Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What is Mobile Compatibility Testing?
- 3 Importance of Mobile Compatibility Testing
- 4 How to Perform Mobile Compatibility Testing
- 5 Types of Mobile Compatibility Testing
- 6 Key Areas of Mobile Compatibility
- 7 Challenges in Mobile Compatibility Testing
- 8 Mobile Compatibility Testing Best Practices
- 9 How to Perform Mobile Compatibility Testing on Real Devices with Testsigma?
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 FAQ
Overview
What is mobile compatibility testing?
Mobile compatibility testing is the process of verifying whether a mobile app or website works correctly across different devices, OS versions, screen sizes, browsers, and network conditions.
How to Perform Mobile Compatibility Testing?
- Define the device matrix: Identify key devices, OS versions, and browsers used by your audience.
- Set up the test environment: Use real devices, cloud device labs, or emulators.
- Prepare test scenarios: Include UI checks, navigation flows, gestures, and performance validations.
- Execute tests across combinations: Run the same scenarios on selected devices and conditions.
- Validate UI and performance: Check layout, responsiveness, alignment, speed, and visual accuracy.
- Log and analyze defects: Capture differences with device details for debugging.
- Fix issues and retest: Re-run tests after fixes to confirm stability.
- Automate repetitive tests: Use automation to expand coverage and save time.
What are the Different Types of Mobile Compatibility Testing?
- Forward compatibility testing: Ensures the app works on upcoming devices, OS versions, and browsers.
- Backward compatibility testing: Confirms the app performs correctly on older devices, OS versions, and browsers.
In 2025, almost every company building mobile apps or mobile-first websites relies on mobile compatibility testing because user experiences vary widely across thousands of devices, OS versions, and browsers. In this blog, you will learn what mobile compatibility testing is, why it matters, the types involved, how companies perform it, and the best practices teams follow today.
What is Mobile Compatibility Testing?
Mobile compatibility testing is the process of checking whether a mobile application or website works consistently across different devices, screen sizes, operating systems, browsers, and network conditions. It ensures that real users get a smooth, functional, and visually accurate experience no matter which mobile device they use.
Companies run mobile compatibility testing to identify layout issues, broken UI elements, performance slowdowns, crashes, and behavior differences that occur because each device and platform works differently. With users accessing products on thousands of device combinations today, mobile compatibility testing helps teams fix problems early and deliver a stable, reliable experience across all environments.
Importance of Mobile Compatibility Testing
Here’s why companies perform mobile compatibility testing:
- Consistent User Experience Across Devices
Brands use mobile compatibility testing to ensure their app or website looks and behaves the same across different devices and screen sizes, reducing user frustration.
- Higher Customer Satisfaction and Retention
Mobile device compatibility testing helps teams identify issues that could cause users to uninstall an app or drop off a website, improving engagement and retention.
- Better App Store Ratings and Reviews
Apps that behave consistently on all devices receive fewer negative reviews. Mobile compatibility testing directly contributes to better ratings on app stores.
- Reduced Production Bugs and Support Costs
With mobile device compatibility testing, companies catch issues before release, saving money on rework, urgent patch fixes, and customer complaints.
- Improved Brand Credibility
A product that works flawlessly everywhere strengthens user trust, which is why brands take mobile compatibility testing seriously.
- Wider Market Reach
Mobile device compatibility testing ensures that the app or site works for users across regions, models, and network conditions, increasing overall coverage.
How to Perform Mobile Compatibility Testing
- Define The Device and Browser Matrix
Identify the most used devices, OS versions, browsers, and screen sizes based on user analytics and market trends.
- Set Up A Mobile Testing Environment
Teams use real devices, cloud-based device labs, or emulators to run mobile device testing at scale.
- Prepare Functional and UI Test Scenarios
Include navigation flows, gestures, loading behavior, layout checks, and functional validations based on expected user journeys.
- Execute Tests Across Selected Device Combinations
Run the same scenarios across different devices, OS versions, network types, and browsers to confirm consistent behavior.
- Validate UI, Performance, and Content Layout
Check for alignment issues, cut-off text, overlapping elements, responsiveness problems, and slow performance.
- Record and Analyze Defects
Document inconsistencies and failures found during mobile device compatibility testing and link them with device and OS details.
- Fix Issues and Retest
Developers resolve compatibility issues and teams re-run mobile testing to ensure everything is fixed properly.
- Automate Repetitive Cases Where Possible
Many organizations automate common compatibility checks to increase coverage and speed.
What is automated mobile app testing?
Types of Mobile Compatibility Testing
Forward Compatibility Testing
Ensures the app works properly on new or future OS versions and devices that are not yet widely available.
Example: Testing how an existing Android app may behave on the upcoming Android version during beta releases.
Tests that come under Forward Compatibility Testing:
- Device Compatibility Testing
Focuses on how the app behaves on newer or upcoming mobile devices with updated hardware, screen types, and resolutions.
Example: A layout that works on current Samsung devices might not render the same way on a new foldable model, which mobile compatibility testing can catch.
- OS Compatibility Testing
Ensures the app functions properly on future or recently released OS versions.
Example: Checking whether gesture-based navigation or new permission models introduced in the latest Android or iOS version affect the app flow.
- Browser Compatibility Testing
For mobile websites, this checks if the site behaves correctly on the latest browser versions.
Example: A button that works perfectly on the current Chrome version may shift alignment on a newly released Safari update.
- Network Compatibility Testing
Verifies app behavior using network technologies that are newer or evolving.
Example: Testing how the app responds when using advanced 5G features during mobile device compatibility testing.
Backward Compatibility Testing
Checks whether the app performs well on older OS versions and older device models that users still use.
Example: Ensuring an app designed for the latest iOS version still works properly on older iPhones.
Tests that come under Backward Compatibility Testing:
- Device Compatibility Testing
Ensures the app works on older mobile devices with limited hardware, smaller screens, and lower performance.
Example: A layout that appears correctly on modern devices may break or slow down on older Xiaomi or Motorola devices.
- OS Compatibility Testing
Checks if the app runs smoothly on previous OS versions still used by the audience.
Example: Validating how the app behaves on older iOS or Android versions that handle permissions or notifications differently.
- Browser Compatibility Testing
For mobile web apps, this ensures compatibility with older browser versions.
Example: Ensuring the site loads correctly on older versions of Chrome or Samsung Internet, where CSS support may differ.
- Network Compatibility Testing
Ensures the app performs well on earlier or slower network types still used in some regions.
Example: Validating stability and load times on 3G or fluctuating WiFi connections during mobile compatibility testing.
Key Areas of Mobile Compatibility
- Device types and models
- Operating system versions
- Screen sizes and resolutions
- Mobile browsers and browser versions
- Network conditions
- Hardware variations such as battery, CPU, and memory
- Orientation changes like landscape and portrait
- Gesture and touch behavior
- Accessibility support
Do you know how to inspect elements on Android?
Challenges in Mobile Compatibility Testing
- Huge device fragmentation: Hundreds of Android models and multiple iPhone versions make testing coverage difficult.
- Frequent OS updates: New OS releases often cause UI or performance issues that require constant mobile compatibility testing.
- Browser inconsistencies: Mobile browsers interpret HTML, CSS, and scripts differently, creating unpredictable behavior.
- Hardware limitations: Devices differ in RAM, CPU, sensors, and screen quality, which impacts how the app performs.
- Network variability: Slow, unstable, or fluctuating networks affect how apps load and respond.
- Time and resource constraints: Maintaining a large device lab or running extensive mobile device compatibility testing can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Inconsistent real-world conditions: User environments such as background apps, battery levels, and temperature can impact behavior.
Mobile Compatibility Testing Best Practices
- Plan device coverage smartly by focusing on top devices and OS versions used by your audience.
- Test early and continuously to avoid last-minute compatibility issues.
- Use real devices whenever possible for accurate mobile compatibility testing results.
- Automate repetitive scenarios to increase speed and coverage.
- Simulate real-world conditions like low battery, slow networks, and background activity during mobile device compatibility testing.
Looking for mobile testing tools?
How to Perform Mobile Compatibility Testing on Real Devices with Testsigma?
Testsigma is an agentic AI-powered test automation platform that allows you to automate end-to-end tests without writing code. Built around its AI coworker Atto, Testsigma mobilizes a team of specialized AI agents to help QA teams at every stage from planning and generating test cases to executing them in parallel, analyzing failures, healing broken tests, and optimizing test coverage.
It is a unified platform for testing web, mobile (iOS/Android), APIs, desktop, Salesforce, and SAP applications, all from one place. With Testsigma, you can test across 3000+ browsers, real devices, and OS combinations, and also integrate with 30+ CI/CD, collaboration, and bug-tracking tools, giving teams powerful automation without the usual maintenance pain.
Here’s how you can perform mobile compatibility testing on real devices using Testsigma:
- Set Up the Testsigma Agent– Download and install the Testsigma Agent on your local machine.
- Register and Start the Agent– Launch the Agent and register it in the Testsigma dashboard through the Agents tab.
- Connect Your Real Device– For Android, enable USB debugging; for iOS, connect via USB and accept trust prompts.
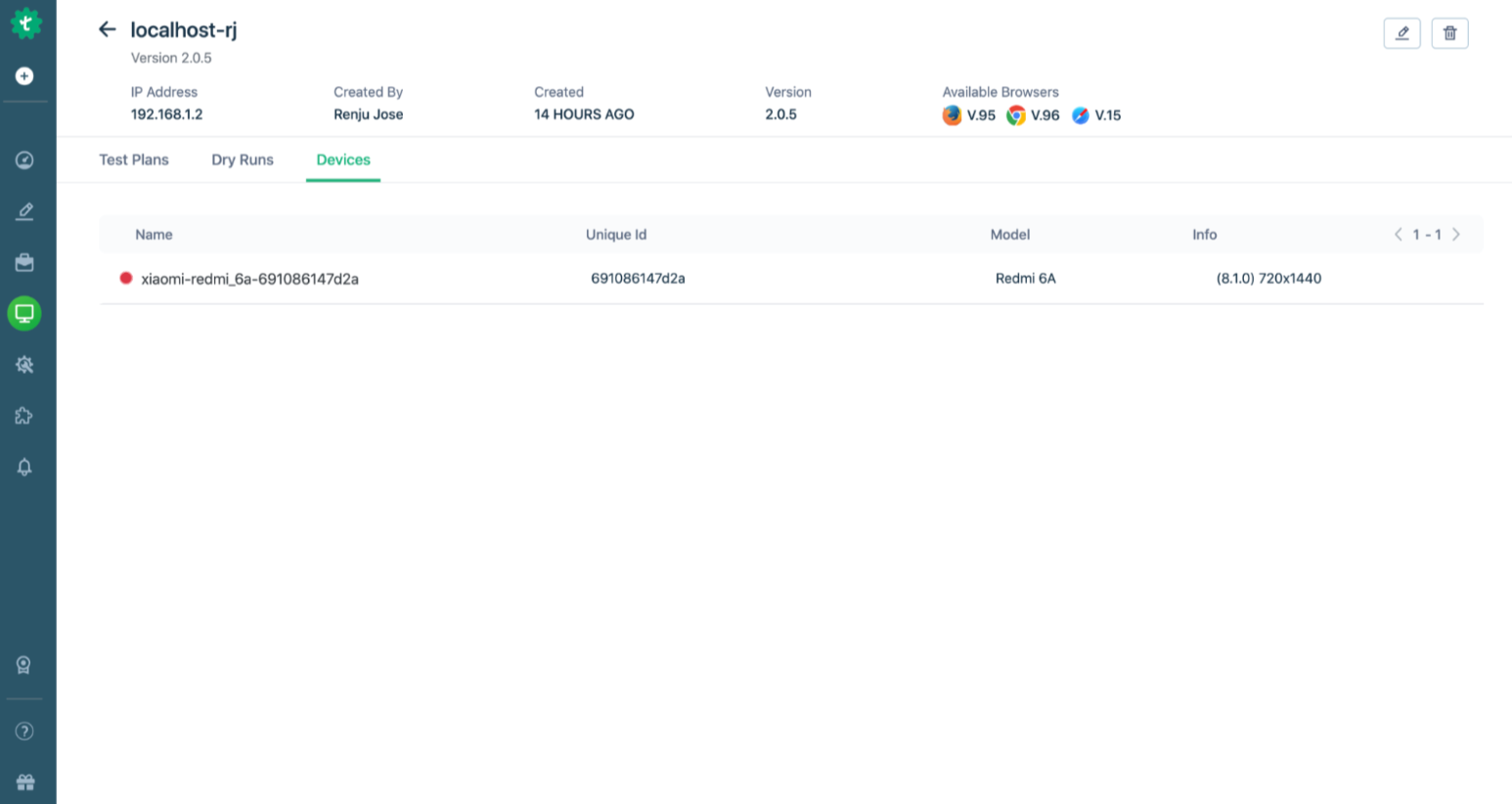
- Create a Mobile Project– In Testsigma, make a new project and choose the app type (Android or iOS), then upload your .apk or .ipa.
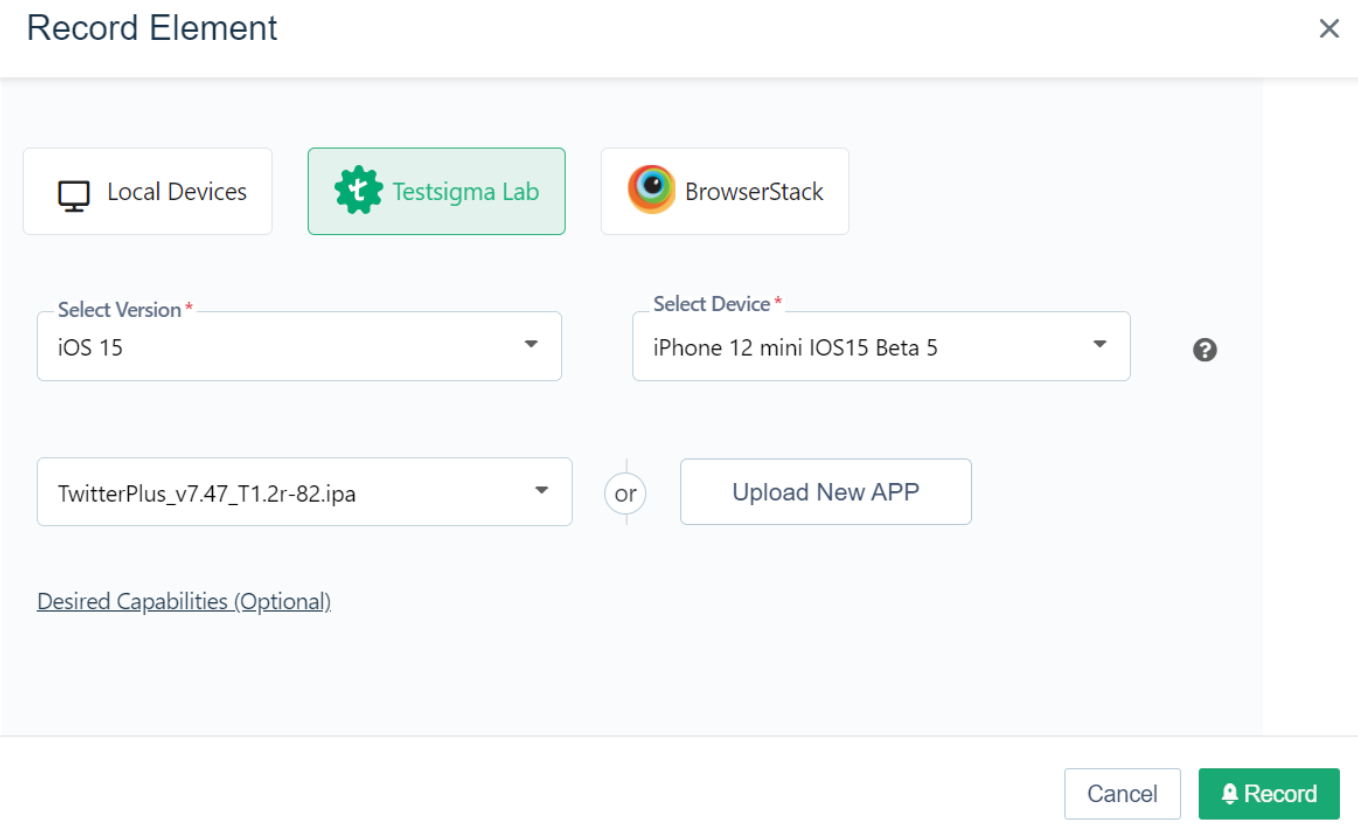
- Launch the Mobile Recorder– Open a test case, click Record, select Local Devices or Cloud Devices, choose your connected device and app version, then start recording.
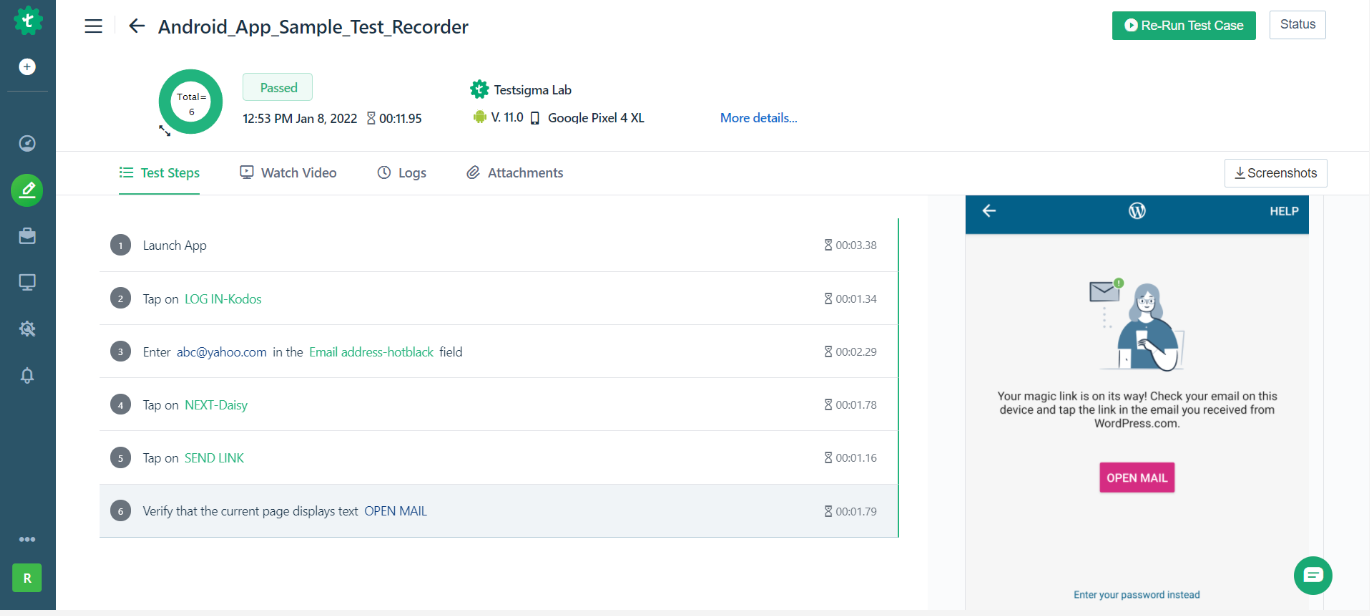
- Record Test Steps– Interact with your app; Testsigma’s recorder captures actions and generates test steps in plain English, which you can edit.
- Save and Run– Exit the recorder to save your test steps, then click Run, choose Local Devices lab, pick your device, and hit Run Now.
- View Results– After execution, you can review step-by-step results, screenshots, and video recordings to analyze failures.
Conclusion
Mobile compatibility testing ensures your app or mobile site works smoothly across devices, OS versions, browsers, and networks, making it a non-avoidable part of modern digital quality. As fragmentation grows, teams depend on no-code test automation platforms with real devices to test faster and more accurately. When these platforms support agentic testing, they remove repetitive work, maintain tests automatically, and improve coverage. This helps teams release reliable mobile experiences at scale.
FAQ
Teams often use platforms that provide access to real mobile devices, along with automation support, to run mobile compatibility testing smoothly. Testsigma is one of the commonly used options because it lets testers create and run mobile tests without coding and provides a wide range of real Android and iOS devices to validate compatibility issues. Along with this, some teams also use tools like UI Automator for Android, EarlGrey for iOS, Robot Framework, or Katalon Recorder. These tools help with basic automation or platform-specific checks, depending on the project’s needs.
Websites need to be compatible with mobile devices because most users today browse through their phones and expect pages to load quickly, look good, and function smoothly. A mobile-friendly site reduces bounce rates, improves engagement, enhances accessibility, and increases conversions. It also supports SEO since search engines prioritize sites that work well on mobile. When a website fails mobile compatibility testing, users often leave immediately and may not return.
Mobile compatibility testing on real devices gives the most accurate results because it reflects actual hardware, screen behavior, touch responses, network conditions, and OS variations that emulators cannot fully simulate. Real devices reveal real-world issues like UI breakage, gesture failures, performance lag, and inconsistent browser behavior. Testing on real devices helps teams catch edge cases early, deliver a reliable experience to users, and ensure the app performs well across the exact devices customers use.


