Adding new functionalities into an existing application or making new code changes due to bug fixes can possibly result in new issues in a software application; QA teams need to follow different procedures to ensure no new issues have been introduced due to code changes, so here comes the Requirement Traceability Matrix in Testing and Regression testing.
Regression testing is a test approach that helps testers make sure there are no new bugs due to code changes or because of the introduction of new functionality to the existing ones. Using a requirement traceability matrix helps achieve the results with better efficiency.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Test Traceability?
- 2 Why does Test Traceability Matter?
- 3 What is a Requirement Traceability Matrix?
- 4 Why is Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) Important?
- 5 Who Needs Requirement Traceability Matrix?
- 6 Parameters in Requirement Traceability Matrix
- 7 Requirements Traceability Matrix Example
- 8 How to Create Requirement Traceability Matrix?
- 9 What are the 3 Types of Requirement Traceability Matrix?
- 10 Advantages of RTM
- 11 Role of Traceability Matrix in Testing
- 12 When to Perform Regression Testing and How it Relates to RTM?
- 13 RTM Opportunities and Risks
- 14 RTM Implementation and Improvement
- 15 Conclusion
- 16 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Test Traceability?
Behind every bug-free software is a QA who followed the requirement criteria by word!
The primary goal of RTM is to offer visibility into all the phases of software development, including design, creation, testing, delivery, and deployment. The higher your QAs have the ability to understand the requirement thoroughly and create positive and negative test cases, the better the chances to produce quality software. But how do we ensure that every test case, positive and negative, is present while validating the final product? And what if you still need to complete all requirements before market release?
You turn to the Requirement Traceability Matrix. It helps to:
- Simplify the defect classification for bigger projects
- Improve test case management by mapping a test case to its source requirement and identifying the defects
- Empower you to move through different project management tools to trace the progress from the requirement to the defects seamlessly
- Make sure to maintain detailed and necessary documentation.
Why Does Test Traceability Matter?
- Test traceability helps to identify and track the progress of the testing process, ensuring that all requirements are met and all defects are resolved.
- This process is especially important in regulated industries such as healthcare and finance, where compliance with government regulations is critical.
- By implementing test traceability, organizations can enhance their testing efficiency, reduce risks, and improve the overall quality of their software.
Let’s discuss this in more detail in the article.
Every QA team needs to understand a client’s requirements and ensure to launch of a defect-free application into the market. And clearly, to achieve this goal, the QA team should be aware of the end-to-end requirements & should draft the test plan covering all the functionalities/requirements. QA team needs to split the software requirements provided by the client into multiple scenarios and then test cases. With regression testing, each of the test cases undergoes separate testing, covering all the dependent requirements as well.
A question arises here on how the QA team ensures that all possible scenarios/cases are covered in the test plan. How do we ensure that all the requirements are covered in the testing cycle? A simple & easy solution is to map the requirement with related test scenarios and respective test cases; this map can be called a ‘Requirement Traceability Matrix(RTM)’.
What is a Requirement Traceability Matrix?
A traceability matrix in software testing is a document that maps and traces user requirements with test cases. Its primary purpose is to ensure that all defined system requirements are tested as per the protocols laid down by the project managers. This matrix helps verify that the software meets its requirements and aids in identifying any missing functionality.
By clearly linking requirements and test cases, the traceability matrix ensures comprehensive test coverage, facilitates change impact analysis, and assists in project tracking and reporting.
It is crucial for maintaining consistency, managing project scope, and ensuring quality throughout the software development lifecycle.
Why is Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM) Important?
Behind every bug-free software is a QA who followed the requirement criteria by word!
The primary goal of RTM is to offer visibility into all the phases of software development, including design, creation, testing, delivery, and deployment. The higher your QAs have the ability to understand the requirement thoroughly and create positive and negative test cases, the better the chances to produce quality software. But how to ensure that every test case, positive and negative, is present while validating the final product? And what if you miss any of the requirements before market release? You turn to Requirement Traceability Matrix.
It helps to:
- Simplify the defect classification for bigger projects
- Improve test case management by mapping a test case to its source requirement and identifying the defects
- Empower you to move through different project management tools to seamlessly trace the progress from the requirement to the defects
- Make sure to maintain a detailed and necessary documentation.
Who Needs Requirement Traceability Matrix?
Basically, any individuals involved in testing and creating test cases need requirement traceability. However, when it comes to software testing, the list is not limited to only the QAs.
Project managers, developers, junior testers, the QA lead, and stakeholders often refer to this document. In some cases, even business analysts and auditors use these specifications to evaluate the product.
Parameters in Requirement Traceability Matrix
In almost every case, an RTM is created in an excel sheet that contains all the necessary information about understanding the software requirements. Generally, it covers a few parameters that QAs and stakeholders want to monitor:
- Requirement ID and Priority
- Test Case Description corresponding to the requirement ID
- Test Case ID and Status (Pass/Fail)
Above is a basic example of what an RTM looks like. But there are many other parameters you can add to and track using RTM, such as test execution environment, defects found, defect status and ID, and requirement coverage status.
Requirements Traceability Matrix Example
A common requirements traceability matrix includes a description of requirements, business needs, project objectives, responsible individuals, Test Case ID, and comments/notes. Based on your needs, this can surely be updated to add other parameters, such as deviation, identified bugs, regression status, and more.
A working example of the requirements traceability matrix is given below:
| Requirement ID | Requirement Description | Responsible Individuals | Priority | Status | Test Case ID | Comments/Notes |
| RQ-001 | User Registration functionality | Dev Team | High | Completed | TC-001 | Registration with email |
| RQ-002 | Product Search feature | Dev Team | Medium | In Progress | TC-002 | Search by keywords and filters |
| RQ-003 | Shopping Cart functionality | Dev Team | High | Completed | TC-003 | Add, remove, and update items |
| RQ-004 | Order History and Tracking | Dev Team | Planned | Medium | TC-004 | View past orders and tracking |
How to Create Requirement Traceability Matrix?
For creating a Requirement Traceability Matrix, QA team needs to collect the necessary artifacts like Business Requirement, Test cases, Test Results, Test Status & Defect details, etc. Mostly, spreadsheet is used to create an RTM where we can easily align all the above-mentioned artifacts & inter-relate to each other. Below is a requirement traceability matrix example, which is derived from sample business & functional requirements.
Business Requirement:
Below are some of the sample business requirements, which the QA team received from a client.
Business Requirement #90: Login process to a mail application
Business Requirement #91: Sending a mail
Functional Requirement:
Below mentioned functional requirements have been derived from the above business requirements.
Functional Requirement #90.1: Directly login with existing credentials
Functional Requirement #90.1: Creating new user & login with new credentials
Functional Requirement #91.1: Creating a new email & sending it.
Functional Requirement #91.2: Sending an email from Draft items
Functional Requirement #91.3: Replying to an inbox email
A sample RTM is given below .
Now we can see how the business & functional requirements are mapped to test cases. This helps the QA teams to ensure all the requirements are covered with all possible test cases & nothing is missed out.
If any code changes / new functionalities are implemented due to requirement changes or bug fixes, RTM helps QA team to identify the possible impact areas/test cases, where code changes have been implemented.
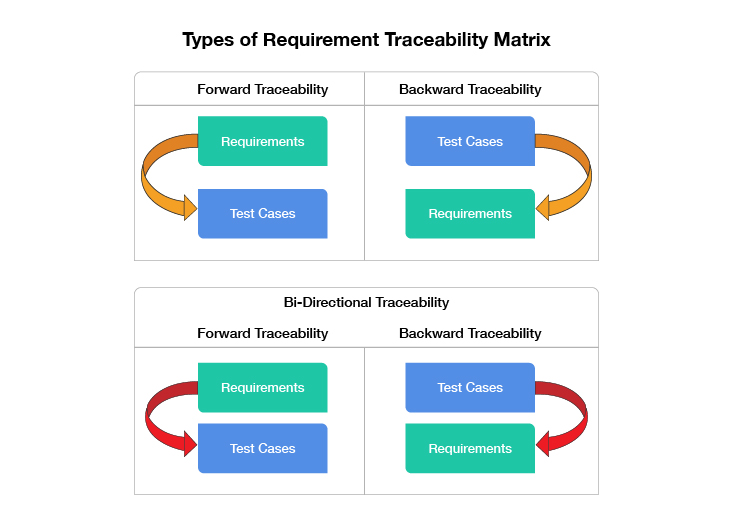
What Are the 3 Types of Requirement Traceability Matrix?
Not every RTM document will work for you. And not every RTM is necessary for every software development and testing process. Here are the 3 different types of Requirement traceability that you should know about:
Forward Traceability
A forward matrix ensures that the project is progressing in the right direction. In simple words, we can say, “Forward Traceability maps the requirements to the test cases”. It helps to make sure that every single business requirement is correctly integrated into the product and that every requirement is thoroughly tested.
Backward Traceability
The backward or reverse traceability matrix is “mapping the test cases with its requirements”. This type of matrix helps us in ensuring that we are not expanding the goals of the testing by covering extra features or functionalities in test coverage that were not a part of the initial requirements.
Bi-directional Traceability
This is the mix of both Forward and Backward traceability matrices.
Advantages of RTM
1. Confirms 100% test coverage.
2. Highlights any missing requirement and document inconsistency.
3. Gives complete “issues filed” and “test case execution” status.
4. Helps analyze and estimate the retest if any changes occur in the requirement.
Role of Traceability Matrix in Testing
The role of the traceability matrix is to align the test cases with the product/testing requirements. But the process runs long; in fact, throughout the testing cycle, RTM stays involved and produces results in every step.
A few of the roles it plays are:
- The traceability matrix helps track the testing process and the test cases, which often undergo updates as the software under test changes and evolves.
- It ensures that the final product meets the expectations of the users.
- The RTM also proves useful in uncovering the root cause of the identified bugs.
- A clearly defined traceability matrix is much more powerful in communicating the testing status to stakeholders, project managers, QAs, and developers simultaneously.
- It further helps in quickly and easily determining the risk factors associated with the errors in the application and accordingly move ahead with development, testing, and delivery of the product.
- If done correctly, it also becomes a crucial document to refer to and use as the application receives updates and new features down the line.
When to Perform Regression Testing and How it Relates to RTM?
- When developers add new functionality to existing functionality – In the RTM, all the test cases related to that functionality should be updated and then executed. Also, all test cases related to dependent functionalities should be executed.
- When there is a change in requirements (CR) – In the RTM, all the test cases related to that requirement should be executed; also, all test cases for dependent requirements should be executed.
- At the time of the performance fix – All the test cases from RTM must undergo execution. If there is less time, high-priority test cases must receive extra attention ahead of other test cases for execution.
- When there is environmental change – All the test cases from RTM should be executed. If there is less time, high-priority test cases must receive extra attention ahead of other test cases for execution.
- At the time of the bug fix – All the test cases related to the area of bug fix/functionality should undergo testing.
Read more about Prioritizing regression test cases.
RTM Opportunities and Risks
Naturally, like any other approach, RTM too has its fair share of opportunities and risks. Lets’ take a look at them.
Opportunities
- RTM ensures that all requirements are accounted for and covered by test cases, reducing the risk of missing critical functionality.
- By tracking requirements through the development and testing process, RTM helps maintain high-quality standards and ensures the final product meets stakeholder expectations.
- RTM provides a clear, documented link between requirements, design, implementation, and testing.
- RTM allows for easy tracking of changes in requirements, which helps teams understand the impact of changes and manage them effectively.
- By providing a clear overview of requirement status, RTM aids project managers in tracking progress, identifying bottlenecks, and making informed decisions.
Risks
- Keeping the RTM up-to-date requires continuous effort and diligence, especially if the project undergoes frequent changes.
- For large projects, managing an RTM can become complex and time-consuming.
- Effective implementation of RTM often relies on specialized tools and software, which may require additional investment and training.
- Without clear and consistent definitions and an understanding of requirements and test cases, RTM can lead to misalignment among team members and stakeholders.
- In highly agile environments, the structured nature of RTM may conflict with the flexibility and speed desired in iterative development processes.
RTM Implementation and Improvement
Follow the below steps to implement and improve the RTM process.
Implementation
- Define the objective and scope of the requirement traceability matrix by clearly establishing its purpose.
- To gather requirements and ensure proper communication, involve the relevant stakeholders and individuals, including project managers, developers, testers, and business analysts.
- Choose tools that support RTM creation and maintenance. This could range from spreadsheets to software like JIRA.
- Collect and document all the requirements, such as design documents, code modules, test cases, and defects.
- Create comprehensive test cases that directly correspond to each requirement, ensuring complete coverage.
- Populate the RTM with all necessary parameters, including requirement IDs, descriptions, sources, priority, status, test case IDs, and verification methods.
- Embed the RTM into the development workflow.
- Review and approve.
Improvement
- Regularly update the RTM to reflect requirements, test cases, and project status changes.
- Use automation tools to link requirements, test cases, and defects.
- Link the RTM with project management and issue-tracking tools like JIRA, Confluence, or Trello.
- Establish clear processes for updating and maintaining the RTM by defining roles and responsibilities for managing and updating the RTM document.
Conclusion
A rigorous and accurate RTM keeps the testing process intact and aligned to the expectations.
At first, it might appear to be laborious to note and track every minute action related to running tests, but eventually, the approach proves to be beneficial and easy to manage. Not to mention that RTM does more than just trail tests, bugs, and their root cause; it safeguards future references, promotes collaboration between teams, acts as a documentation repository, and proves useful in training the new joinees.
If you are leaning towards introducing RTM approach in your organization or lookin to improve the current way, by now you would have gained high-level idea of how to approach the topic.
And if you can find Testsigma to be an interesting tool to explore to reduce your testing efforts without compromising on the product quality, click on the link below!
Frequently Asked Questions (Faqs)
What is the Main Purpose of RTM?
The main purpose of RTM is to document the details of the technical requirements associated with a test scenario and its status. It helps the testing team understand and follow the testing level of the product.
Is RTM Required in Agile?
RTM is a useful option to implement if you follow the Agile methodology. It assists teams in keeping track of requirements for every sprint, along with the evolving changes that add to the requirements with time.
What is the RTM Format?
Usually, RTM format is in an excel sheet in the form of a table with necessary information/parameters to understand the status of the test scenarios and cases.









