breaches.
- Compliance and Regulatory Checks: Validate that the trading application complies with regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) regulations.
- Reporting and Audit Trails: Verify the accuracy and completeness of transaction reports, audit trails, and regulatory filings generated by the trading application.
Test Cases for Testing a Trading Application
For comprehensive test coverage, consider the below test cases to check a trading platform.
- Verify the login functionality with valid and invalid credentials.
- Verify that users can place various types of orders (e.g., market orders, limit orders, stop orders) by specifying the quantity, price, and duration of orders.
- Test if users can modify or cancel the order types within a set time limit.
- Test if the users can view their portfolio holdings, including positions, quantities, and market values.
- Also, check if the portfolio data is updated in real-time and accurately reflects current market prices.
- Verify that sensitive information such as login credentials and financial data is encrypted and protected and users are required to authenticate themselves before accessing account-related features or performing trades.
- Test that the trading platform can handle concurrent user sessions and trading activity without performance degradation.
- Also, check the response times for order placement, trade execution, and portfolio updates to meet acceptable benchmarks under different load conditions.
- Verify that appropriate error messages are displayed for invalid inputs, system errors, or failed transactions.
- Verify that transaction data, account balances, and audit trails are accurate, complete, and tamper-proof.
- Test the trading application’s compatibility with different web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari) and operating systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, iOS, Android).
- Verify that risk management features such as position limits, margin requirements, and stop-loss orders are enforced correctly.
- Verify that the trading application complies with regulatory requirements and industry standards, such as KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations.
- Validate that the trading application has robust disaster recovery measures in place to mitigate the impact of system failures and data breaches.
- Check the trading application’s integration capability with external systems such as market data providers, clearinghouses, and regulatory reporting platforms.
Challenges in Testing Trading Platforms
Testing trading platforms presents several unique challenges due to the complexity, high stakes, and regulatory requirements associated with financial markets. Keep a track of these issues to eliminate them when the need arises.
- It can be challenging to handle the data feeds from multiple sources, including exchanges, market data providers, and third-party APIs.
- If not done correctly, users may experience difficulties and delays in performing a wide range of order types, including market orders, limit orders, stop orders, and advanced order types such as OCO (One Cancels Other) and IOC (Immediate or Cancel).
- Trading platforms must comply with strict regulatory requirements imposed by financial authorities such as the SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) and FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority).
- Since these systems deal with confidential data, including monetary transactions, taxes, user information, and stock accounts, security, and risk management is always a huge and ongoing challenge for them.
- Even a crash or delay of a second can prove to be disastrous for a trading platform that works in real-time, and it is quite challenging to keep the system up when the load increases.
- Trading platforms often feature complex user interfaces with multiple modules, dashboards, and analytical tools, which makes it difficult to manage the usability, accessibility, and intuitiveness of the platform.
How to Create Test Cases for Trading Application Testing Using Test Management by Testsigma
Test Management by Testsigma is a cloud-badsed Agentic AI-powered test management platform that helps you centralize, organize, and execute tests for complex applications like trading platforms, across mobile and web. Whether you’re testing user onboarding, stock search, order placement, or transaction history, Testsigma enables you to generate and manage both functional and edge-case scenarios effortlessly.
Here’s how you can test trading app workflows with ease:
Step 1. Generate Trading App Test Cases Using AI Agents
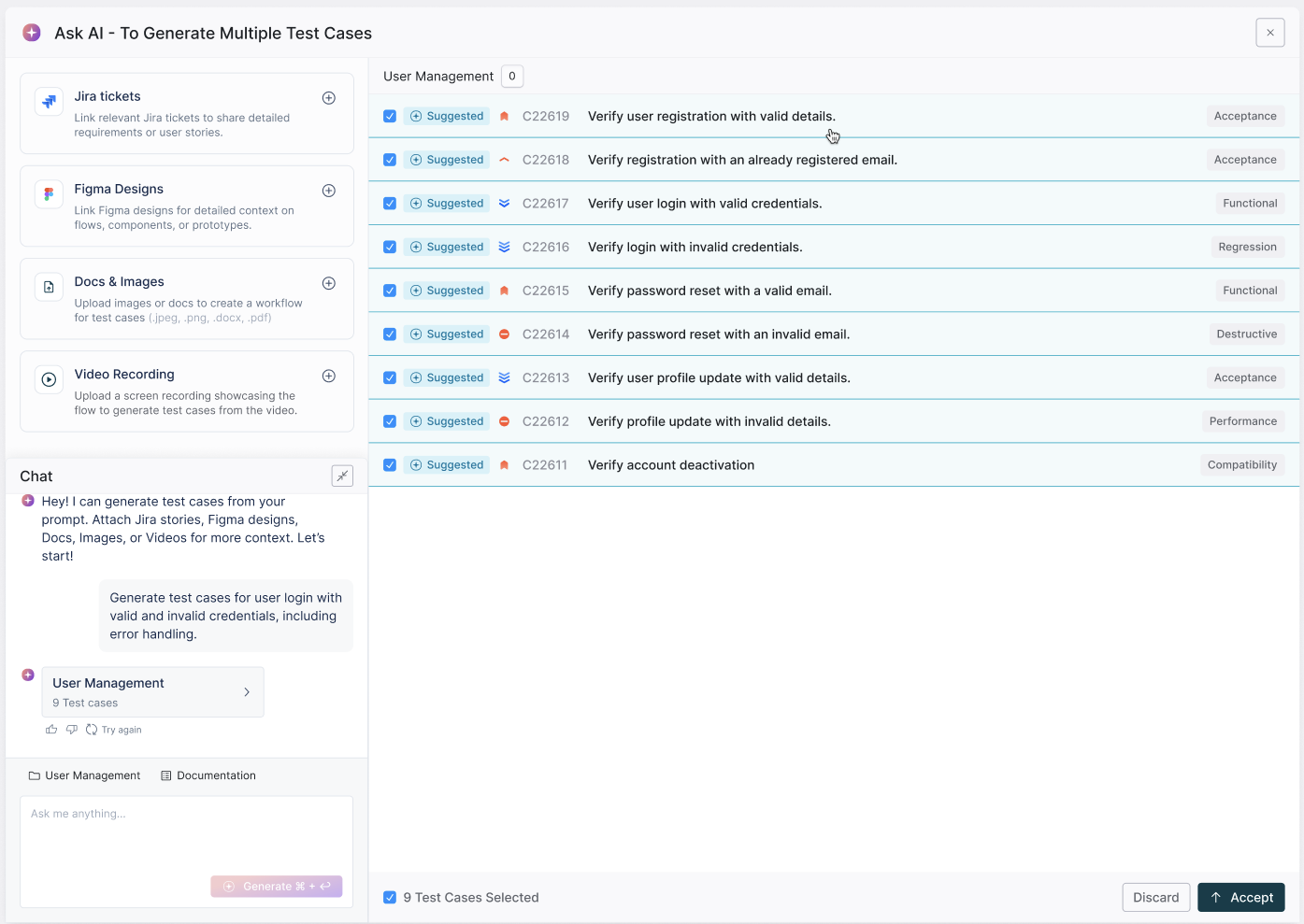
- Go to the Test Cases tab in the Test Management dashboard.
- Create a new folder to organize your trading feature test cases, such as stock search, login, order execution, and portfolio updates.
- Select the Generator Agent and enter prompts like:
- “Functional test cases for placing a market order in a trading app”
- “Test cases for portfolio display and stock price refresh in a mobile trading platform”
- You can also auto-generate test cases using:
- Jira stories describing trade workflows
- Figma UI designs for order screens or stock detail pages
- Screenshots of dashboards, price alerts, or charting tools
- Walkthrough videos showing user interactions (placing orders, checking balance, etc.)
- Testsigma will automatically generate test cases such as:
- Verify that the user can search and view stock details.
- Validate market and limit order placements.
- Check balance updates after a trade is executed.
- Ensure price feeds refresh in real time.
- Confirm alerts are triggered for price thresholds.
Step 2. Create and Configure a Test Run
- Go to the Test Runs tab and click Create Test Run.
- Name your run.
- Select the trading test cases generated earlier.
- Click Execute with Atto, Testsigma’s AI coworker. Atto will prepare and queue test cases for execution across selected devices or environments.
Step 3. Execute Trading Test Cases with Atto
- Click Start next to the test case to begin execution.
- Input relevant test data (e.g., stock ticker, order quantity, order type) when prompted.
- Click Send, then Start Testing.
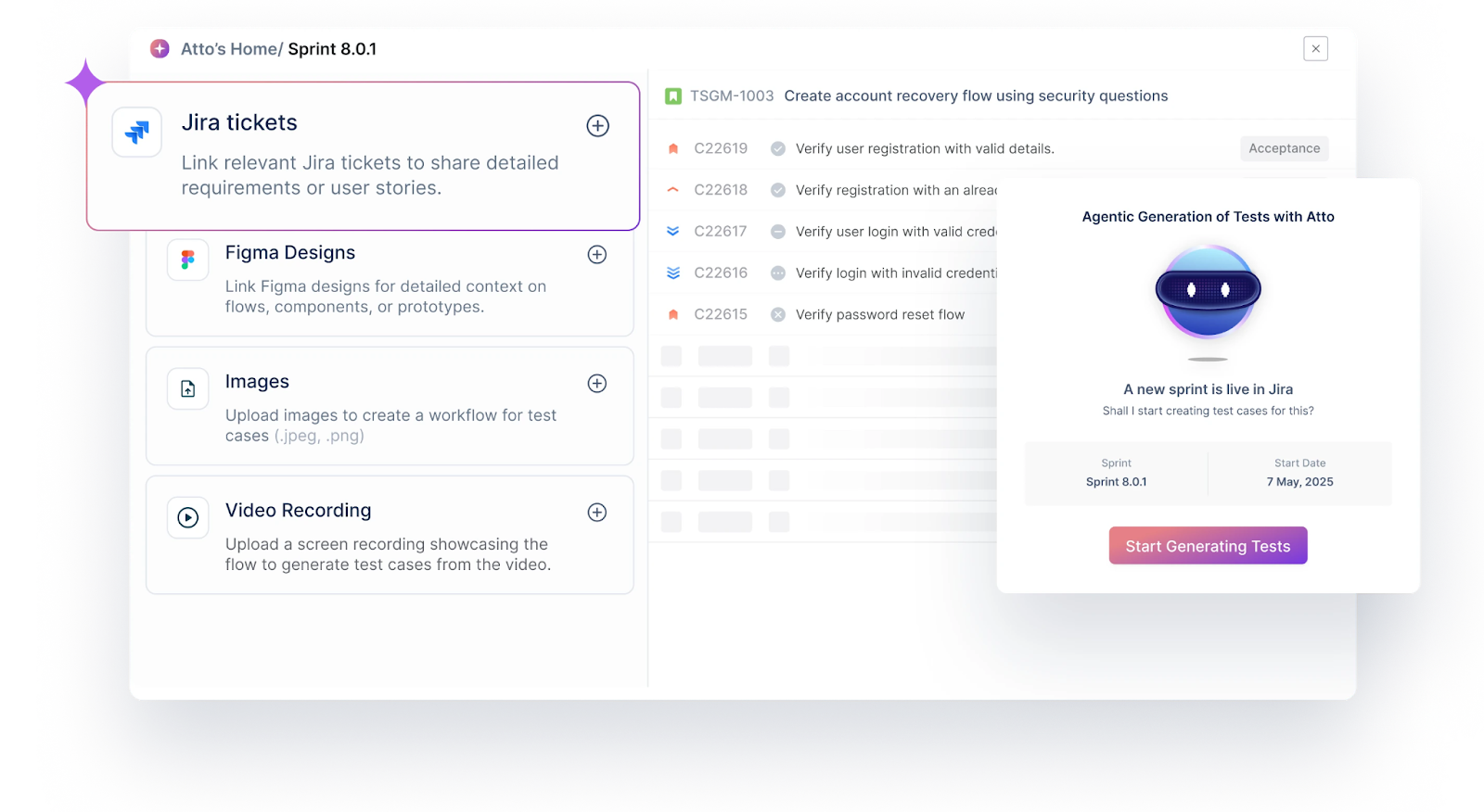
- Atto will:
- Launch the appropriate test environment (mobile or web).
- Identify and interact with UI elements like order forms, stock tickers, and charts.
- Simulate user actions such as placing orders or applying filters.
- Validate that outputs (e.g., order confirmation, balance update) match expected outcomes.
Step 4. Review Test Results and Manage Test Status
- Update each test’s status: Passed / Failed / Retest / Skipped / Blocked / In Progress.
- Manually proceed or let Atto move to the next queued test.
- Repeat until all test cases are executed.
Step 5. View Execution Reports and Log Issues
- Click View Results to access execution logs, screenshots, and data.
- Review key steps such as:
- UI interactions (e.g., placing a trade, canceling an order)
- Backend validations (e.g., order status API calls)
- Timings (e.g., price refresh rate or transaction delay)
- Use Report to Jira to log bugs instantly with test context and evidence.
6. Complete the Test Run
After completing all executions and reviews, click Exit to close the run.
Conclusion
Trading applications are a mix of real and complex functions. All the modules within the application work together to deliver seamless and secure transactions. They even pull data in real time from external systems to keep the users updated of the changing market conditions.
All this clearly points to the need for a comprehensive testing strategy that undertakes more than just functional and UI testing.
Tools that offer precise testing abilities and end-to-end system testing features are the best choice for validating such trading systems. And if they happen to come with a negligible learning curve and the intelligence of AI, the possibilities become endless.
Testsigma is the automated testing platform that combines all the requirements of testers with the power of AI to offer a smart way of testing software, even as complex as trading applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do You Test a Financial Application?
Testing a financial application involves verifying its functionality, accuracy, security, and performance. Testers conduct functional testing to validate features like account management and transaction processing. They also ensure data accuracy by testing real-time market data integration. Security testing is crucial to identify and address vulnerabilities, while performance testing evaluates the application’s responsiveness under various load conditions.
What Are the Types of Testing in Trading?
Various types of testing are essential to ensure trading platform reliability and compliance. Functional testing verifies order placement, execution, and portfolio management features. Performance testing evaluates system responsiveness and scalability under high load. Security testing ensures compliance with regulatory standards and protects against cyber threats. Integration testing validates seamless data exchange with external systems like market data providers.




