- collaboration
Invite Team Members
Assign Projects
Users & Role Management
Review Management [Test Cases]
Review Management [Elements]
Execution Controls
- test cases
Test Cases
Test Case List Actions
Import and Export Test Cases
Import Test Project Test Cases
Importing Postman Collections and Environments
Test cases for Desktop Windows
Update Test Case result in a Test Plan
Test cases for Mobile Web Application
- Test Step Types
Type: Natural Language
Type: REST API
Type: Step Group
Type: For Loop
Type: While Loop
Type: Block
Type: If Condition
Nested Step Groups
Create Test Steps
- Create Test Steps Using Simple English
Test Step Settings
Test Step Options
Reuse Elements
Test Step Reordering
Bulk Actions
Add Steps Before & After
- Web Applications
Test Step Actions
Test Step Settings
Test Data in Steps
Add Steps Manually
Reuse Elements
Update Elements
Create an Element
Reorder Test Steps
Bulk Actions
Add Steps Before & After
Record steps anywhere in a Test Case
Image Injection
Cross-application testing
- Test Data Types
Raw
Parameter
Runtime
Random
Data Generator
Phone Number
Mail Box
Environment
Concat Test Data
Create Test Data [Parameter]
Update Test Data Profile
Updating Value in TDP
Import TDP
Bulk Deletion of a Test Data Profile
Create Test Data [Environment]
- Elements (Objects)
- Web Applications
Record Multiple Elements
Record Single Element
Create Elements
Supported Locator Types
Formulating Elements
Shadow DOM Elements
Verifying elements in Chrome DevTools
Handling iframe Elements?
Dynamic Locators using Parameter
Dynamic Locators using Runtime
Using Environment Test Data for Dynamic locators
Import/Export Elements
AI Enabled Auto-Healing
- test step recorder
Install Chrome Extension
Install Firefox Extension
Install Edge Extension
Exclude Attributes/Classes
- test plans
Add, Edit, Delete Test Machines
Add, Edit, Delete Test Suites
Schedule Test Plans
Run Test Suites In Parallel
Cross Browser Testing
Distributed Testing
Headless Testing
Test Lab Types
Disabling Test Cases in Test Plans
AfterTest Case
Post Plan Hook
AfterTest Suite
Email Configuration in Test Plan
Execute Partial Test Plans via API
Ad-hoc Run
Test Plan Executions
Dry Runs on Local Devices
Run Tests on Vendor Platforms
Run Test Plans on Local Devices
Test Locally Hosted Applications
Debug Test Case Failures
Parallel and Allowed queues
- debugging
Debug results on local devices (Web applications)
Debug Results on Local Devices
Launch Debugger in the Same Window
- Testsigma Agent
Pre-requisites
Setup: Windows, Mac, Linux
Setup: Android Local Devices
Setting up iOS Local Devices
Update Agent Manually
Update Drivers Manually
Delete Corrupted Agent
Triggering Tests on Local Devices
- troubleshooting
Agent - Startup and Registration Errors
Fetching Agent logs
Upgrade Testsigma Agent Automatically
Testsigma Agent - FAQs
- continuous integration
Test Plan Details
REST API(Generic)
Jenkins
Azure DevOps
AWS DevOps
AWS Lambda
Circle CI
Bamboo CI
Travis CI
CodeShip CI
Shell Script(Generic)
Bitrise CI
GitHub CICD
Bitbucket CICD
GitLab CI/CD
- desired capabilities
Most Common Desired Capabilities
Browser Console Debug Logs
Geolocation Emulation
Bypass Unsafe Download Prompt
Geolocation for Chrome & Firefox
Custom User Profile in Chrome
Emulate Mobile Devices (Chrome)
Add Chrome Extension
Network Throttling
Network Logs
Biometric Authentication
Enable App Resigning in iOS
Enable Capturing Screenshots (Android & iOS)
Configure Android WebViews
Incognito/Private mode
Set Google Play Store Credentials
- addons
What is an Addon?
Addons Community Marketplace
Install Community Addon
Prerequisites(Create/Update Addon)
Create an Addon
Update Addon
Addon Types
Create a Post Plan Hook add-on in Testsigma
Create OCR Text Extraction Addon
- configuration
API Keys
- Security(SSO)
Setting Up Google Single Sign-On(SSO) Login in Testsigma
Setting Up Okta Single Sign-On Integration with SAML Login in Testsigma
Setting up SAML-based SSO login for Testsigma in Azure
iOS Settings
Creating WDA File for iOS App Testing
- uploads
Upload Files
Upload Android and iOS Apps
How to generate mobile builds for Android/iOS applications?
- Testsigma REST APIs
Environments
Elements
Test Plans
Upload Files
Get Project wide information
Upload and update test data profile
Trigger Multiple Test Plans
Trigger Test Plan remotely and wait until Completion
Run the same Test Plan multiple times in Parallel
Schedule, Update and Delete a test plan using API
Update Test Case results using API
Create and update values of Test Data Profile using REST API
Rerun Test Cases from Run Results using API
- open source dev environment setup
macOS and IntelliJ Community Edition
macOS and IntelliJ Ultimate Edition
Windows and IntelliJ Ultimate Edition
Setup Dev Environment [Addons]
- NLPs
Unable to retrieve value stored in text element
Unable to capture dropdown element
Unable to Select Radiobutton
Unable to Click Checkbox
- setup
Server Docker Deployment Errors
Secured Business Application Support
Troubleshooting Restricted Access to Testsigma
Why mobile device not displayed in Testsigma Mobile Test Recorder?
Unable to create new test session due to unexpected error
- web apps
URL not accessible
Test Queued for a Long Time
Issues with UI Identifiers
Missing Elements in the Recorder
- mobile apps
Failed to Start Mobile Test Recorder
Troubleshooting “Failed to perform action Mobile Test Recorder” error
Test Execution State is Queued for a Long Time
Mobile app keeps stopping after successful launch
More pre-requisite settings
Unable to start WDA Process on iPhone
Most Common causes for Click/Tap NLP failure
- on premise setup
On-Premise Setup Prerequisites
On-Premise Setup with Docker-compose File
Post-Installation Checklist for On-Premise Setup
Install Docker on an Unix OS in Azure Infrastructure
SMTP Configuration in Testsigma
Configure Custom Domains
Shadow DOM Elements
Shadow DOM elements allow you to encapsulate and isolate styling and functionality in a webpage, maintaining a clean structure. The Document Object Model (DOM) attaches a hidden DOM to a chosen element, keeping local styles and markup separate. Although it benefits developers, it poses challenges for automation testing since shadow root elements do not exist in the main DOM.
To perform reliable tests, you need to find these elements. This guide will explain how Testsigma can help you locate and capture Shadow DOM elements for effective testing.
Prerequisites
You must understand specific concepts such as creating Projects, Test Cases, Elements, and Recording Test Steps.
Identifying Shadow DOM in a Webpage
Follow the below steps to identify if a webpage uses Shadow DOM:
- To open the Chrome Developer Tools and highlight webpage elements, right-click on the webpage and select Inspect.
- Expand the
<body>tag in the Elements tab and verify if it contains#shadow-rootto indicate the presence of Shadow DOM on the webpage.

Basic Shadow DOM Terminologies
- Shadow Host: The HTML element is the entry point for encapsulated components by attaching a shadow DOM.
- Shadow Tree: A component encapsulates and isolates its internal structure and styling through a hidden tree of DOM elements within a shadow DOM.
- Shadow Boundary: An invisible wall separates the shadow DOM from the main DOM, keeping styles and functionality isolated.
- Shadow Root: The shadow DOM's starting point is the hidden tree's root node, where everything begins.

Create Element for Shadow DOM
This section will demonstrate how to capture and store shadow DOM elements using Testsigma. For this demonstration, we'll use the shopping website shop.polymer-project.
- Navigate to Create Tests > Elements in the left side navbar. Click on Create Element at the top right corner of the Elements List page to capture the Element on the webpage.
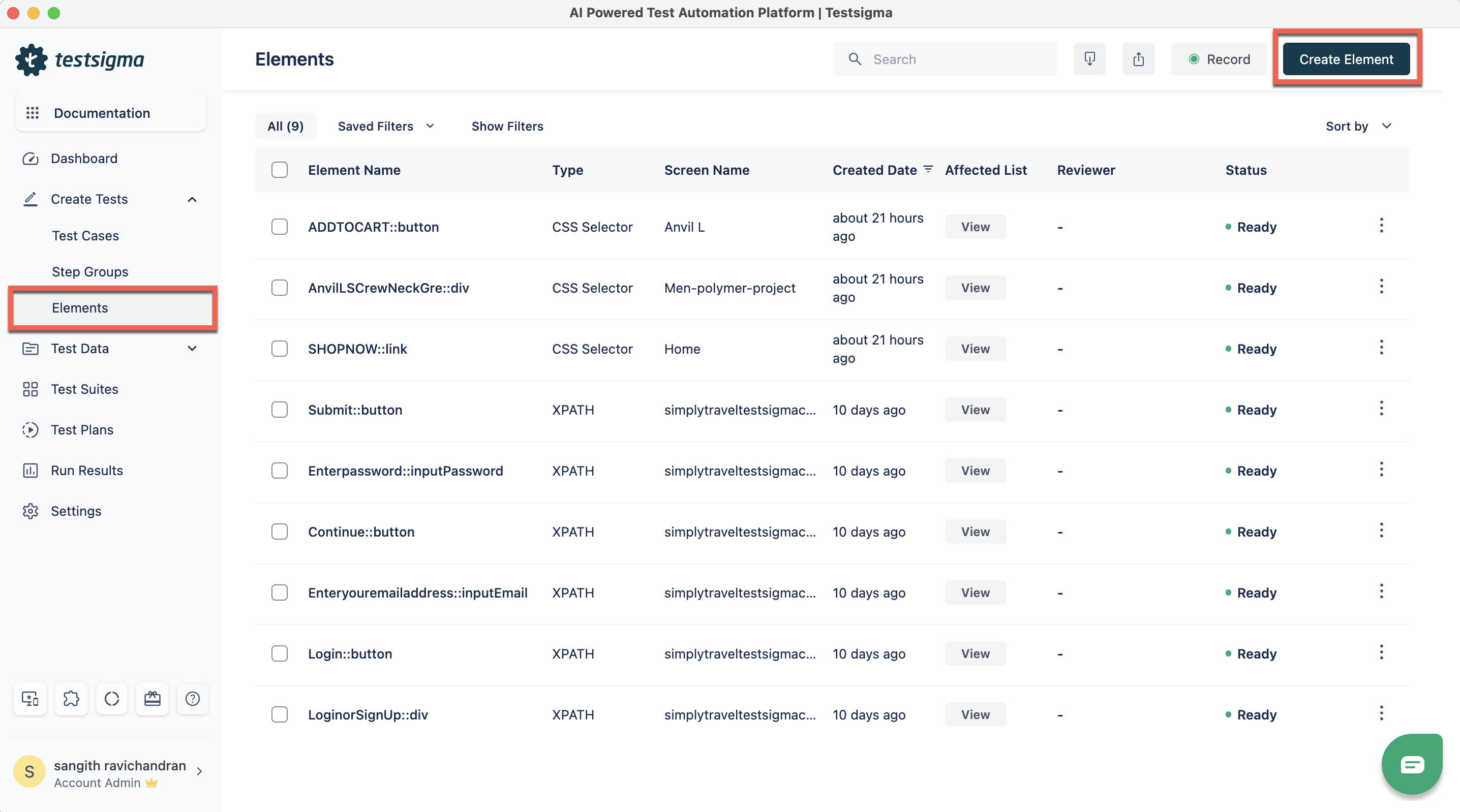
- Click Create Element to open an overlay screen on the right side of the page. Click Record Element within this overlay to easily capture the Element. Open the webpage in a new tab and click on the Element you want to capture. Then, click Capture to record the Element in the Record Element pop-up menu.
- Alternatively, manually fill in the Name and Screen Name, Element Type, Element Value, and Host Values fields to capture the Element.
- Fill in the fields with the element Name and Screen Name. Then, choose CSS Selector as the Element Type from the dropdown menu since only CSS selectors can access elements within shadow DOM.
- To obtain the CSS Selector, right-click on the webpage and choose Inspect to open Chrome Developer Tools. Then, you must locate the Element you need using the Select Element in the page to inspect it icon.
- Once you have located the Element, right-click on it and choose Copy from the menu. Next, select Selector from the dropdown menu and copy the CSS selector value that appears. Finally, paste it into the Enter the value field.

- Check the box Present inside Nested Context to specify the hosts from the parent host to the current element host in the order.
- Follow the order from the Parent Host to the Current Host and specify each shadow host element's Shadow DOM and CSS Selector values.
- Click Create Element and use it in Test Cases.

To create an element in a Test Case, use NLP to add a new step to the test case and include a placeholder for the Element. Capture elements on the webpage by clicking Create Element, or use Testsigma Record to capture the steps and their associated elements during test step recording.