Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What is Selenium mobile testing and what are its benefits?
- 3 Native vs hybrid app testing with Selenium
- 4 Selenium mobile testing setup: Step-by-step guide
- 5 Implementing Selenium with Appium for mobile devices
- 6 Best practices for Selenium mobile test automation
- 7 Common Selenium mobile testing challenges and solutions
- 8 Why choose Testsigma for mobile testing?
- 9 Frequently Asked Questions
Overview
Get the best Selenium mobile testing practices: use dynamic waits, implement Page Object Model (POM), and prioritize cross-device testing. Plus, tips on efficient setup, leveraging Appium, and integrating CI/CD for seamless mobile test automation.
When it comes to testing mobile apps, you’ve probably wondered how developers manage to test apps across so many devices without losing their sanity. Enter Selenium mobile testing: a tool that automates the process, making mobile testing smoother and faster.
If you’re new to it, Selenium for mobile testing allows you to test Android and iOS apps automatically, ensuring they perform well on multiple devices without manual effort. It’s a real time-saver and helps you catch bugs before they reach your users.
By the end of this, you’ll know exactly how to set up Selenium for mobile testing and make it work for you. Plus, we’ll also cover some tips to ensure you’re completely prepared.
What is Selenium Mobile Testing and What Are Its Benefits?
Essentially, Selenium mobile testing extends the power of Selenium WebDriver to mobile apps. Just picture taking the same automation tools you use for web testing and applying them to smartphones and tablets, that what this does. It allows you to cross platform test across both iOS and Android, saving you time and effort.
Selenium for mobile testing works by integrating with tools like Appium, which connects your Selenium scripts to real mobile devices or emulators. Testing native apps, hybrid apps, or mobile websites becomes smooth and efficient with Selenium mobile testing.
Benefits of Selenium Mobile Testing
With, 64.2% of companies use Selenium for test automation, it’s easy to see why Selenium mobile testing is widely adopted.
Here’s why:
- Cross-platform compatibility: Test on both iOS and Android with one framework.
- Familiar syntax: Leverage existing Selenium knowledge for mobile testing.
- Cost-effective: Open-source, backed by a strong community.
- Parallel execution: Run tests across multiple devices at once.
- CI/CD integration: Easily fits into your existing workflows.
By automating mobile testing, you can catch bugs faster and ensure your apps work seamlessly across all devices.
Native Vs Hybrid App Testing with Selenium
When it comes to selenium mobile testing, there are basically two main paths you can take: testing native apps or hybrid apps.
Here’s the breakdown of selenium for mobile testing approaches:
| Aspect | Native app testing | Hybrid app testing |
| What it is | Apps built specifically for iOS/Android using platform languages | Apps built with web technologies wrapped in a native container |
| Selenium Approach | Requires Appium + Selenium for automated mobile testing selenium | Direct selenium mobile app testing using WebDriver |
| Setup Complexity | More complex – need device simulators/emulators | Simpler – can test in mobile browsers |
| Element Identification | Uses native selectors (accessibility IDs, XPath) | Standard web selectors (CSS, XPath) work fine |
| Performance Testing | True device performance insights | Limited native performance visibility |
| Cross-platform | Separate tests for iOS/Android | One test suite for mobile automation testing using Selenium |
| Best for | Apps with heavy native functionality | Content-heavy apps, mobile web apps |
The key is matching your Selenium mobile app testing strategy to what you’re actually building.
Selenium Mobile Testing Setup: Step-by-step Guide
Now that you’ve decided on your testing approach, it’s time to set everything up. While a mobile testing tool like Selenium might have a daunting setup at first, it’s more manageable than it appears.
Here are the steps you can follow to get everything up and running smoothly:
1. Installing Java and Setting up Your Environment
First things first – Selenium for mobile testing runs on Java, so you’ll need JDK 8 or higher installed. Download it from Oracle’s website and make sure your JAVA_HOME environment variable is pointing to the right directory.
Half the setup issues people face usually come from skipping this basic step. You can verify everything’s working by running java -version in your terminal.
2. Setting up Appium for Native App Testing
If you’re doing automated mobile testing for native apps, Appium is your best friend. Install it via npm with npm install -g appium, then grab the Appium Desktop client for easier server management. You’ll also need the specific drivers for iOS (XCUITest) or Android (UiAutomator2). Don’t forget to start the Appium server before running your tests!
3. Browser Setup for Hybrid App Testing
You can skip Appium and go straight to mobile browsers for hybrid apps using Selenium mobile app testing. Chrome DevTools and Safari’s responsive design mode are your main testing environments.
Install ChromeDriver and set up mobile device emulation in your browser settings. This approach is way simpler than native testing but gives you solid coverage for web-based mobile apps.
4. Configuring Device Connections and Emulators
For mobile automation testing using Selenium, you need either real devices or emulators ready to go. Here’s what you need to set up:
- Install Android Studio for Android emulators or Xcode for iOS simulators
- Enable USB debugging on real Android devices
- Verify device recognition with adb devices command
- Configure emulator specifications to match your target devices
5. Setting up Selenium Webdriver Dependencies
The final piece of your Selenium mobile app testing puzzle involves adding the right dependencies to your project:
- Add selenium-java and appium-java-client to your build file
- Include TestNG or JUnit for test management and assertions
- Use Maven or Gradle for easier dependency management
- Verify all dependencies are properly resolved before writing tests
With these steps, you’re all set to start Selenium mobile testing and ensure your app works flawlessly across devices.
Implementing Selenium with Appium for Mobile Devices
Earlier, we covered installing and setting up Appium, but now let’s dive into the actual implementation – how do you write code that makes Selenium and Appium work together seamlessly?
Below, we’ve outlined the key steps to make sure your implementation is smooth and efficient:
1. Setting up Desired Capabilities
Before your automated mobile testing Selenium can start, you need to tell Appium exactly what device and app you’re targeting.
Desired Capabilities are like your device’s ID card; they specify everything from platform version to app location. For Android, you’ll set platformName to “Android”, deviceName to your device identifier, and app to your APK file path. iOS follows a similar pattern but uses platformName “iOS” and points to your .app or .ipa file.
2. Establishing Webdriver Connection with Appium Server
Here’s where selenium for mobile testing gets interesting; instead of connecting directly to a browser, your WebDriver connects to the Appium server running on your machine.
Start your Appium server (usually on localhost:4723), then create a new RemoteWebDriver instance pointing to that URL with your desired capabilities. This connection lets you use all your familiar Selenium commands on mobile elements.
3. Locating Mobile Elements Effectively
Mobile automation testing using Selenium requires different element location strategies than web testing. Here’s what works best:
- Use accessibility IDs for cross-platform compatibility – they’re your most reliable option
- XPath works, but it can be fragile when UI changes happen frequently
- For Android, resource-id and class name selectors are solid choices
- iOS apps respond well to predicate strings and class chain selectors
4. Writing Your First Mobile Test Script
Your selenium mobile app testing script structure stays familiar: create driver, find elements, perform actions, verify results. The main difference is how you initialize your driver with mobile-specific capabilities and locate elements using mobile selectors instead of CSS selectors.
Start with simple actions like tapping buttons or entering text, then build up to more complex user flows as you get comfortable with mobile element interactions.
Best Practices for Selenium Mobile Test Automation
When it comes to Selenium mobile test automation, following best practices is essential to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Adopting the right strategies not only improves your test outcomes but also saves you time in the long run.
Let’s look at some of the key best practices for effective mobile test automation:
- Use Page Object Model (POM): Implement the Page Object Model pattern to keep your code clean, reusable, and maintainable. This helps in separating the test logic from the UI elements, making updates easier when the app’s interface changes.
- Prioritize cross-device testing: Ensure your tests cover multiple devices with varying screen sizes and OS versions. This helps in identifying device-specific issues, making your app truly cross-platform.
- Leverage parallel execution: Run your tests in parallel across different devices and emulators to speed up the testing process. It reduces overall test execution time and enhances test coverage.
- Use real devices for critical tests: Testing on actual devices ensures that you catch issues related to hardware, sensors, and device-specific behaviors that might not show up on emulators.
- Implement Continuous Integration (CI): Integrating your tests with a Continuous Integration (CI) tool like Jenkins or CircleCI ensures that tests are run automatically with each code change. This promotes early bug detection, faster feedback loops, and streamlined development cycles.
- Handle dynamic elements with care: Mobile apps often have dynamic elements that change based on user actions. Use appropriate waits (e.g., explicit or fluent waits) to ensure elements are visible and interactive before interacting with them.
Adopting these best practices will help you execute Selenium mobile testing with confidence and precision.
Common Selenium Mobile Testing Challenges and Solutions
Despite following best practices, Selenium mobile testing often presents its own set of challenges that can be frustrating. A survey even found that 51.6% of testers struggle with cross-browser testing, and 27.3% rate it as moderately challenging.
But don’t worry, below, we’ve listed some of the most common challenges along with the proven solutions to overcome them:
Flaky Tests Due to Timing Issues
You’ve likely seen it – tests pass locally but fail in CI or work on one device but time out on another. Network calls or heavy UI rendering cause mobile apps to have unpredictable load times, making automated mobile testing Selenium unreliable.
Solution: Replace Thread.sleep() with explicit waits like WebDriverWait and implement retry mechanisms for network-dependent actions. Use dynamic waits based on element visibility to ensure consistent results.
Element Locator Instability across Updates
App updates can break perfectly working tests by changing element IDs or restructuring the UI. This issue is common in Selenium for mobile testing, as mobile UIs change often.
Solution: Start with accessibility IDs, followed by resource IDs and class names as fallbacks. Use a centralized element repository and work with developers to establish stable naming conventions.
Device Fragmentation and Compatibility Issues
What works on one device might fail on another. Different screen sizes, OS versions, and hardware create a testing challenge in mobile automation testing using Selenium.
Solution: Use cloud-based device farms like AWS Device Farm or BrowserStack. Create device capability matrices and run targeted test suites for specific device categories. Implement responsive design and orientation checks in your tests.
App State Management between Tests
Tests can interfere with each other if app states or authentication carry over, causing false positives or negatives in your Selenium mobile app testing.
Solution: Implement proper test teardown methods and use app reset features in Appium. Ensure tests are independent by creating fresh test data for each scenario, avoiding reliance on previous states.
Why Choose Testsigma for Mobile Testing?
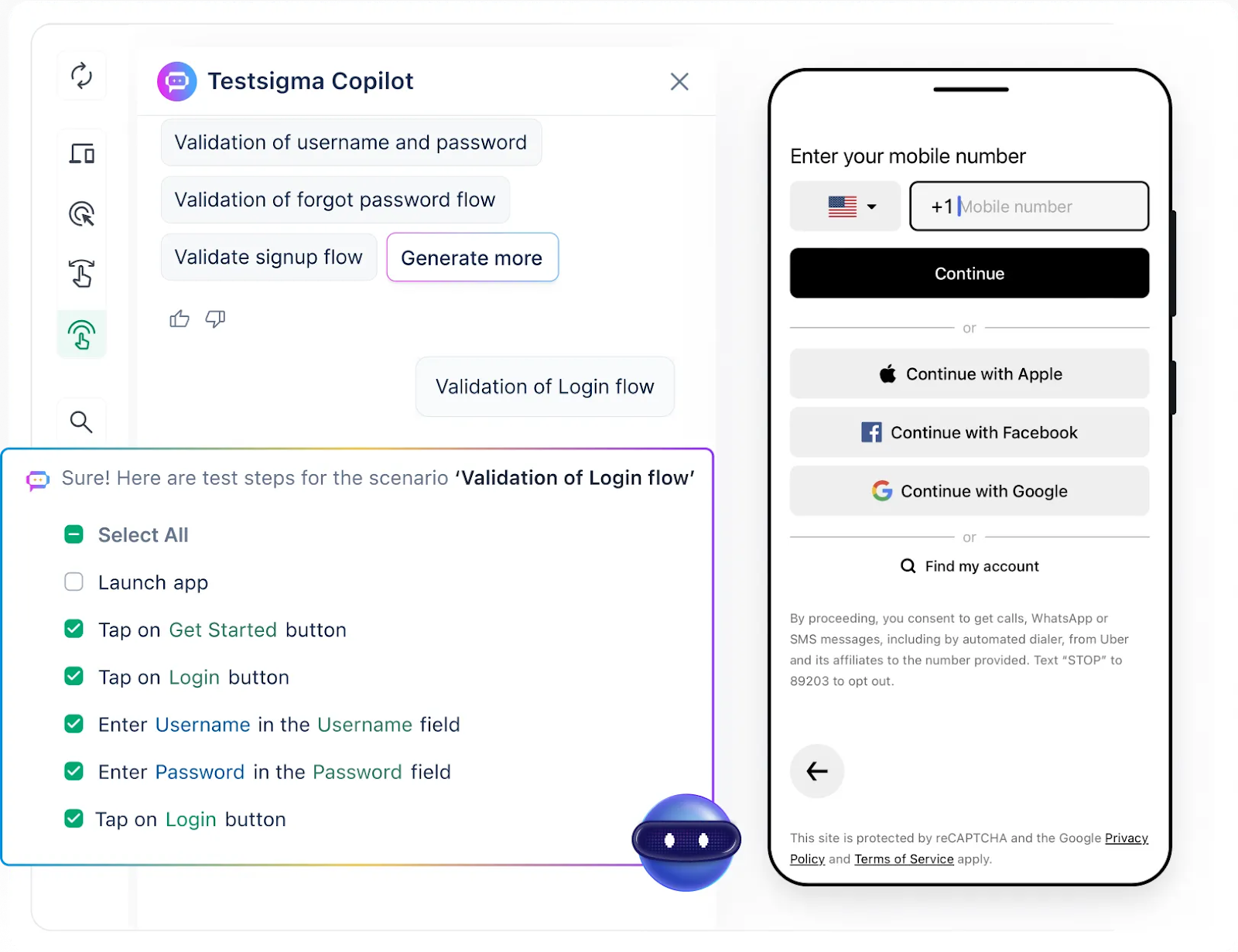
After exploring Selenium mobile testing setup, challenges, and best practices, it’s easy to feel a little overwhelmed. Appium configurations, device fragmentation, flaky tests; it’s a lot to manage. While Selenium is powerful, it can also be complex and time-consuming to maintain.
Here’s the thing: you can still enjoy all the benefits of robust mobile automation testing using Selenium without all the headaches. That’s where Testsigma comes in. Instead of getting bogged down with complicated setups and constant maintenance, Testsigma offers a no-code platform that simplifies the entire process.
With Testsigma, you can focus on real test coverage, not on managing infrastructure. It offers built-in device farms, automatic healing for failing tests, and AI-powered test generation, making mobile testing smoother than ever.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, Selenium can automate both native and hybrid mobile apps when integrated with Appium, providing a robust solution for mobile automation testing.
Selenium integrates with Appium by using the WebDriver protocol, enabling mobile automation testing using Selenium for native, hybrid, and mobile web apps.
To set up Selenium mobile testing, you’ll need Java, Appium, mobile device/emulator setup, and Selenium WebDriver dependencies configured in your project.
Synchronization issues like flaky tests and timeouts can be resolved by using explicit waits in Selenium mobile testing instead of fixed time delays. This ensures elements are ready for interaction.
For mobile automation testing using Selenium, accessibility IDs are the most reliable locators, followed by resource IDs and class names as fallbacks.


