“Acceptance testing is not just about finding bugs. It is about ensuring the software is ready for users.” – Michael Bolton, Software tester.
Acceptance testing is the final stage before the software is released to users. Ensuring that the software meets the business requirements and the users’ needs is essential.
I would like to share some interesting facts here:
- According to a study by IBM, acceptance testing can find up to 90% of the defects in software.
- The cost of fixing a defect after it has been released to users is up to 100 times higher than during acceptance testing.
- Acceptance testing can reduce the risk of customer dissatisfaction and costly recalls.
This page talks about the basics of acceptance testing all in detail, including:
- What it is
- Why it is important
- The different types of acceptance testing
- How to do it effectively

Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What is Acceptance Testing?
- 3 Purpose or Reasons to Perform Acceptance Testing
- 4 Objectives of Acceptance Testing
- 5 Importance of Acceptance Testing
- 6 When Do You Perform Acceptance Testing?
- 7 Who Performs Acceptance Testing?
- 8 Type of Acceptance Testing
- 9 Advantages and Disadvantages of Acceptance Testing
- 10 Entry and Exit Criteria for Acceptance Testing
- 11 Acceptance Test Plan – Attributes
- 12 How to Write Acceptance Tests?
- 13 Quick Steps to Perform Acceptance Testing
- 14 How to Perform Acceptance Testing – Manual and Automated Approaches?
- 15 Acceptance Test Report – Attributes
- 16 Streamlining Acceptance Tests
- 17 Common Challenges of Acceptance Testing
- 18 List of Acceptance Testing Frameworks
- 19 Acceptance Testing Comparison with Other Testing
- 20 Conclusion
Overview
What is Acceptance Testing?
Acceptance testing checks if a system meets its business and user requirements before it’s released to production.
Importance of Acceptance Testing
- Validates that the software meets project and user requirements
- Detects defects before release to improve reliability
- Confirms end-user acceptance based on real feedback
- Identifies risks before deployment
- Ensures compliance with legal and industry regulations
- Verifies performance, functionality, and integration
- Improves software quality and stability before going live
Types of Acceptance Testing
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Performed by end-users to confirm the system meets business requirements
- Alpha Testing: Done internally to catch critical issues before external release
- Beta Testing: Carried out by selected external users to gather feedback
- Operational Testing: Validates maintenance, backup, and monitoring processes
- Contract Testing: Ensures the product meets contractual agreements
- Regulatory Testing: Verifies compliance with industry regulations
- Compliance Testing: Confirms adherence to internal organizational standards
- Performance Testing: Checks response time, scalability, and load stability
- Security Testing: Validates the system’s defense against threats and vulnerabilities
Quick Steps to Perform Acceptance Testing
- Requirement Analysis: Review business goals, user expectations, and acceptance criteria
- Test Plan Creation: Define scope, strategy, schedule, and resource needs
- Test Case Design: Write test cases based on requirements and expected outcomes
- Test Case Execution: Run test cases and log actual vs expected results
- Result Analysis and Reporting: Verify test results, confirm readiness for deployment, and document findings
What is Acceptance Testing?
Acceptance testing is software testing that evaluates whether a system meets its business and user requirements. It is the final testing stage before a system is released to production.
The main purpose of acceptance testing is to verify that a system:
- Meets all of its functional and non-functional requirements
- Easy to use and navigate
- Reliable and functions as expected
- Secure and comply with all applicable regulations
This testing is performed by end users or an expected group of users. This ensures that the system is tested from the perspective of the people using it daily.
Here are some specific examples of acceptance tests:
- A user can successfully create an account and log in to the system.
- A user can successfully search for and purchase a product from the system.
- A user can successfully add and remove items from their shopping cart.
- A user can successfully checkout and complete a purchase.
- The system can process a certain number of transactions per second without any errors.
- The system can handle several concurrent users without any performance degradation.
- The system is resistant to common security attacks.
This testing is an essential part of the software development process. It helps to ensure that systems are high-quality and meet the needs of their users.
Purpose OR Reasons to Perform Acceptance Testing
Here are the major reasons :
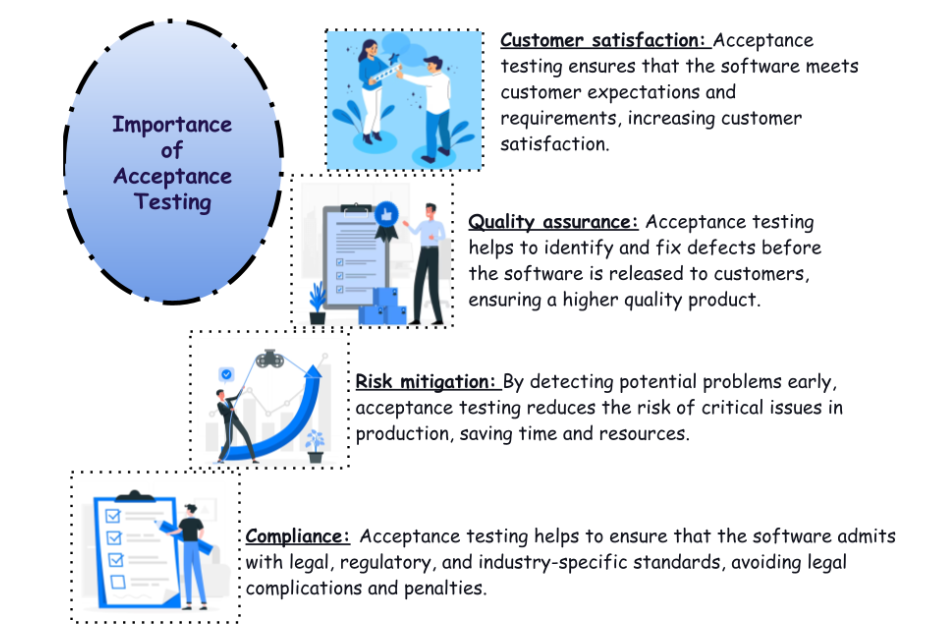
- Validate requirements compliance: Testing ensures software meets project requirements and user expectations. This aligns the software with the expectations of stakeholders and end-users.
- Ensure quality and reliability: Testing helps to identify and fix any defects, issues, or inconsistencies in the software before it is released to end-users. This enhances the overall quality and reliability of the software.
- Verify user acceptance: Testing involves end-users or client representatives interacting with the software to validate its usability, functionality, and overall satisfaction. The feedback ensures the software meets user requirements and expectations.
- Mitigate risks: Testing helps to identify potential risks associated with the software before its release. This allows for timely mitigation, reducing the risk of critical problems in the production environment.
- Ensure compliance: In many industries, compliance with legal, regulatory, or industry-specific standards is crucial. This testing helps to ensure that the software complies with these requirements, avoiding legal issues and penalties associated with non-compliance.
Objectives of Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing aims to ensure that the final product meets the expectations of the end-users. And if it does not, this testing in software testing again attempts to right the wrong readily. The objectives revolve around the same philosophy:
- It verifies the functionality and performance of the system for customer use.
- It identifies and addresses any defects or issues before the software is deployed.
- This testing checks the integration capabilities of the application.
- One objective is to make sure that the software matches the stakeholders’ expectations and delivers a positive user experience.
- It aims to improve the product quality and reliability.
- It focuses on mitigating risks associated with software deployment and usage in a real-world environment.
Importance of Acceptance Testing
Some primary importance of this testing is presented in the below image
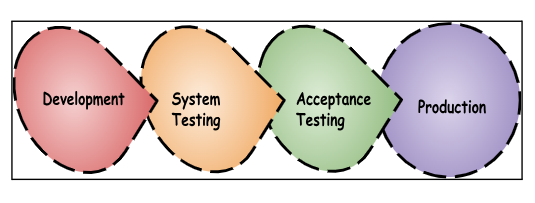
When Do You Perform Acceptance Testing?
Acceptance testing is typically performed after system testing and before product deployment. It occurs in the final stages of the software development life cycle.
This testing begins once the software has undergone system testing and the development team has addressed identified issues.
This phase involves end-users or client representatives interacting with the software to validate its
- functionality,
- usability, and
- requirements compliance.
Who Performs Acceptance Testing?
This testing is typically performed by end-users or client representatives, who are the intended users of the software.
- They understand the software’s business needs, expectations, and requirements, allowing them to validate its functionality and usability effectively.
- They simulate real-world usage scenarios to ensure the software meets their needs and preferences, providing critical feedback and final approval before it is released to production.
- Quality assurance (QA) teams may also facilitate and guide the acceptance testing process, ensuring it is conducted systematically and in line with predefined test criteria.
Type of Acceptance Testing
There are several types of acceptance testing, each serving a unique purpose.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Performed by end-users or client representatives to validate whether the system meets their business requirements and expectations. It typically includes real-world scenarios and helps ensure the software is ready for production deployment.
- Alpha Testing: Conducted by the internal development team before releasing the software to a selected group of users. The goal is to identify any critical issues early on and make necessary improvements before moving to beta testing.
- Beta Testing: This involves releasing the software to a limited set of external users who provide feedback based on their experience using the application. This helps uncover potential issues and gather insights for further improvements before a broader release.
- Operational Testing: Focuses on validating the operational aspects of the software, including backup and recovery procedures, system monitoring, and maintenance processes. It ensures the system is supportable and can be managed effectively in a live production environment.
- Contract Testing: Ensures the software development meets the contractual requirements and specifications outlined in the project contract. It involves checking if the delivered product aligns with what was agreed upon in the contract.
- Regulatory Testing: Ensures the software complies with relevant industry-specific regulations, standards, or legal requirements. This is particularly important in healthcare, finance, or government industries, where strict regulatory compliance is necessary.
- Compliance Testing: Focuses on confirming that the software complies with internal organizational policies, guidelines, and standards. It ensures the software aligns with the organization’s rules and regulations.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the software’s performance to ensure it meets predefined performance criteria, such as response time, scalability, and stability under various load conditions.
- Security Testing: Focuses on validating the security features and controls of the software, ensuring that it is protected against potential security threats and vulnerabilities.
Choosing the Right Type of Acceptance Testing
The choice of acceptance testing types depends on the project requirements, the software’s nature, and the testing phase’s specific objectives.
Multiple types of acceptance testing may often be conducted to ensure a thorough evaluation of the software’s readiness for deployment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Acceptance Testing
Let us look into some of the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages :
- Direct user feedback: This testing involves users directly, which helps the project team understand their needs and expectations better.
- Automated test execution: This testing can save time and effort, especially for large or complex software applications.
- Improved user satisfaction: When users are directly involved in the testing process, they are more likely to be satisfied with the final product.
- Thorough testing: This testing covers all aspects of the software’s functionality, including the user interface, business logic, and performance.
Disadvantages :
- User knowledge requirements: Users must have basic knowledge about the software to participate effectively in this testing.
- Low user participation: Some users may be reluctant to participate in acceptance testing because they need more time or are uninterested.
- Slow feedback: It can take time to collect and analyze feedback from a large group of users, mainly if their opinions differ.
- Development team involvement: The development team is typically not involved in acceptance testing, which can lead to communication gaps and misunderstandings.
Entry and Exit Criteria for Acceptance Testing
Here are the points of the criteria for Acceptance Testing
Entry Criteria:
- All requirements have been documented and analyzed.
- A test plan has been created and approved.
- The test environment is set up and ready to use.
- All test cases have been designed and reviewed.
- The necessary test data has been prepared.
Exit Criteria:
- All test cases have been executed.
- All defects have been identified and reported.
- All critical defects have been fixed.
- The software meets all of the acceptance criteria.
- The software is ready for user acceptance and deployment.
Acceptance Test Plan – Attributes
The following are some of the key attributes of an ATP:
- Introduction: This section provides an overview of the project, the software being tested, and the purpose of the ATP.
- Acceptance Test Category: This section identifies the types of acceptance testing that will be performed, such as user acceptance testing, system acceptance testing, and integration testing.
- Operation Environment: This section describes the hardware and software environment where the acceptance testing will be performed.
- Test Case ID: This is a distinctive identifier for each test case.
- Test Title: This is a brief description of a test case.
- Test Objective: This section describes what a test case is designed to verify.
- Test Procedure: This section describes the steps in executing a test case.
- Test Schedule: This section specifies the dates and times when test cases will be executed.
- Resources: This section identifies the resources required to execute the acceptance testing, such as personnel, equipment, and software.
How to Write Acceptance Tests?
Acceptance test cases are written to ensure that the software meets the requirements and expectations of end-users. Before creating test cases, it’s essential to have clear acceptance criteria and pre-conditions, which define the conditions that must be met for a user story or feature to be considered complete.
Let’s consider an example to write acceptance tests.
User Story: As a Registered User, I Want to Be Able to Reset My Password.
Acceptance Criteria:
- The “Forgot Password” link is accessible on the login page.
- Clicking the link navigates the user to a page with a password reset form.
- After resetting the password, the user receives a confirmation email.
Before running the tests, satisfy the below criterias:
- Clearly state the objective of the test case, e.g., Reset Password Functionality.
- Define any necessary pre-conditions, e.g., User is registered and logged out.
Further Reading: Acceptance Criteria vs Acceptance Testing
Outline step-by-step actions to execute the test cases for forgot password:
Step 1: Access the login page.
Step 2: Click on the “Forgot Password” link.
Step 3: Verify the user is redirected to the password reset page.
Step 4: Complete the password reset form.
Step 5: Confirm the receipt of the password reset confirmation email
Expected Outcome:
- The login page is displayed.
- The password reset page is displayed.
- The user sees the password reset form.
- The user receives a success message after submitting the form.
- The user receives a confirmation email.
Acceptance Criteria Verification:
- Validate that the acceptance criteria are met:
- Verify that the “Forgot Password” link is present and functional.
- Confirm successful redirection to the password reset page.
- Validate the receipt of the confirmation email.
Similar to this, you can create and run acceptance tests for other features.
Quick Steps to Perform Acceptance Testing
Here are some quick steps to perform better acceptance testing.
- Requirement Analysis:
- Understand and analyze the project requirements, including business objectives, user expectations, and acceptance criteria. This step helps identify the scope of acceptance testing and the critical functionalities to be validated.
- Test Plan Creation:
- Develop a comprehensive test plan outlining the acceptance testing strategy, scope, objectives, resources, schedules, and acceptance criteria. The plan serves as a roadmap for the acceptance testing process, ensuring organized and structured testing activities.
- Test Case Design:
- Create detailed test cases based on the identified requirements and acceptance criteria. These test cases define specific steps, input data, and expected outcomes for validating the software’s behavior and functionalities against the defined criteria.
- Test Case Execution:
- Execute the designed test cases in the testing environment, following the steps outlined in the test cases. During this phase, testers interact with the software, record results, and identify expected and actual outcomes discrepancies.
- Result Analysis and Reporting:
- Evaluate the test results against the predefined acceptance criteria to confirm whether the software meets the specified objectives. Verify if all critical functionalities are working as intended and if the software is ready for user acceptance and deployment.
- Prepare a comprehensive test report summarizing the testing activities, results, and findings. This report is a valuable resource for stakeholders to make informed decisions about the software’s deployment.
Following these steps in a structured manner helps ensure that the software meets the intended requirements, functions adequately, and is aligned with the business goals, ultimately preparing it for successful deployment.
How to Perform Acceptance Testing – Manual and Automated Approaches?
Here are two approaches to performing :
1. Manual Acceptance Testing
Manual acceptance testing involves human testers executing test cases without using automation tools. This approach is often used for smaller projects or scenarios where automation must be more practical and cost-effective.
Steps for Manual Acceptance Testing:
- Requirements Review: Understand the software requirements and acceptance criteria to design relevant test cases.
- Test Case Creation: Based on the requirements and acceptance criteria, create test cases covering all relevant scenarios.
- Test Data Preparation: Prepare necessary test data and ensure it aligns with the test cases.
- Test Environment Setup: The testing environment should have the required configurations and prerequisites.
- Test Execution: Manually execute the test cases in the testing environment.
- Defect Reporting: Document any defects found during testing and report them to the development team.
- Regression Testing: After defect fixes, perform regression testing to ensure the reported defects are resolved and no new issues have been introduced.
- Test Closure: Summarize the testing activities, report the test results, and obtain stakeholders’ approval for software release.
2. Automated Acceptance Testing
Automated acceptance testing involves using automated testing tools and scripts to execute test cases. This approach suits large or complex projects to save time and increase efficiency.
Steps for Automated Acceptance Testing:
- Tool Selection: Choose an appropriate automated testing tool based on the project requirements, technology stack, and budget.
- Test Script Development: Write test scripts using the selected automated testing tool, translating test cases into executable scripts.
- Test Data Preparation: Prepare and input the necessary test data into the automated test scripts.
- Test Environment Setup: The testing environment should have the necessary configurations and dependencies for automated testing.
- Script Execution: Run the automated test scripts to execute the test cases.
- Defect Reporting: Automated tools can also log and report defects automatically.
- Regression Testing: After defect fixes, rerun the automated tests to ensure the reported defects are resolved, and no new issues have been introduced.
- Test Result Analysis: Review and analyze the test results generated by the automated testing tool.
- Test Closure: Summarize the testing activities, report the test results, and obtain stakeholders’ approval for software release.
Which Approach to Choose?
Let me clarify your doubts about which one to choose. Actually, the choice is yours!
The approach depends on the project’s specific requirements, budget, timeline, and the complexity of the software being developed.
Manual testing is typically used for:
- Complex or subjective test cases
- Exploratory testing
- Testing with real users
- Testing user interfaces
- Testing performance and security
Automated testing is typically used for:
- Repetitive or regression testing
- Testing with large volumes of data
- Testing complex business processes
- Testing integrations with other systems
Teams can ensure software quality and success by choosing the right combination of manual and automated testing based on the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
Acceptance Test Report – Attributes
The following are some of the key attributes of an ATR:
- Report Identifier: This is a unique identifier for the ATR.
- Summary of Results: This part provides a high-level overview of the test results, including the number of test cases passed, failed, and blocked.
- Variations: This section describes any variations from the test plan, such as any test cases that were not executed or defects that were not fixed.
- Recommendations: This section recommends whether the software is ready for user acceptance and deployment. It may also include additional testing recommendations or fixing any outstanding defects.
- Summary of To-Do List: This section summarizes the outstanding defects and any other tasks that must be completed before the software is ready for user acceptance and deployment.
- Approval Decision: This section indicates whether the software has been approved for user acceptance and deployment.
Streamlining Acceptance Tests
Optimizing and streamlining acceptance testing types for end users and the business is necessary to reduce efforts on the end users. It involves adopting efficient practices to enhance collaboration, speed up testing cycles, and ensure thorough validation. Here are several ways to achieve this:
- Involve end users and business stakeholders early in the development process to gather feedback and align expectations from the beginning.
- Define clear and specific acceptance criteria for user stories or features.
- Conduct parallel testing, where multiple acceptance tests can be executed simultaneously.
- Utilize user story mapping techniques to prioritize features and acceptance testing based on user needs.
- Organize collaborative testing workshops involving developers, testers, end users, and business analysts to enhance communication and understanding of testing requirements.
- Implement visual validation tools to automatically compare UI changes.
- Make use of automated testing tools to for defect tracking and reporting from the users to the testers and developers.
- Provide comprehensive documentation and training materials to support end users during the run of any type of acceptance testing.
- Employ mocks and stubs to simulate external dependencies and streamline testing when certain components are not available or ready.
- Create scalable testing environments that can accommodate various configurations and mimic production scenarios.
Common Challenges of Acceptance Testing
Like any other testing process, acceptance testing in software testing has some associated challenges.
- Unclear or ambiguous requirements can lead to misunderstandings between stakeholders and testing teams.
- Achieving comprehensive test coverage for all possible scenarios and user interactions is challenging.
- Frequent changes in requirements during the development process can impact test planning and execution.
- The difficulty in obtaining realistic and comprehensive test data for testing various scenarios is a huge challenge.
- Coordinating and scheduling involvement from actual end-users for testing can be logistically challenging.
- The subjective nature of user acceptance can introduce variability in interpretation and evaluation.
- Ensuring compatibility with testing tools and environments can be problematic, impacting the test execution.
List of Acceptance Testing Frameworks
Here are some significant frameworks you have to know.
Testsigma
Testsigma is a tool for automating acceptance tests and allows you to scale your test automation efforts when needed. Some features that make it ideal for the automation testing frameworks are:
- It’s a no-code test automation tool; thus, writing your tests is like writing them in simple English. You don’t need to be an expert in coding here.
- You begin your test automation in minutes.
- Testsigma lets you automate your tests for web, mobile, desktop, and APIs from the same place.
- The test cases are very easy to edit too.
Cucumber
Cucumber is a popular acceptance testing framework that uses the Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) approach. It allows testers to write test cases in a natural language format, which makes them easier to understand and maintain.
Cucumber supports multiple programming languages, including Java, JavaScript, Python, and Ruby.
Selenium WebDriver
Selenium WebDriver is a powerful and widely adopted application acceptance testing framework. It provides a platform for automating browser interactions and validating the application’s behavior against defined acceptance criteria.
Selenium WebDriver supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, C#, and more, making it versatile and adaptable to various projects.
SpecFlow
This is another popular acceptance testing framework that uses the BDD approach. It is similar to Cucumber but specifically designed for .NET development. SpecFlow supports multiple programming languages, including C#, F#, Visual Basic, and .NET.
Robot Framework
This generic acceptance testing framework can be used to test any software application. It is a keyword-driven framework, meaning test cases use keywords specific to the application being tested. Robot Framework supports multiple programming languages, including Python, Java, and JavaScript.
Acceptance Testing Comparison with Other Testing
Acceptance Testing VS System Testing: Key Differences
Here get the key difference between acceptance testing and system testing below. Click the link here to read more on System Testing.
| Acceptance Testing | System Testing |
| We perform acceptance testing to check if the product meets the requirements of use/business | We perform system testing to test the software as a whole.A complete end to end test is performed to check if all the features work as expected |
| It includes only functional testing and is performed by end-users or stakeholders | It includes both functional and non-functional testing.The tests are performed by a team of testers. |
| We use real data from production to perform acceptance testing | Mocked or test data is used to perform system testing |
| It verifies the business requirement and what the customer wants | It tests the performance, regression,reliability, compatibility,security and other such aspects of the product. |
| It is a combination of alpha and beta testing | It is a combination of system and integration testing |
| The product is considered as a failure if a defect or bug is found | Any bugs if found are fixed and retesting is done. |
| Here, we only check if the new product meets specified requirements | Here, we tests the system’s integrity and whether it interacts well with subsystems and external applications. |
Conclusion
Overall, acceptance testing is an essential part of the software development lifecycle. It helps to ensure that the software meets the users’ needs and is ready for production deployment. By following these tips, you can maximize its benefits.

