Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What Is Mobile App Accessibility Testing? Along With Examples
- 2 Overview
- 3 When Should A Mobile App Be Accessible?
- 4 Compliance For Mobile App Accessibility
- 5 Manual Vs. Automated Accessibility Testing
- 6 Checklist For Mobile App Accessibility Testing
- 7 Top 3 Mobile App Accessibility Testing Tools You Should Try In 2025
- 8 How To Find The Right Mobile App Accessibility Tool?
- 9 4 Key Mobile App Accessibility Issues And Best Practices
- 10 Make Mobile Accessibility Testing Easier With Testsigma
- 11 FAQs
What is Mobile App Accessibility Testing? along with Examples
Here’s a sobering reality: nearly half of disabled users report a poor or failing experience with popular mobile apps. That’s a substantial problem when you realize we’re talking about 40% of users – a big portion of your audience.
Mobile accessibility testing is how you find and fix those breakdowns. It goes beyond surface-level checks to ensure your app works for users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments.
This means testing things like screen reader compatibility, proper touch target sizing, sufficient color contrast, and alternative input methods. Done right, it removes barriers that would otherwise lock people out of your product.
Here are a few examples of tests you can incorporate into your process:
- Banking app – Screen reader test: Checking if account balances, transaction histories, and transfer buttons are properly announced by VoiceOver or TalkBack so blind users can manage finances independently.
- E-commerce app – Touch target test: Verifying that “Add to Cart” buttons, filters, and checkout elements meet the minimum size (44×44 points) so users with motor impairments can tap accurately.
- Social Media app – Color contrast test: Ensuring text posts, usernames, and navigation elements meet a 4.5:1 contrast ratio so content is readable for users with low vision.
- Navigation app – Voice control test: Making sure users can input destinations, start routes, and change settings using voice commands or switch controls when touch gestures aren’t possible.
Overview
Importance of Mobile Accessibility Testing
Mobile accessibility testing checks if your app actually works for people with disabilities. Such as screen readers, voice controls, and larger text sizes. It’s crucial for accessibility testing for mobile apps to meet WCAG compliance and dodge lawsuits.
Here are three tools that make mobile app accessibility testing less painful:
- Testsigma – Write tests in plain English, no coding nightmares
- Google Accessibility Scanner – Free Android tool that spots issues instantly
- Axe DevTools for Mobile – Heavy-duty testing for serious compliance needs
These are just a few of the tests you can start with. In the coming sections, we’ll look at the tools you can use to build accessibility testing for mobile apps into your workflow.
When Should a Mobile App Be Accessible?
From day one! Integrating mobile accessibility testing from the start ensures your app works for users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments, and saves you time and rework later.
Below are the stages where you should be designing and testing accessibility into your app:
- Wireframing: Plan navigation flows and interactions that work with screen readers and voice commands.
- Design phase: Select color palettes that meet contrast requirements, design touch targets that meet minimum size standards, and create layouts that scale with larger text.
- Development sprints: Build accessibility into each feature as you code. Test with VoiceOver or TalkBack regularly.
- Before each release: Run accessibility testing for mobile apps on new features to prevent accessibility debt from accumulating.
Starting early with mobile app accessibility testing ensures your app is inclusive, usable, and future-proof.
Learn the essentials of mobile first design with our complete guide
Compliance for Mobile App Accessibility
Legal requirements make accessibility mandatory, not optional. Following these rules ensures your app reaches everyone and protects you from fines or lawsuits.
Key compliance laws to know:
| Standard / Law | What it means | Key details | Relevance |
| WCAG 2.1 Level AA | Guidelines for making digital content accessible to users with visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments | International standard; Level AA covers common accessibility barriers; ongoing updates (WCAG 2.2 coming) | Widely adopted globally; considered the benchmark for accessibility |
| EN 301 549 | European standard for ICT accessibility | Aligns with WCAG 2.1; used to demonstrate compliance with the European Accessibility Act | Required for public procurement and ICT products/services in the EU |
| European Accessibility Act (EAA) | EU law is improving accessibility of products and services | For apps in banking, e-commerce, transportation, public services accessibility standards must be met | Mandatory for businesses offering digital services in the EU |
| ADA (Title I & II, US) | US law prohibiting discrimination based on disability | Covers digital services; while ADA doesn’t specify technical standards, courts often use WCAG 2.1 Level AA as the benchmark in lawsuits | Required for apps serving US users; meeting WCAG 2.1 Level AA helps demonstrate reasonable accessibility |
Note, you don’t have to submit your app to a government body, but you must make sure it meets the relevant standards.
Ensure you’re conducting regular accessibility audits and maintaining documentation of your compliance efforts to demonstrate that your app is accessible and inclusive.
Ensure your digital apps are EAA compliant for free – Check Accessibility Score
Manual Vs. Automated Accessibility Testing
While you might think accessibility testing is one thing, there are actually two types. Knowing the difference will help you test efficiently and cover all user needs. Mobile accessibility testing is most effective when you combine both approaches.
Here’s what they are:
| Type | What it means | Pros | Cons |
| Manual testing | Human testers evaluate your app for accessibility issues, using screen readers, voice commands, and other assistive tech | Detects real user experience problems, context-aware | Time-consuming, requires expertise |
| Automated testing | Tools scan your app for issues like color contrast, missing labels, and touch targets | Fast, repeatable, scalable | Cannot catch all usability issues or context-specific problems |
Checklist for Mobile App Accessibility Testing
Accessibility is a huge factor in your mobile testing, and keeping track of all the steps can get overwhelming. Fear not – we’ve collated a checklist you can keep handy so you don’t forget anything.
Mobile app accessibility testing – quick checklist
| Area | Key points |
| Visual | Color contrast, scalable text, alt text |
| Auditory | Captions, visual/audio alerts |
| Motor | Touch target size, alternative input, gesture-free |
| Cognitive | Clear language, consistent layout, easy instructions |
| Assistive Tech | Screen readers, voice control, switch devices |
| Documentation | Record tests & fixes, run regular audits |
1. Visual Accessibility
- Ensure color contrast meets WCAG 2.1 AA standards
- Support larger text and scalable layouts
- Provide alt text for images and icons
2. Auditory Accessibility
- Provide captions or transcripts for audio/video
- Ensure alerts or notifications are both visual and auditory
3. Motor Accessibility
- Verify touch targets meet minimum size requirements
- Support alternative input methods (switch devices, keyboard)
- Test gesture-free navigation
4. Cognitive Accessibility
- Use clear language and consistent layouts
- Provide easy-to-understand instructions and error messages
- Avoid unnecessary distractions or animations
5. Assistive Technology Compatibility
- Test with screen readers (VoiceOver, TalkBack)
- Verify compatibility with voice control and switch devices
6. Documentation & Auditing
- Keep a record of tests and fixes
- Conduct regular audits to maintain compliance
This mobile accessibility testing checklist helps your app be inclusive, usable, and compliant without missing a step.
Want a full checklist for mobile testing, too? Grab it here
Top 3 Mobile App Accessibility Testing Tools You Should Try in 2025
In this day and age, there are tons of mobile accessibility testing tools available, but which ones are truly effective and fit your needs? After thorough research, we’ve narrowed it down to the following 3 tools for mobile app accessibility testing.
Here they are:
1. Testsigma
Forget cryptic code. Testsigma lets you write mobile accessibility testing scripts in plain English, so your entire team can contribute.
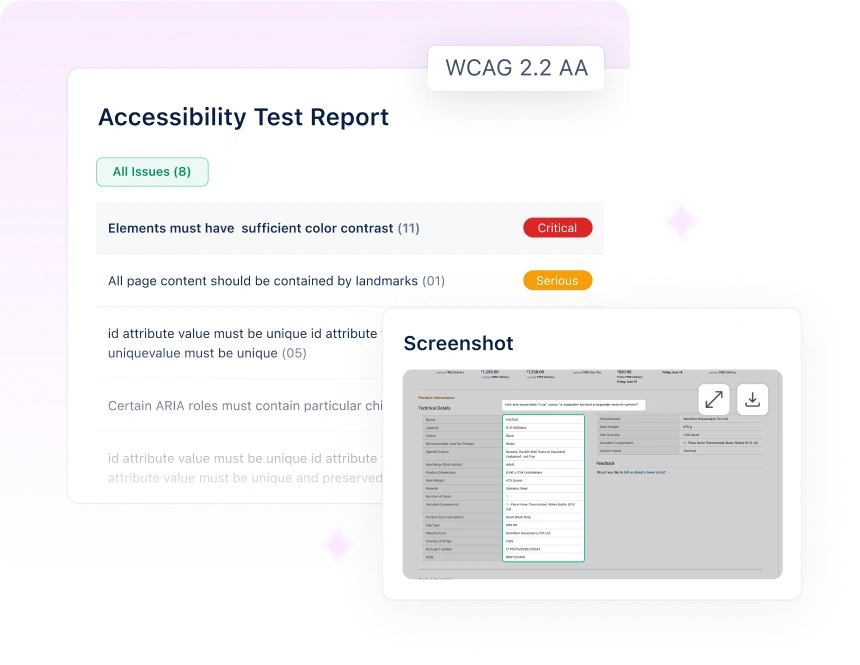
Need to check if that checkout button works with screen readers? Just type it out naturally. This automated accessibility testing platform handles WCAG 2.1 Level AA compliance while fitting right into your existing CI/CD workflow.
Features:
- Supports WCAG 2.1 Level AA standards
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines
- Provides detailed accessibility reports
Pros:
- Actually user-friendly (shocking, we know)
- Your PM can write tests too
- Scales without breaking your budget
Cons:
- Takes time to set up properly
- Advanced features need some learning
2. Google Accessibility Scanner
If you just want a simple way to spot accessibility issues on Android, Google Accessibility Scanner can help. It highlights low contrast elements, missing labels, and small touch targets right on your device. This makes it a handy tool for developers doing accessibility testing for mobile apps without extra setup.
Features:
- On-device scanning for accessibility issues
- Highlights missing content descriptions and touch targets
- Provides improvement suggestions
Pros:
- Free and easy to use
- Works offline
Cons:
- Android-only
- Limited to basic scanning, no CI/CD integration
3. Axe Devtools
You know that moment when you wish your app could just tell you what’s wrong? That’s what Axe DevTools does. It scans mobile apps for issues, integrates with your workflow, and gives detailed, actionable reports, so you can focus on building features, not hunting bugs.
Features:
- Automated testing for iOS and Android
- Integrates with existing test frameworks
- Provides detailed accessibility reports
Pros:
- Supports multiple platforms
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines
- Comprehensive reporting
Cons:
- May require technical expertise
- Some features may be complex for beginners
How to Find the Right Mobile App Accessibility Tool?
Choosing the right tool for mobile accessibility testing isn’t always easy. Here are a few things to keep in mind when picking one that fits your app and team:
- Define your goals – Are you testing for visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive accessibility? Knowing this narrows down your options.
- Check platform compatibility – Make sure it supports iOS, Android, or both depending on your app.
- Evaluate testing types – Some tools focus on automated scans, others on manual testing, and some do both.
- Look for standards compliance – Ensure it checks against WCAG 2.1 Level AA or other relevant accessibility guidelines.
- Consider integration & reporting – Pick tools that fit your workflow and give clear, actionable reports.
- Trial and feedback – Try a few with real scenarios to see which works best for your team.
Note these, so you can pick the one that actually works for your app and team.
4 Key Mobile App Accessibility Issues and Best Practices
Ever wonder why some users abandon your app within seconds? Often, it’s not your design; it’s hidden accessibility barriers. Here are some common issues and best practices to fix them:
1. Missing OR Useless Labels
A button that just says “button” or an icon labeled “image” leaves users guessing what it does. Screen reader users have no clue whether they’re submitting a form, adding an item to a cart, or performing some other action, making the app confusing and frustrating.
Fix: Every interactive element needs a clear, descriptive label. “Add hiking boots to cart” beats “button” every time.
2. Tiny Touch Targets
Those tiny social media sharing buttons? Nightmare for anyone with motor impairments. When buttons are too small or too close together, it leads to accidental taps and frustration.
Fix it: Give buttons breathing room. Make them finger-friendly, not toothpick-sized.
3. Poor Color Contrast
Light gray text on a white background might look sleek, but users with low vision can’t read it. Important information disappears, making your content effectively invisible.
Fix it: Test your color combinations. Tools like ColorSlurp help catch invisible text.
4. Text That Refuses to Scale
When users enlarge the text, content that doesn’t resize properly can break or get cut off, making the app hard or impossible to use for people who need larger fonts. It’s like trying to read a comic strip through a keyhole – impossible and completely avoidable.
Fix Design layouts that handle text scaling up to 200%. Test with Dynamic Type on iOS and Large Text on Android.
Make Mobile Accessibility Testing Easier with Testsigma
Mobile app accessibility testing can feel like a minefield. Tiny touch targets, missing labels, unreadable text, and color contrast issue. It’s a lot to juggle, especially when deadlines are looming. Keeping accessibility in mind while building your app isn’t easy, but it’s essential.
The key is to plan early, integrating accessibility from the design phase rather than trying to fix it after launch. Keep interactions simple, use clear labels, properly sized touch targets, and intuitive navigation, and of course! Don’t forget to test with real users.
Tools like Testsigma can make all of this easier. You can run accessibility checks across devices, catch issues before they reach users, and get reports that actually make sense with zero jargon and spreadsheets.
It’s like having a teammate who’s always on top of every detail, so your app works for everyone without the stress.
FAQs
Honestly, from day one. If you build accessibility in during design and development, mobile accessibility testing becomes way easier, and you avoid scrambling to fix issues later.
Think of them as POUR: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust. Following these makes sure your app works for everyone, and guides accessibility testing for mobile apps in a clear, structured way.
It’s about making sure anyone can use your app, no matter their abilities. Mobile app accessibility testing helps spot barriers so your UI/UX works for everyone, from visually impaired users to people who need larger text or simpler interactions.




