Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
When it comes to software testing, functional testing is a big deal. It ensures that the software does what it’s supposed to do and meets the users’ needs. To make this happen, functional test cases are created. These cases tell us what steps to take, what results to expect, and what conditions must be met to test the software properly.
Crafting good functional test cases is an art. It requires a deep understanding of the software needs, a sharp eye for detail, and a talent for predicting potential problems. A good test case should be easy to understand, short, and concise.
No ambiguity allowed!
This blog talks more! Read along…….
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is a Functional Test Case?
- 2 What should a Functional Test Case have?
- 3 How to Write a Functional Test Case?
- 4 Examples of Functional Test Cases
- 5 How to Ensure that Your Functional Test Cases Cover the Product Area?
- 6 Manage Functional Test Cases Using Test Management By Testsigma
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Functional Test Case?
A functional test case is a set of instructions that describe how to test a specific function in a software application. It outlines the steps to take, the expected results, and the preconditions that must be in place before the test can be run.
When writing functional test cases, it’s crucial to identify input conditions, expected outcomes, and the steps to execute the test. Clear documentation helps testers, developers, and other stakeholders understand the testing process and results.
Functional test cases contribute to the overall quality assurance process by systematically addressing various functionalities and helping deliver reliable and error-free software to end-users.
What Should a Functional Test Case Have?
A functional test case should clearly define what is being tested:
- the steps to execute the test,
- the expected results, and
- the preconditions that must be met before the test can be run.
Here’s a summary of the key components of a functional test case:
1. Test Case Identifier: A unique identifier to easily reference the test case.
2. Test Case Description: A clear and concise description of the specific function or feature being tested.
3. Preconditions: The conditions must be in place before the test can be executed, such as logging in as a particular user or having specific data available.
4. Test Steps: A detailed list of the steps to execute the test, including inputs and actions.
5. Expected Results: The anticipated outputs or outcomes of the test.
6. Actual Results: The actual results obtained when the test is executed.
7. Pass/Fail Criteria: A precise determination of whether the test passed or failed based on comparing expected and actual results.
8. Assumptions: Any assumptions made during the test case design or execution.
9. Notes: Additional information or observations related to the test case.
How to Write a Functional Test Case?
Steps to write:
- Identify the Function or Feature: Clearly define the specific function or feature of the software you want to test.
- Understand the Requirements: Thoroughly review the software requirements to grasp the expected behavior and functionality.
- Determine Test Steps: Break down the testing process into detailed steps, including inputs, actions, and validations.
- Define Expected Results: Specify the expected outcomes or outputs for each test step.
- Set Preconditions: Identify the conditions to be met before executing the test.
- Establish Pass/Fail Criteria: Determine how you will assess whether the test passed or failed based on comparing expected and actual results.
- Document the Test Case: Document the test case, including its identifier, description, preconditions, test steps, expected results, and pass/fail criteria.
Examples of Functional Test Cases
Here is a table format to better understand:
| Feature | Test Case Description | Preconditions | Test Steps | Expected Results | Pass/Fail Criteria |
| Login | Verify successful user authentication | The user account exists, and the password is correct | 1. Open the login page. 2. Enter a valid username and password. 3. Click the login button. | The user is redirected to the home page. A welcome message is displayed. | The user is redirected to the home page, and a welcome message is displayed. |
| Search | Test product search functionality | A search function is available, and the product catalog is loaded | 1. Open the product search page. 2. Enter a valid product name in the search bar. 3. Click the search button. | A list of matching products is displayed. Product details are displayed for each product. | A list of matching products is displayed with product details for each product. |
| Add to Cart | Verify product addition to the shopping cart | The user is logged in, and the product is available in stock | 1. Open the product page. 2. Select the desired quantity. 3. Click the “Add to Cart” button. | Product quantity is updated in the shopping cart icon. A confirmation message is displayed. | Product quantity is updated in the shopping cart icon, and a confirmation message is displayed. |
| Checkout | Process a successful order | The user is logged in, the shopping cart contains items, and payment information is valid. | 1. Proceed to checkout. 2. Enter shipping and billing details. 3. Select a payment method and provide payment information. 4. Click the “Place Order” button. | The order confirmation page is displayed. Order details are displayed, including shipping and payment information. | The order confirmation page displays order details, including shipping and payment information. |
Read here – test case template
How to Ensure That Your Functional Test Cases Cover the Product Area?
Ensuring that your functional test cases cover all aspects of your product area is essential to delivering top-notch software.
Here are some useful tactics to achieve this:
- Understand the Product Requirements: Review and analyze the requirements thoroughly to grasp the expected functionality and user behavior.
- Identify Testing Scenarios: Break down the product’s features and functionalities into individual testing scenarios, considering all possible user interactions, edge cases, and error conditions.
- Design Test Cases: For each testing scenario, create detailed functional test cases that outline the test steps, expected results, preconditions, and pass/fail criteria.
- Utilize Testing Tools: Leverage test management tools to efficiently organize, track, and execute test cases.
- Perform Exploratory Testing: Supplement your structured test cases with exploratory testing to uncover hidden defects and edge cases.
- Continuous Review and Update: Regularly review and update test cases as the product evolves to maintain comprehensive coverage.
Manage Functional Test Cases Using Test Management by Testsigma
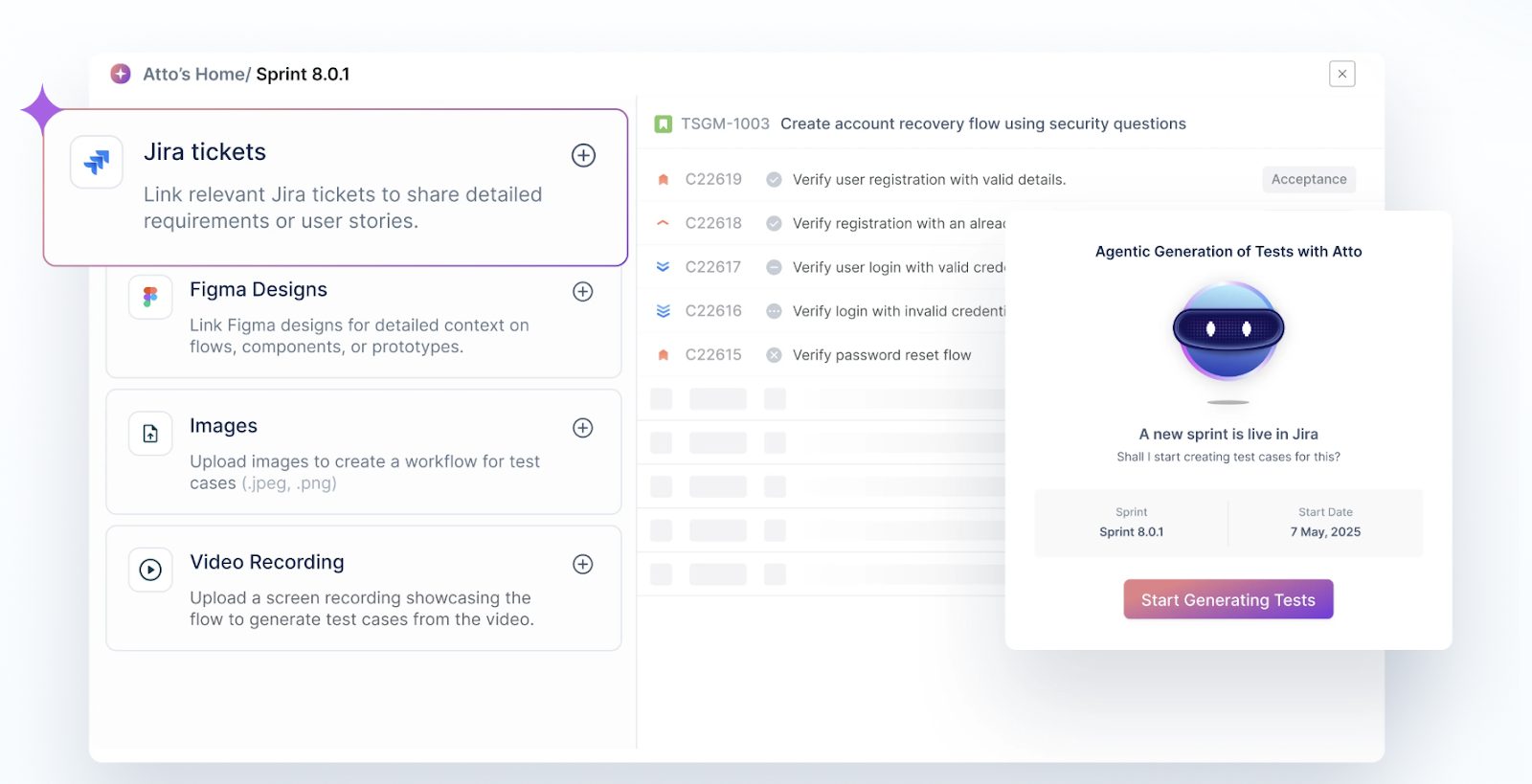
Test Management by Testsigma is a cloud-based, Agentic AI-powered test management software that simplifies the end-to-end management of functional test cases. It enables testers to efficiently create, execute, and manage both manual, automated, and exploratory test cases from a single platform. It has a built-in AI coworker, Atto, that mobilizes specialized AI agents to generate functional test cases automatically, execute them within the browser, and report bugs with detailed context. This ensures faster feedback, reduced maintenance, and higher test coverage, making it easier to validate whether every feature works as intended.
Agentic AI Capabilities in Test Management by Testsigma
Atto: An intelligent AI coworker that handles key testing tasks by deploying AI agents for test creation, execution, and bug reporting. It helps teams save time and focus on delivering high-quality software.
Sprint Planner Agent: Start planning your tests once a JIRA sprint begins.
Generator Agent: Powered by Atto, this agent automatically creates test cases using inputs from prompts and tools like JIRA, Figma, XRay, as well as images, videos, and documents. It also suggests edge cases to improve test coverage.
Runner Agent: Executes your tests within the browser. To execute tests on multiple test environments in parallel, choose a test automation platform like Testsigma.
Bug Reporter Agent: This AI agent automatically generates detailed bug reports with steps to reproduce, logs, and screenshots, and sends them directly to your bug tracking tools, reducing manual work and improving visibility.
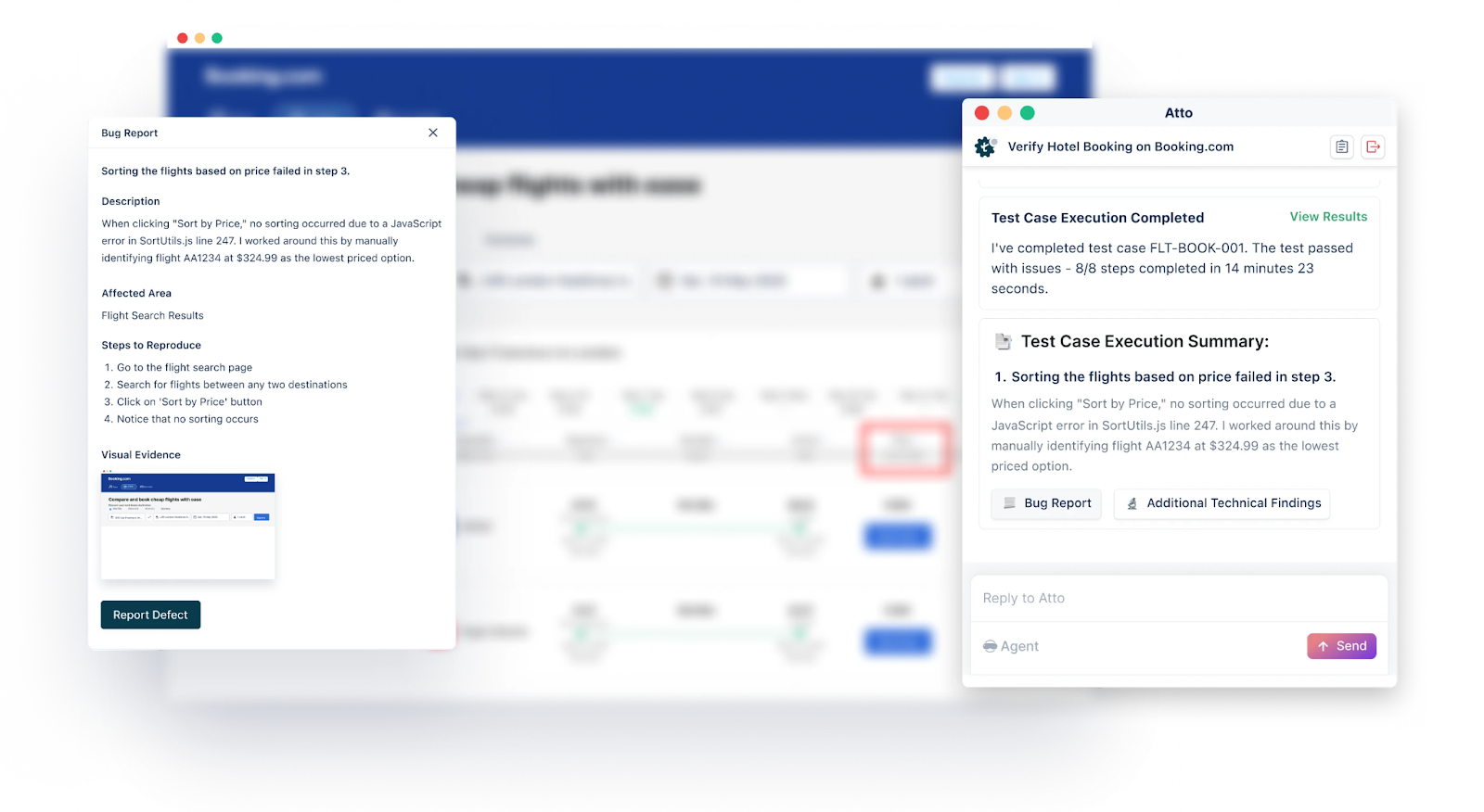
Why is Agentic Test Management by Testsigma the Right Choice?
- Atto automatically updates test cases when the UI changes, saving 90% test maintenance time. This helps reduce flaky tests and saves time on maintenance since you don’t need to fix broken tests manually.
- Move from Spreadsheets or Excel to a modern test management tool, which makes it easier to keep everything organized and traceable.
- You can manage manual, automated, and exploratory test cases in one place. This reduces context switching and the need for multiple tools.
- Test cases can be imported easily from Excel, CSV files, JIRA, and commonly used open-source tools. This allows you to get started quickly without complications.
- The tool also smoothly connects with JIRA, Azure DevOps, Jenkins, and more, ensuring that your testing process stays aligned with your development pipeline.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, functional testing is a must-have in software development. It helps us make sure that the products we use work the way they should and give us a good user experience. And well-written test cases make this process even smoother.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Functional Test Cases and Non-Functional Test Cases?
Functional test cases validate specific functionalities of the software, ensuring they meet defined requirements. In contrast, Non-functional test cases assess performance, reliability, and usability, ensuring the software’s overall quality.



