Test Driven Development (TDD) is widely regarded as the most rigorous software development methodology. By continuously running the tests, developers can ensure that their code is maintainable and efficient, making it easier to identify and fix any issues that may arise. With TDD, developers can be confident that their code is working as intended, reducing the risk of bugs and making the development process more streamlined. In this blog, let us understand the importance of TDD and how Testsigma streamlines your entire testing process.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Test Driven Development(TDD)?
- 2 Test-Driven Development Cycle: The Three Phases
- 3 Pros of Test Driven Development:
- 4 Cons of Test Driven Development:
- 5 How to Perform Test Driven Development?
- 6 Frameworks for Test-Driven Development
- 7 How does TDD Fit into Agile Development?
- 8 Difference between TDD Vs Traditional Testing
- 9 What are Acceptance TDD and Developer TDD?
- 10 Examples of Test Driven Development
- 11 Best Practices for Test-Driven Development
- 12 So, is TDD a reliable development approach?
- 13 Testsigma for Automated Testing
- 14 Why use Testsigma for Automated Testing?
- 15 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Test Driven Development(tdd)?
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development methodology that ensures all code changes made to a system are correctly tested and do not introduce any new bugs. Testers can help developers create robust and reliable software applications by adding tests to the current test suite before any code is added to an existing build.
The main idea behind TDD is that by writing tests before the code, developers can use them as a guide for writing the code and quickly identify potential problems before it goes into production. TDD ensures that any changes to the system are adequately tested and do not introduce any new bugs.
With TDD, developers can quickly identify areas of their application that need more attention or further testing. Additionally, TDD allows for faster development cycles since the tests can be re-run after each code change, enabling developers to make changes quickly without worrying about introducing new bugs or breaking existing functionality.
Test-driven Development Cycle: the Three Phases
The Test-driven development (TDD) cycle is a software development approach where tests are written before the code. This cycle can be summarized in three main steps:
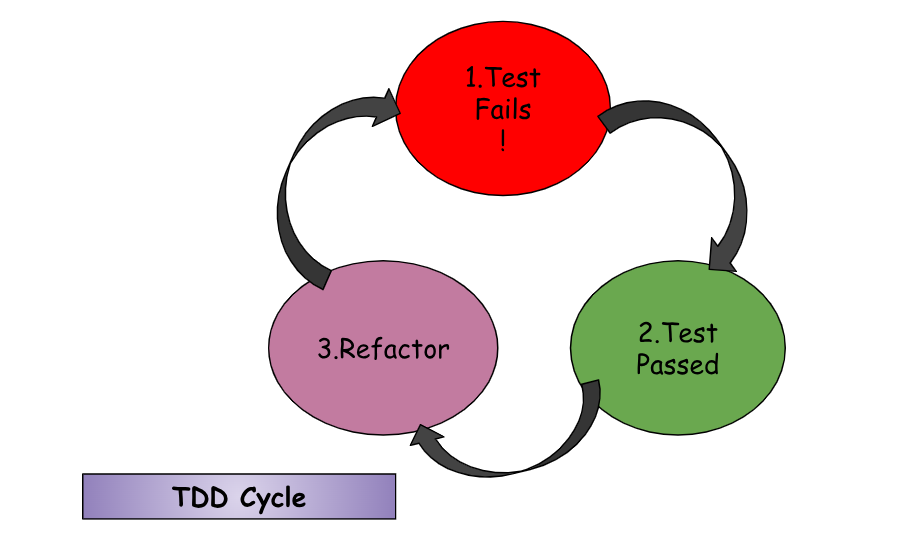
1. Red:
- In the Red phase, the developer writes a test for the functionality they want to implement. This test initially fails because there is no corresponding code to make it pass.
- The test in this phase is usually minimal and focuses on a specific aspect of the desired behavior.
- The purpose of this phase is to clearly define the expected behavior of the code and provide a concrete goal for implementation.
2. Green:
- In the Green phase, the developer writes the minimal amount of code necessary to pass the test from the Red phase.
- The code written in this phase might not be the most efficient or complete solution but is solely focused on making the test pass.
- Once the test passes, the code should satisfy the requirements outlined in the test.
3. Refactor:
- In the Refactor phase, the developer improves the code without changing its functionality.
- This phase involves cleaning up the code, improving its readability, removing duplication, and optimizing performance.
- This phase’s goal is to ensure that the code remains maintainable and extensible while still passing all the tests.
- After refactoring, the tests are run again to ensure the code behaves as expected.
This cycle encourages developers to write only the necessary code and consider design and requirements before writing the code.
It aims to improve both the quality of the software and the development process.
Pros of Test Driven Development:
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development process in which tests are written for new code before the code is written. Some benefits of TDD include:
- Writing tests before code can help you write better, faster, and more reliable code. It makes it easier to spot any mistakes as you work, so you don’t have to spend time fixing them later.
- When you’re done writing your code, a suite of tests will give you confidence that your code is doing what it should.
- Plus, if you ever need to make changes in the future, having these tests will make sure nothing breaks!
- Continuous testing allows you to set up a process that helps you find and fix bugs faster.
- The tests are like instructions on how the code should be used, which can help new people who join the project get up to speed quickly.
However, like any other development method, TDD also has a few drawbacks.
Cons of Test Driven Development:
- Test driven development (TDD) can take up a lot of time and slow down the progress of your project. It can also be hard to write tests for big or complicated tasks, which takes a lot of effort.
- TDD can be too rigid when making changes or adding new features, which isn’t ideal if you need to adjust your project quickly. You might spend too much time testing and not enough time developing, so watch out for that.
- TDD requires a good understanding of test automation, so it could not be easy if you don’t know how to do that.
- All the emphasis on tests and following the rules of testing can stop you from being creative and coming up with new ideas during the making process.
Test-Driven Development (TDD) has many benefits like making your code more reliable, easier to maintain, and able to handle more users. But it also takes longer and isn’t as flexible as other code-writing methods. So you must consider the pros and cons before deciding if TDD suits your project.
Check here – Development Testing
How to Perform Test Driven Development?
To perform TDD, you must follow steps, including writing tests, code, and refactoring. Here are the steps in detail:
- Before writing any code, a test should be reported to define the expected behavior of the functionality and should fail when run.
- The minimum code needed to pass the test should then be written.
- After re-running the test to confirm that it passes and meets the requirements defined in the trial, refactoring is necessary to make the code more readable, maintainable, and performant.
- This process should be repeated until all project requirements have been met.
- Continuously run all the tests and make sure all previously passing tests still pass after refactoring. This will ensure that refactoring doesn’t break any existing functionality.
Frameworks for Test-driven Development
Several frameworks and tools are available for implementing Test-Driven Development (TDD) across various programming languages. Here are some popular ones:
- JUnit (Java): JUnit is a widely used unit testing framework for Java. It provides annotations to define test methods and assertions to verify the expected behavior of the code.
- RSpec (Ruby): RSpec is a behavior-driven development (BDD) framework for Ruby that can also be used for TDD. It provides a domain-specific language (DSL) for writing expressive and readable tests.
- Pytest (Python): Pytest is a flexible and powerful testing framework for Python. It supports TDD and provides a simple syntax for writing tests along with rich features for customization and extensibility.
- Mocha (JavaScript): Mocha is a feature-rich JavaScript testing framework that supports TDD and BDD. It can be used with various assertion libraries like Chai and provides support for asynchronous testing.
- PHPUnit (PHP): PHPUnit is a unit-testing framework for PHP that supports TDD. It provides a rich set of assertion methods and features for mocking and stubbing objects.
- NUnit (C#): NUnit is a unit testing framework for .NET languages like C# and VB.NET. It is inspired by JUnit and provides similar features for writing and organizing tests.
- RSpec (C#): RSpec.NET is a port of the RSpec framework from Ruby to C#. It allows developers to write expressive tests using a fluent syntax and supports TDD and BDD approaches.
- JUnit (Kotlin): Kotlin developers can also use JUnit for writing tests, similar to Java. Kotlin is fully interoperable with Java so that JUnit can be seamlessly integrated into Kotlin projects.
- Go Testing Framework (Go): Go’s standard library includes a testing framework that supports TDD. It provides features for writing tests, organizing test cases, and running tests in parallel.
- JUnit (Scala): Scala developers can also leverage JUnit for TDD, similar to Java and Kotlin. Scala integrates well with Java libraries so that JUnit can be used seamlessly in Scala projects.
These frameworks provide essential features for writing and running tests in a Test-Driven Development workflow.
How Does TDD Fit Into Agile Development?
Test-driven development (TDD) is an important part of Agile software development. Agile is about working together, making changes quickly, and doing things in small steps.
TDD helps with this by allowing us to write tests that help us develop our software bit by bit.
Here’s how TDD fits into Agile development:
- Incremental Development: Agile methodologies advocate for delivering working software in small increments. TDD aligns well with this principle by encouraging developers to write tests and code in small, incremental steps.
Each test written in TDD represents a small functionality implemented and tested before moving on to the next. - Continuous Feedback: Agile promotes continuous feedback loops between developers, testers, and stakeholders. TDD enhances this feedback loop by ensuring that tests are written before code is implemented.
This helps developers gain immediate feedback on the correctness of their code and ensures that any issues are caught early in the development process. - Flexibility to Change: One of Agile’s core principles is the ability to respond to change quickly. TDD supports this principle by providing a safety net of tests, allowing developers to refactor and modify code confidently.
Since changes are made incrementally and tests are continuously run, developers can quickly identify and address any regressions resulting from changes. - Collaboration: Agile methodologies emphasize collaboration and teamwork among cross-functional teams. TDD encourages collaboration by providing a common language for discussing requirements and behavior through tests.
Tests serve as executable specifications that capture the software’s intended behavior, allowing developers, testers, and stakeholders to have a shared understanding of what the system should do. - Quality Assurance: Agile strongly emphasizes delivering high-quality software. TDD helps ensure quality by promoting the development of automated tests that validate the code’s correctness.
By writing tests first, developers are forced to think about the expected code behavior before implementation, resulting in more robust and reliable software.
Difference between TDD VS Traditional Testing
Test-Driven Development (TDD) and traditional testing are two ways to ensure your software works correctly. Traditional testing looks after writing the code, while TDD is a process you use before writing any code. It helps make sure the code you write is bug-free and working correctly.
| TDD | Traditional Testing |
| Tests are written before writing any code. | Tests are written after writing the code |
| Emphasizes writing the minimum amount of code needed to pass the test | Emphasizes writing all the code and testing it later |
| Focuses on testing the code at the unit level | Focuses on testing the entire application as a whole |
| It helps developers catch bugs early on and produce more maintainable code | This can lead to bugs being discovered later in the development process |
| Involves continuous refactoring of code while running all the tests | Involves testing after the development process is completed |
In a nutshell, TDD helps you find bugs early on and makes it easier to keep your code organized. It also enables you to break down the problem into smaller parts. On the other hand, Traditional testing is all about finding bugs after you’ve already finished coding and tested everything out.
What Are Acceptance TDD and Developer TDD?
Test Driven Development (TDD) can be applied at two levels: acceptance TDD and developer TDD.
Acceptance TDD
Acceptance TDD tests an entire system from the user’s perspective to ensure it meets what everyone wants. This includes checking the code and interface to ensure it does what it’s supposed to do.
Developer TDD
Developer TDD ensures that individual bits of code (like functions and methods) do what they’re supposed to, ensuring the code runs correctly and any problems are caught quickly. In short, Acceptance TDD looks at the whole system while Developer TDD looks at single parts; both are important for ensuring everything works as it should and meets all requirements.
Examples of Test Driven Development
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is used in many scenarios, from small projects to large-scale enterprise applications. Here are a few examples of how TDD can be used:
- We can employ Test-Driven Development (TDD) to evaluate the performance of a web application, from the user interface to the underlying code. This method can identify potential errors early on and guarantee that the application functions as anticipated.
- You can use TDD to test how your mobile apps work, like pushing the buttons, navigation, and other parts of the user interface. This way, you can ensure that your app works correctly on different phones and systems.
- Testing embedded systems with TDD can help ensure things are working as they should. It can test how different parts of the system communicate and how certain sensors respond to specific inputs. This makes it easier to spot any problems early on so that you don’t have to deal with them later!
Many scenarios can apply TDD, ranging from web and mobile application development to embedded systems development.
It helps to catch bugs early on and ensure that the system behaves as expected.
Best Practices for Test-driven Development
Here are some best practices for TDD:
- Write tests before code: In TDD, you always start by writing a failing test that specifies a small improvement or new functionality you want to implement.
- Keep tests small and focused: Each test should focus on one specific functionality aspect. This makes it easier to pinpoint failures and understand the purpose of each test.
- Run tests frequently: Running tests helps catch errors early in development, making them easier and cheaper to fix.
- Write the minimum amount of code to pass the test: Write the simplest code necessary to make the test pass after writing a failing test. Avoid adding unnecessary functionality at this stage.
- Refactor code: Once the test passes, refactor it to improve its structure, readability, and performance. Ensure that all tests still pass after refactoring.
- Use descriptive and meaningful test names: Clear and descriptive test names make it easier to understand the purpose of each test and the behavior it is testing.
- Follow the Red-Green-Refactor cycle: This is the core of TDD. Start by writing a failing test (Red), then write the code to make the test pass (Green), and finally refactor the code while ensuring that all tests still pass.
- Test all edge cases and boundary conditions: Make sure to test both the expected behavior and edge cases to ensure the code’s robustness and correctness.
- Keep tests independent and isolated: Tests should not depend on each other or external factors such as databases or network connections. Each test should be able to run independently of others.
- Automate testing: Use automated testing frameworks and tools to automate test execution. This ensures that tests can run frequently and consistently throughout development. Try Testsigma for 10x faster automation testing.
- Continuous Integration (CI): Integrate testing into your CI/CD pipeline to automatically run tests whenever changes are made to the codebase. This helps catch errors early and ensures that the codebase remains stable.
- Write both unit and integration tests: While TDD primarily focuses on unit tests, it’s also important to write integration tests to test the interactions between different system components.
- Seek feedback: TDD encourages frequent feedback loops by continuously writing tests and code in small increments. This helps ensure that the development process stays on track and that the final product meets the desired requirements.
So, is TDD a Reliable Development Approach?
There is a lot of debate on the internet about whether TDD is good or bad for development. Some believe that test driven approach simplifies development, whereas a few think it only increases the complexity.
- There is a lot of confusion surrounding TDD. TDD works best when there is the right balance of time, quality, and cost.
- One of the main deciding factors in striking the right balance is the Testing Harness(testing tool/framework).
- Tools like Selenium increases need additional frameworks for data-driven testing and generating reports and are not the best solution for TDD.
- TDD is a software development process involving tests before the actual code. It helps developers focus on the code’s design and ensure that it meets the requirements.
- The tests are written so that they can be used to verify the correctness of the code. This process helps identify errors early in the development process, thus reducing rework and increasing productivity.
- With TDD, developers can ensure that their code is robust and reliable by running tests frequently and ensuring that all tests pass before pushing any changes into production. It also reduces manual testing efforts as most test cases are automated, thus saving time and cost.
- TDD also encourages better coding practices like refactoring and clean coding, which leads to better codebase maintainability. TDD requires a lot of discipline from developers as they need to write tests for every change made in the codebase. If not done correctly, it may lead to increased complexity due to redundant test cases or a lack of enough test coverage.
Moreover, TDD requires additional effort to set up testing environments, maintain test data, etc., which adds to the overall development cost. Hence, organizations must carefully analyze their requirements before adopting TDD as their development methodology.
Refer How to select the right Automation Testing Tool?
A unified solution like Testsigma would be a better alternative. Testsigma is a cloud based AI-driven test automation platform in which the automated tests are written using simple English.
Testsigma for Automated Testing
Testsigma is a robust cloud-based low-code GenAI-powered test automation platform that allows you to test web, mobile, desktop, API, and Salesforce applications in one place. It helps you automate testing in plain English with no coding skills required.
You can test continuously by integrating automated tests into your existing CI/CD and DevOps pipelines, which will speed up the feedback loop and release cycles.
With Testsigma, you can automate your entire functional testing in one place without switching between multiple tools, thus saving your time and effort.
Why Use Testsigma for Automated Testing?
- Zero setup time, start testing with a one-click sign in to the cloud platform
- Zero coding required, start writing automated tests in plain English
- Minimal learning curve, you don’t have to spend time learning any programming language
- 10x faster testing with simplified test creation, execution, reporting, and maintenance.
- Unified platform to automate web, mobile, desktop, API, and Salesforce apps in one place.
- Quality testing, you can automate even complex workflows in plain English.
- Ship confidently by continuously testing your code to speed up the feedback and release cycles.
- Get 100% automation coverage with GenAI-driven test suggestions to cover edge case scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is TDD in Agile?
Test-Driven Development (TDD) is a way of making sure that your code works properly before you finish writing it. Agile software development uses a process in which tests are written first, and then the code is written to ensure the tests pass. This helps make sure there are no bugs or errors in the code.
How is TDD Different From Agile?
Agile development is a way of working that involves teams making quick progress on projects in short bursts. TDD (Test-Driven Development) is a tool that can be used within Agile to ensure the code works and there are no bugs. This helps teams spot problems early on and makes it easier to keep the code running smoothly. But TDD isn’t the same as Agile – Agile focuses more on being flexible and working together, while TDD concentrates on testing the code. You don’t have to use TDD when you do Agile, but it can help!
Is TDD a Scrum?
Scrum is an Agile way of dealing with complicated projects. Like Agile, it encourages being adaptable and working together and has specific roles and ceremonies. TDD (Test Driven Development) can be used in a Scrum system to ensure the code works correctly each time you do something, but it isn’t needed for Scrum.








