Software testing has many types of testing – Functional, unit, integration, system, smoke, regression, and sanity testing. Despite their differences, they all fall under Positive or Negative Testing. This blog post will explain how to implement negative testing in test automation tools. It provides an overview of negative testing with examples of common negative test scenarios.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Negative Testing?
- 2 Why Negative Testing?
- 3 What is an Example of Negative Testing?
- 4 What are the Characteristics of Negative Testing?
- 5 Importance of Negative Testing in SDLC
- 6 Types of Negative Testing
- 7 Negative Testing Techniques
- 8 What Is a Negative Test Case?
- 9 How to Identify Negative Test Cases?
- 10 Parameters for Writing Negative Test Cases
- 11 How to Design a Negative Test Case
- 12 How to Write a Negative Test Case
- 13 Negative Test Case Management: Manual or Automated Testing?
- 14 How to Do Negative Testing?
- 15 Should Negative Testing be Automated?
- 16 Testsigma for Automating Your Negative Testing
- 17 Advantages of Negative Testing
- 18 Disadvantages of Negative Testing
- 19 Challenges in Negative Testing
- 20 Best Practices for Negative Testing
- 21 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Negative Testing?
In simple words, Negative testing is when you try to make the app fail or go down the wrong path to see if it can handle it. It’s important to make sure the app is stable in all possible scenarios!
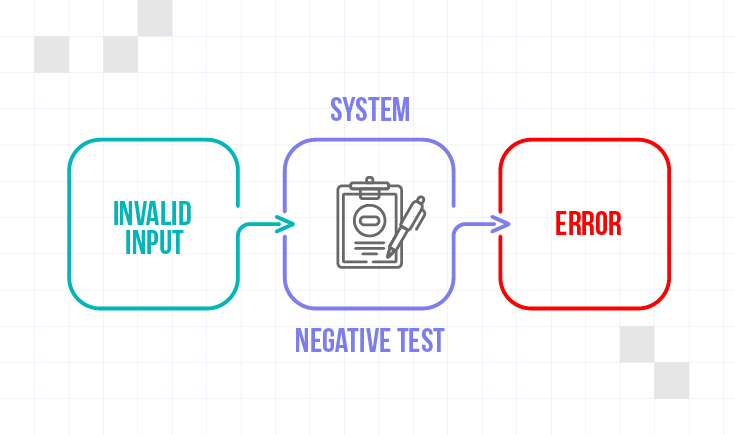
Negative testing is a technique to ensure a system or application can handle unexpected input and conditions. This testing focuses on inputting invalid or out-of-range data and performing actions under unusual circumstances. This testing aims to identify vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the system’s error-handling capabilities. It ensures the system fails gracefully rather than crashing or providing incorrect results. By identifying such issues beforehand, you can improve the application’s robustness and ensure users have a seamless experience even under negative conditions.
Why Negative Testing?
Negative testing is key to building reliable, secure software that meets user needs while minimizing risk.- It helps identify vulnerabilities in the system, including areas with insufficient validation and weak error handling. – Negative tests can simulate real-world scenarios where users may make mistakes or deliberately attempt malicious actions. – Testing edge cases, boundary conditions, and unexpected situations can prevent costly errors from happening down the line. – By testing for failure scenarios, developers can build more resilient systems that continue to operate even in the face of unexpected inputs or errors.
What is an Example of Negative Testing?
A simple example of this testing could be testing a login form by entering incorrect credentials, such as an invalid username or password. The objective is to verify whether the system provides appropriate feedback and error messages in response to the wrong input. It ensures that the system doesn’t crash or behave unexpectedly when it encounters faulty data, which may lead to severe consequences in actual usage scenarios.
What Are the Characteristics of Negative Testing?
The primary objective of this testing is to identify specific issues, such as security vulnerabilities and unintended interactions between different system components. It necessitates skilled testers with a deep understanding of programming languages and significant experience conducting a thorough analysis of functional requirements.
Importance of Negative Testing in SDLC
Here’s how negative testing contributes to a successful SDLC:
1. Uncovers hidden defects: Negative testing reveals how the software responds to abnormal scenarios and identifies potential bugs, weaknesses in error handling, and security loopholes that might go unnoticed with positive testing alone.
2. Enhances software quality: Negative testing finds and fixes errors early in the development process, resulting in a more reliable software product with fewer crashes, better user experience, and lower bug-fixing costs.
3. Validates requirements: Negative testing helps ensure the software meets its specified requirements. It verifies that the system behaves as expected when presented with invalid inputs, preventing unexpected behavior and ensuring the software functions as intended.
4. Improves security: Negative testing is crucial to identify and mitigate security risks by testing the software’s response to malicious inputs, which helps prevent security breaches.
5. Encourages graceful degradation: Negative testing helps ensure that the software gracefully handles unexpected situations. Instead of crashing or behaving erratically, the software should provide informative error messages, guide users toward valid inputs, or enter a safe state when encountering invalid data.
Types of Negative Testing
Here’s a breakdown of the different negative testing techniques you mentioned:
1. Boundary Value Analysis (BVA):
Focuses on testing inputs at the edges or boundaries of expected values. This includes testing values:
-Just below and above the minimum and maximum allowed values.
-At the exact minimum and maximum values.
-One value is less than and one greater than the valid range.
2. Fuzz Testing:
Injects invalid or unexpected data in various formats (invalid characters, special symbols, large data sets) to identify vulnerabilities like crashes, memory leaks, or unexpected behaviour.
Tests show the system handles scenarios related to user sessions, such as:
-Logging in and out multiple times.
-Concurrent login attempts from the same user.
-Session timeout behavior and handling.
It involves actively exploring the application, thinking critically, and trying different inputs and actions to uncover potential issues not covered by pre-defined test cases.
5. Field Size Test:
Tests the system’s behavior when input data exceeds or falls below the allowed field size limitations. This might involve entering
-More characters than the field allows.
-Empty fields if mandatory fields are left blank.
6. Allowed Data Bounds and Limits: Like BVA, this technique tests data within the allowed bounds and limits defined for specific fields. This might involve:
-Testing values at the beginning and end of allowed ranges (e.g., dates, times).
-Testing specific characters or data formats that are not allowed within the field.
7. Data Bound Test:
Like Boundary Value Analysis (BVA), this technique tests inputs at the edges or boundaries of expected values.
8. Exception Testing:
Tests show the application handles unexpected situations and errors. This might involve:
-Dividing by zero.
-Accessing non-existent data.
-Providing invalid file formats.
9. Input Validation Testing:
Specifically, it tests the mechanisms to validate user input and ensure the system accepts and processes only valid data.
10. Numeric Bound Test:
Similar to BVA, but applied specifically to numeric fields. It involves testing values at the
-Minimum and maximum allowed values.
-Values slightly above and below these limits.
-Non-numeric characters are entered in numeric fields.
11. Performance Changes:
While not strictly a negative testing technique, it’s important to consider how the system performs under unexpected loads or data volumes. This can help identify potential performance bottlenecks or stability issues under stress.
12. Required Data Entry:
Tests whether the system enforces the mandatory fields and prevents submission if required data is missing.
Negative Testing Techniques
Here are some simple techniques you can try out:
- Boundary Value Analysis involves testing the extremes of input values, such as the minimum and maximum values.
- Input Validation means testing for invalid or unexpected inputs, such as special characters or incorrect data types.
- Error Guessing involves using your intuition and experience to guess potential errors and testing for them.
- Compatibility Testing means testing the application on different platforms, browsers, and devices to see if it works as expected.
- Stress Testing involves testing the system under heavy loads or high traffic to see how it performs.
- Security Testing means testing the application for vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit.
What is a Negative Test Case?
A negative or error path or failure test case is a deliberately designed test used in software development to verify a system’s behavior when provided with invalid, unexpected, or erroneous data. It’s like trying to “break” the system in controlled ways to identify potential weaknesses and ensure it handles errors gracefully.
How to Identify Negative Test Cases?
Identifying negative test cases involves a systematic approach to finding invalid or unexpected inputs that could expose weaknesses in a software system.
Here are some key strategies to effectively identify them:
1. Leverage Positive Test Cases:
- Start by analyzing existing positive test cases. These define the valid scenarios and expected behavior of the system.
- Reverse engineer these cases to identify opposite or invalid scenarios. For example, if a positive test case involves entering a valid username and password, a negative test case could involve entering an invalid username or password.
2. Analyze Requirements and Specifications:
- Carefully review the system requirements, user stories, and design documents.
- Identify the expected behavior and limitations of the system.
- Look for edge cases or scenarios not explicitly mentioned but implied within the requirements. These can be potential areas for negative test case creation.
3. Employ Boundary Value Analysis (BVA):
- Identify the valid range of inputs for each field or parameter (e.g., age range for registration).
- Design negative test cases that target the boundaries of this range:
- Values just below the minimum valid value.
- Values just above the maximum valid value.
- Values exactly at the minimum and maximum valid values.
4. Utilize Equivalence Partitioning:
- Divide the input space into equivalence partitions, groups of similar inputs expected to behave similarly.
- Design at least one negative test case from each partition to ensure all possible scenarios are covered.
- Example: A login form requires a username and password. Partitions could be valid and invalid usernames and valid and invalid passwords. Negative test cases would include combinations like an invalid username with a valid password, a valid username with an invalid password, and both invalid.
5. Consider Error-Prone Situations:
- Analyze the system’s functionality and identify potential areas prone to errors.
- Design test cases that simulate common user errors or unexpected inputs, such as
Entering special characters in a field meant for numbers.
Leaving required fields blank.
Submitting incomplete forms.
6. Explore Invalid Data Types:
- Identify the expected data type for each input field (e.g., numbers, text, dates).
- Design test cases that provide inputs of incorrect data types.
- Example: Entering alphabetic characters in a field expecting numbers, entering negative numbers where only positive ones are allowed, using special characters instead of plain text.
7. Simulate Missing or Incomplete Data:
- Test the system’s behavior when required fields are left blank or incomplete data is submitted.
- This helps identify potential errors in data handling and validation.
8. Think Outside the Box:
- Consider unusual user interactions or sequences of actions that deviate from the expected flow.
- Design test cases that explore these scenarios to ensure the system handles them gracefully.
- Example: Clicking buttons rapidly, repeatedly submitting the same form with minor variations, trying to access unauthorized functionalities.
Parameters for Writing Negative Test Cases
Here are some key parameters to consider when writing effective negative test cases:
1. Boundary Value Analysis (BVA):
- Identify the valid range of inputs for a specific field or parameter.
- Design test cases that target the boundaries of this range, including
- Values just below the minimum valid value.
- Values just above the maximum valid value.
- Values exactly at the minimum and maximum valid values.
- Example: If a field accepts age between 18 and 65, negative test cases would include ages less than 18 (e.g., 17), greater than 65 (e.g., 66), and exactly 18 and 65.
2. Equivalence Partitioning:
- Divide the input space into equivalence partitions, groups of similar inputs expected to behave similarly.
- Design at least one negative test case from each partition to ensure all possible scenarios are covered.
- Example: A login form requires a username and password. Partitions could be valid and invalid usernames and valid and invalid passwords.
Negative test cases would include combinations like an invalid username with a valid password, a valid username with an invalid password, and both invalid.
3. Error Guessing:
- Analyze the system’s functionality and identify potential error-prone situations.
- Design test cases that simulate common user errors or unexpected inputs.
- Example: Entering special characters in a field meant for numbers, leaving required fields blank, submitting incomplete forms.
4. Invalid Data Types:
- Identify the expected data type for each input field.
- Design test cases that provide inputs of incorrect data types.
- Example: Entering alphabetic characters in a field expecting numbers, entering negative numbers where only positive ones are allowed, using special characters instead of plain text.
5. Missing or Incomplete Data:
- Test the system’s behavior when required fields are left blank or incomplete data is submitted.
- This helps identify potential errors in data handling and validation.
6. Unexpected Actions:
- Consider unusual user interactions or sequences of actions that deviate from the expected flow.
- Test the system’s response to such scenarios to ensure it handles them gracefully.
- Example: Clicking buttons rapidly, repeatedly submitting the same form with minor variations, trying to access unauthorized functionalities.
How to Design a Negative Test Case
Designing a negative test case involves a deliberate and thought-out approach to identifying and creating scenarios that intentionally provide invalid or unexpected inputs to a system. This helps expose potential weaknesses and ensure the system behaves gracefully when encountering errors.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively design negative test cases:
Think Like a Troublemaker
The whole point of a negative test case is to see if you can “break” the software with bad inputs or unexpected actions. So, channel your inner troublemaker and ask yourself:
- “What should I NOT put into this field?” If a box asks for your age, would it work with letters instead? A negative number? A huge number?
- “What would happen if I leave this important part out?” Try leaving fields blank or skipping steps in a process.
- “Can I do things out of order?” Click buttons randomly go back and forth between pages in odd ways.
- “What if I make an obvious mistake?” Misspell common words, use incorrect dates or wrong formats.
Example: Login Page
Let’s say you have a simple login page with a username and password field:
- Invalid data types: Try entering numbers in the username or special symbols in the password field.
- Boundary testing: For a password field that requires at least 8 characters, try 7 characters or a huge password of 50 characters.
- Missing information: Try leaving one or both fields empty and see the error message.
- Weird actions: Repeatedly hit the “Enter” key and click “Login” without entering anything.
How to Write a Negative Test Case
Here’s a breakdown of how to write a negative test case, using a simple login scenario as an example:
1. Identify the functionality to test: Login functionality
2. Analyze the requirements: Username and password are required fields, with specific length and character restrictions.
3. Apply Negative Testing Techniques:
a) Boundary Value Analysis:
- Minimum values: Try usernames or passwords with zero characters (empty field).
- Maximum values: Exceed the maximum allowed characters for username or password.
b) Equivalence Partitioning:
- Invalid usernames: Test with usernames containing special characters, numbers only, or exceeding the allowed length.
- Invalid passwords: Test with passwords containing only special characters, lowercase letters only, or exceeding the allowed length.
c) Missing/Incomplete Data:
- Leave username and password fields blank.
- Leave only one field (username or password) blank.
d) Unexpected Actions:
- Try logging in with a username that doesn’t exist.
- Enter an incorrect password multiple times.
4. Document the test case:
Test Case ID: 01 (unique identifier)
Description: Test login functionality with invalid usernames and passwords.
Steps:
- Open the login page.
- Enter an invalid username (e.g., containing special characters).
- Enter a valid password.
- Click the “Login” button.
Expected Result: The system should display an error message indicating an invalid username.
Repeat steps 2-4 with various other invalid usernames and passwords.
5. Refine and execute:
- Review the test case for clarity and completeness.
- Execute the test case and document the actual results.
- Analyze the results and identify any bugs or unexpected behavior.
- Report and track identified issues for resolution.
This is a simplified example for better understanding.
Negative Test Case Management: Manual OR Automated Testing?
While traditionally managed manually, negative test case management can benefit from automation depending on the specific scenario. Here’s a breakdown of both approaches:
- Pros:
- Flexibility: Manual testing allows for creative exploration and adapting to unexpected situations. Testers can think outside the box and develop new negative scenarios based on their experience and understanding of the system.
- Cost-effective: Manual testing can be more cost-effective than setting up automation frameworks for simple applications or scenarios with limited negative test cases.
- Better suited for complex user interactions: Manual testing is better suited for testing complex user interactions or scenarios requiring human judgment and system response interpretation.
- Cons:
- Time-consuming: Manually executing negative test cases can be time-consuming, especially for large and complex applications.
- Repetitive: Repetitive tasks can lead to human error and inconsistencies in testing execution.
- Difficult to maintain: Maintaining many negative test cases can be challenging and prone to errors, especially as the application evolves.
Automated Testing:
- Pros:
- Speed and efficiency: Automation helps execute test cases quickly and efficiently, saving time and resources.
- Consistency: Automated tests are consistent and repeatable, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring consistent test coverage.
- Scalability: Automation becomes more valuable as the number of negative test cases and the complexity of the application grow.
- Cons:
- Initial setup cost: Setting up the automation framework and scripting negative test cases can require an initial investment of time and resources.
- Maintenance overhead: Maintaining automated tests requires effort to keep them updated as the application evolves or new functionalities are added.
- Limited creativity: Automated scripts and human testers might need help to handle unexpected scenarios or adapt to new situations.
How to Do Negative Testing?
Effective negative testing requires a systematic approach that considers all possible input scenarios.
- The first step is to clearly define test scenarios and boundaries that will challenge the system under test. Attempt to trigger common input errors, such as entering invalid data types or exceeding maximum input lengths.
- Once a set of well-defined scenarios has been established, it’s important to execute them once.
- Testers should try to introduce environment-related errors like uneven load distribution and network disruption.
- Finally, study the output of each test carefully for any irregularities or deviations from the expected results. Also, ensure that appropriate debugging tools are utilized when necessary.
- If the tests need to be executed repeatedly, then going for automation is recommended.
Should Negative Testing Be Automated?
Yes, automated negative testing can be beneficial. Automating these tests lets you catch potential bugs and issues that slip through the cracks. Plus, automated tests are faster and more reliable than manual ones.
Testsigma for Automating Your Negative Testing
Testsigma is an easy-to-use test automation tool that allows you to perform automated negative testing easily. Its intuitive interface lets you quickly create and execute tests that simulate negative scenarios.
Here are the step-by-step processes to automate negative testing using Testsigma:
Step-1: Create a new project in Testsigma.
Step 2: Name your test and add your test cases. For example, here I want to check an e-commerce website – by giving login details. I click on the record button so that creating test cases are automatically done.
Step 3: In Testsigma, you can create test cases using natural language syntax, which makes your work easy. Choose the environment to execute those test cases.
Step 4: Add steps to your test case that simulate the negative scenario. Run and see the results. Here you can see the negative test has passed.
With Testsigma, you can easily create and execute these test cases, allowing you to quickly identify and fix any issues before they impact your users.
You can also automate your negative tests for web, mobile, APIs, and desktop from the same.
Advantages of Negative Testing
Some of the advantages of negative testing are:
- Identifying potential bugs: Negative testing helps identify bugs in the software by stressing it with unexpected input and conditions.
- Enhancing software quality: By exposing issues early in the development cycle, negative testing can help improve the overall quality of the software.
- Saving time and money: Fixing bugs during development is less expensive than fixing them after release, making negative testing a cost-effective approach.
- Increasing user confidence: When a product fails gracefully, even in unexpected scenarios, it also builds the user’s confidence in it.
Disadvantages of Negative Testing
Here are some of the main drawbacks:
- Negative testing can be time-consuming and complex, as testers need to think creatively about all the possible ways a user might try to break the system.
- This testing may only sometimes accurately reflect real-world usage scenarios, as users may not necessarily deliberately try to input incorrect data or perform unexpected actions.
- This testing may result in false positives or false negatives, where issues are either reported when they don’t exist or missed when they do.
- Negative testing can be challenging to automate, requiring human intuition and creativity to develop effective test cases.
- This testing is not a substitute for positive testing, which focuses on verifying that the system behaves correctly under normal conditions. Therefore, both techniques should be used in combination for comprehensive software testing.
Challenges in Negative Testing
While negative testing offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges that software testers must be aware of:
1. Identifying All Negative Scenarios:
- The vast number of potential negative scenarios can be overwhelming.
- It requires creativity, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of the system’s functionality to identify all possible edge cases and unexpected user behaviors.
2. Generating Meaningful Invalid Inputs:
- Creating realistic and impactful negative test cases requires knowledge of the system’s limitations, data types, and potential user errors.
- Simply entering random invalid inputs may not effectively uncover relevant weaknesses.
3. Automation Limitations:
- While automation can be valuable for repetitive negative tests, it can be challenging to automate complex scenarios that require judgment and adaptation based on the system’s response.
- Developing and maintaining automated negative test cases requires additional time and resources.
4. Resource Constraints:
- Thorough negative testing can be time-consuming and require significant effort to design, execute, and analyze the results.
- This can be a challenge for teams with limited time and resources, especially when dealing with large and complex applications.
5. Balancing with Positive Testing:
- It’s important to balance negative and positive testing to cover expected and unexpected behaviors thoroughly.
- Overemphasizing negative testing can lead to neglecting crucial positive test cases and potentially missing critical functionality issues.
6. Managing False Positives:
- Negative testing may sometimes trigger unexpected error messages or system behavior, even when the input is technically valid.
- Identifying and differentiating between genuine issues and false positives can be time-consuming and require careful analysis.
7. Ethical Considerations:
- When designing negative test cases, it’s essential to consider ethical boundaries.
- Avoid scenarios that exploit vulnerabilities, violate user privacy, or have unintended negative consequences.
Best Practices for Negative Testing
These are the things you must do:
1.Plan and Design Early:
Integrate negative testing into your overall test plan from the beginning of the development process.
Consider potential negative scenarios during the design phase to identify issues-prone areas.
2.Focus on Key Areas:
Prioritize negative test cases for critical functionalities, security-sensitive areas, and user interactions with high error potential.
Utilize Boundary Value Analysis (BVA) and Equivalence Partitioning to identify test cases covering valid and invalid input ranges.
3.Embrace Error Guessing:
Think like a user who might make mistakes or use the system unexpectedly.
Design test cases simulating common user errors like leaving required fields blank, entering invalid data types, or providing incorrect formats.
4.Leverage Automation:
Automate repetitive negative tests, especially for regression testing, to save time and resources.
Focus your manual efforts on exploring creative and complex negative scenarios.
5.Document Everything:
Document your negative test cases, including the intended behavior, expected outcome, and steps to be followed.
Maintain and update your documentation as the software evolves to ensure test cases remain relevant.
6.Think Outside the Box:
Beyond basic negative test cases, explore unexpected user actions or sequences that may reveal hidden issues.
Consider testing edge cases, invalid combinations of inputs, and scenarios exceeding system limitations.
7.Validate Error Handling:
Verify that the system handles unexpected inputs and errors.
Ensure informative error messages are displayed, guiding users to correct their inputs and preventing system crashes.
8.Learn and Adapt:
Analyze the results of your negative testing to identify potential bugs and weaknesses.
Report and fix issues promptly and adapt your testing strategies based on the findings.
9.Continuous Improvement:
Refine your negative testing approach based on experience and project requirements.
Share best practices and lessons learned with your team to improve testing effectiveness.
10.Combine with Positive Testing:
Negative testing does not replace positive testing.
Utilize both positive and negative testing strategies in a balanced manner to achieve comprehensive test coverage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Do Testers Avoid Performing Negative Testing?
Testers may avoid negative testing due to its perceived time consumption and potential to delay release despite its valuable contribution to software quality and security.
| Read More: Positive and Negative Testing Scenarios |








