Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Automated test scripts are instructions or code designed to automatically perform specific actions on a software application and verify the expected outcomes. These scripts play a crucial role in modern software development and quality assurance. Using automation test scripts, software testing teams can execute repetitive tests quickly, accurately, and consistently without manual intervention.
As we delve deeper into this guide, we will explore the automation testing lifecycle, essential steps, and best practices to create and effectively run automated test scripts, empowering you to optimize your testing efforts and deliver top-notch software solutions.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What Are Automated Test Scripts?
- 2 Why Automate Test Scripts?
- 3 Real World Example of an Automated Test Script:
- 4 Types of Test Automation Scripts
- 5 Best Practices for Writing Automated Test Scripts
- 6 Advantages of Using Tools to Automate Test Scripts
- 7 Best tools for Automated Test Scripts
- 8 How to Run the Automated Test Script in Testsigma?
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Automated Test Scripts?
Automated test scripts are sets of code or instructions written to automate the testing process for software applications. They play a critical role in software testing, allowing for the automatic execution of predefined actions and validations. These scripts simulate user interactions, such as clicking buttons, inputting data, and navigating through the application, to ensure its functionality is working as expected.
Why Automate Test Scripts?
Automated testing helps save time, cost, and effort. Let’s consider a sample scenario. Whenever an application undergoes a code change due to a new feature update or upgrade, the testers must run the test scripts manually on all the supported platforms and hardware configurations throughout the development cycle. This is time-consuming, costly, and error-prone.
That’s where intelligent test automation comes to the rescue. Unlike manual testing, automated tests can be reused many times once set up. This helps reduce the time for repetitive tests from days to hours, saving time, effort, and cost.
Also Read: Hyperautomation
Real World Example of an Automated Test Script:
Consider an e-commerce website with a registration feature. The automated test script for this scenario might follow these steps:
- Test Setup: Launch the web browser and navigate to the e-commerce website’s registration page.
- Test Execution Steps: Enter valid user details, such as name, email address, password, and phone number, into the registration form. Then, click the “Sign Up” button to submit the form.
- Assertions/Verifications: After submitting the form, the script checks if the user is redirected to the login page, indicating successful registration. Additionally, it may verify that a confirmation email is sent to the user’s email address.
- Cleanup and Teardown: The script logs out the registered user and deletes the test data created during registration.
This automated test script can be run repeatedly and consistently to ensure that the registration feature functions correctly with various test scenarios, helping identify any potential issues early in the development cycle.
Types of Test Automation Scripts

- Record/Playback test automation script
In record/playback automation, various user actions, such as clicks, scrolls, notifications, etc., are recorded using a recorder. This approach doesn’t involve coding or any technical knowledge.
- Code-based test automation script
A code-based script uses programming languages like Java, Python, or JavaScript, providing complete flexibility and control over the test logic. This approach involves coding and programming knowledge to perform more efficiently.
- Keyword-driven test automation script
In keyword-driven testing, tests are written using keywords that represent actions. These keywords are mapped to functions or actions internally, allowing non-coders to build tests.
Best Practices for Writing Automated Test Scripts
Writing effective and maintainable automated test scripts requires adherence to industry best practices. Here are some valuable tips and test automation best practices:
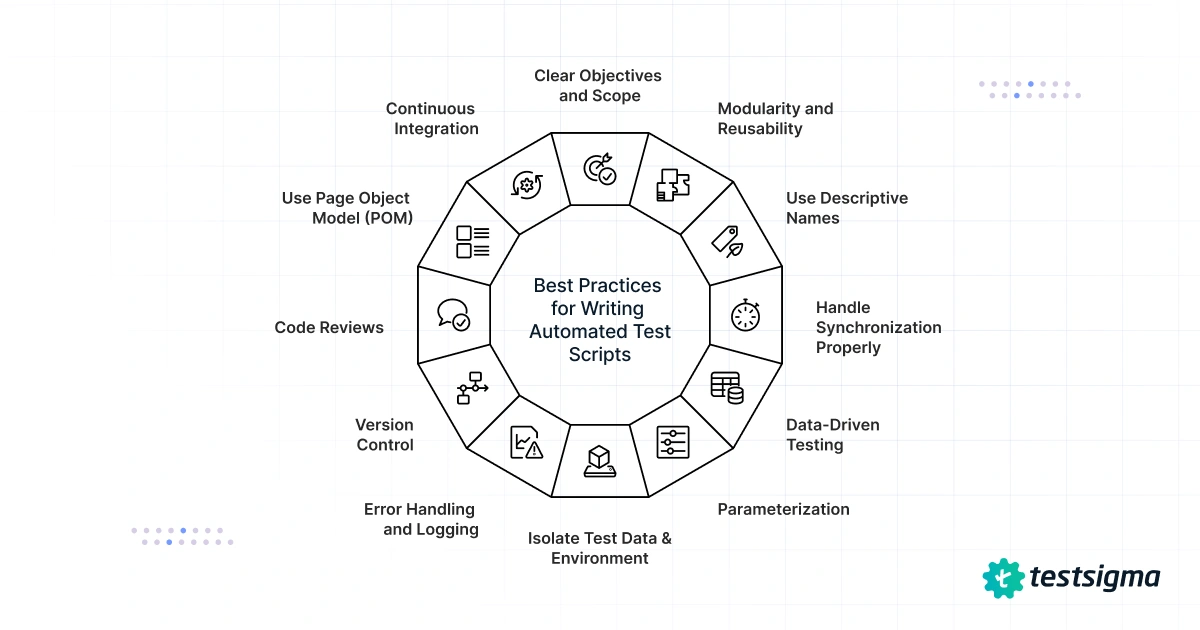
- Clear Objectives and Scope: Define clear objectives and scope for each test script. Understand what functionality the script will test, what scenarios it will cover, and the expected outcomes. This clarity helps in focused script development and targeted testing.
- Modularity and Reusability: Organize test scripts into modular components or functions that can be reused across multiple test cases. This enhances script maintainability and reduces redundancy, saving time and effort in script creation and updates.
- Use Descriptive Names: Give meaningful and descriptive names to test scripts, functions, and variables. This makes the code more readable and understandable for both current and future team members.
- Handle Synchronization Properly: Incorporate appropriate wait mechanisms to handle synchronization issues. Use explicit waits to ensure the script waits for elements to load or appear on the screen before proceeding with actions or verifications.
- Data-Driven Testing: Implement data-driven testing by separating test data from the test script. Store test data in external files or databases, enabling easy modification and retesting with different datasets.
- Parameterization: Parameterize test data and inputs to increase script flexibility and coverage. This allows you to run the same script with various data combinations, validating different scenarios efficiently.
- Isolate Test Data and Environment: Isolate test data and test environment setup from the application code. Avoid using hardcoded test data within the script to ensure data independence and easier maintenance.
- Error Handling and Logging: Implement error handling mechanisms to gracefully handle exceptions and failures during script execution. Additionally, include logging functionality to record test execution details, aiding in debugging and analysis.
- Version Control: Use version control systems (e.g., Git) to manage test script versions effectively. Version control allows you to track changes, collaborate with team members, and roll back to previous versions if needed.
- Code Reviews: Conduct code reviews with team members to ensure adherence to coding standards, identify potential issues, and improve script quality.
- Use Page Object Model (POM): Adopt the Page Object Model design pattern to separate the test script logic from the application’s user interface. POM enhances script maintainability and reduces code duplication.
- Continuous Integration: Integrate automated test scripts with continuous integration (CI) systems like Jenkins or Travis CI. This ensures that tests are automatically triggered on code changes, providing fast feedback to the development team.
In conclusion, writing effective and maintainable automated test scripts demands adherence to a set of crucial tips and best practices. Following these guidelines empowers teams to create robust and efficient automated test scripts, enhancing the overall success of their test automation endeavors.
Advantages of Using Tools to Automate Test Scripts
By optimizing resources, automating repetitive tasks, and delivering higher-quality software, test automation becomes an indispensable tool for modern software development teams. Employing specialized test automation tools, commonly known as test automation frameworks, offers several significant advantages:
- Ease of Script Creation: Test automation frameworks typically provide user-friendly interfaces, record-and-playback functionality, and codeless scripting options. This ease of use empowers both technical and non-technical team members to create automated test scripts effortlessly. The intuitive interfaces reduce the learning curve, making test automation accessible to a broader range of team members.
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Platform Testing: Apps often offer built-in support for testing across multiple browsers and platforms, such as Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android. This capability ensures that the application is thoroughly tested on various environments, including different operating systems and web browsers. Cross-platform testing helps identify platform-specific issues and ensures a consistent user experience across devices.
- Code Reusability: Automation frameworks encourage the use of modular and reusable code structures. Test cases and components can be abstracted into functions or libraries, allowing testers to reuse them across different test scenarios. Code reusability not only saves time and effort in script creation but also simplifies script maintenance and reduces the likelihood of errors.
- Enhanced Test Coverage: Automated test scripts can execute a vast number of test cases quickly and accurately. This comprehensive test coverage enables teams to validate multiple functionalities and scenarios, including edge cases and boundary conditions, in a fraction of the time required for manual testing. Enhanced test coverage contributes to higher software quality and more thorough validation of application behavior.
- Faster Test Execution: Automated testing significantly reduces test execution time compared to manual testing. Once test scripts are created, they can be executed repeatedly and reliably, delivering fast feedback on application performance. Rapid test execution allows developers to address identified issues promptly, leading to faster bug resolution and quicker software releases.
- Consistent Test Execution: Automated test scripts execute test steps consistently and precisely, eliminating the variability that can occur in manual testing due to human errors. This consistent test execution ensures repeatable and reliable results, enhancing the trustworthiness of test outcomes and reducing false positives/negatives.
- Integration with Continuous Integration (CI): Automation frameworks can seamlessly integrate with CI systems, enabling automated tests to be triggered automatically whenever new code changes are made. Continuous integration and automated testing create a continuous feedback loop, providing developers with real-time insights into application quality. CI integration streamlines the development process, allowing for faster identification and resolution of defects.
Hence, utilizing automation frameworks to automate test scripts offers a multitude of advantages that elevate the effectiveness and efficiency of software testing. From simplified script creation and cross-platform testing to improved test coverage and faster execution, test automation enhances the overall quality of software products. By embracing automation technologies, testing teams can optimize their workflows, identify issues early, and deliver reliable and high-performing software applications.
Best Tools for Automated Test Scripts
Testsigma
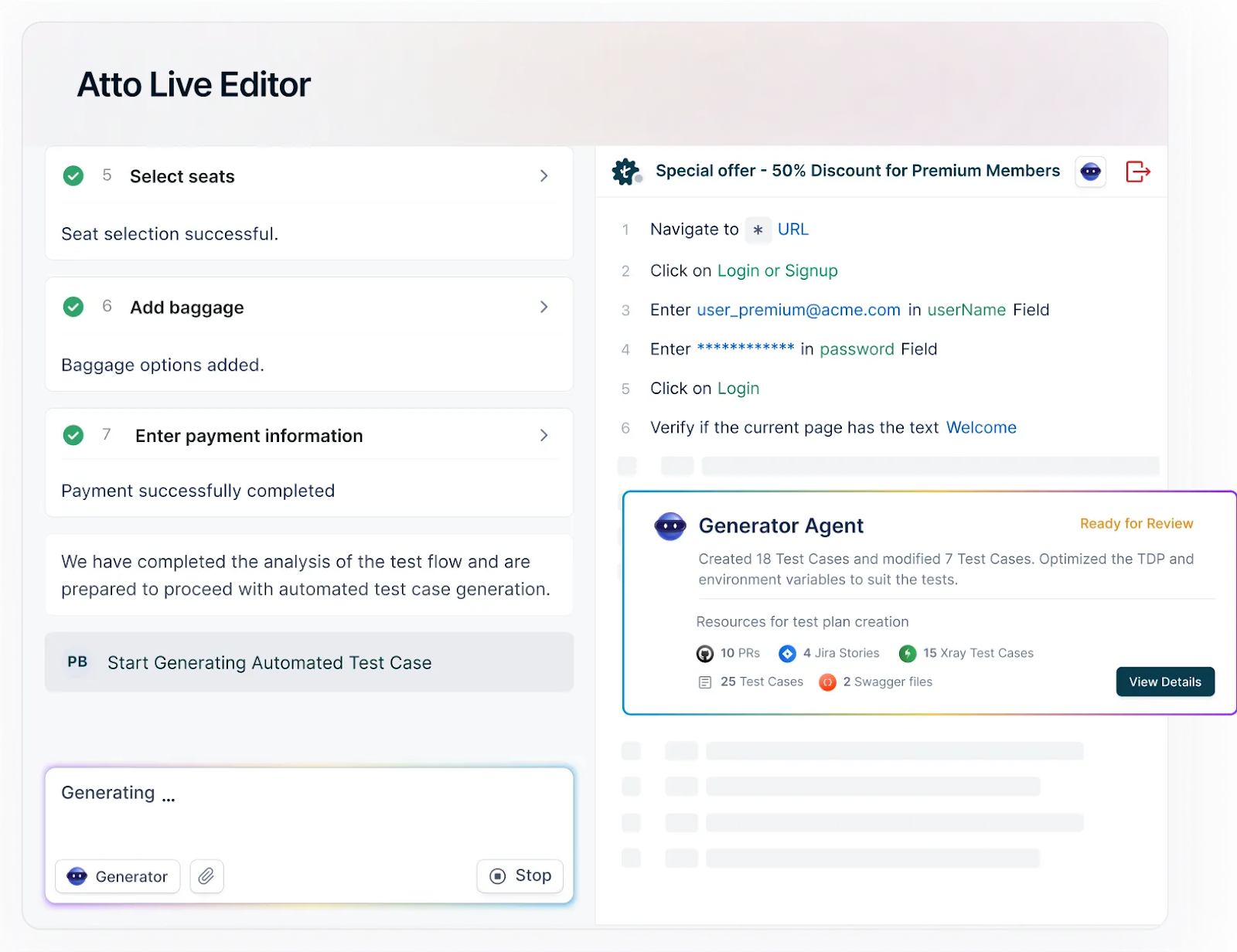
Testsigma is a cloud-based test automation platform that embraces an AI-driven scriptless test automation approach. It stands out for its AI-powered capabilities, offering testers a simplified and intelligent test case creation experience. With Testsigma, you can easily write your test cases, group them into a test suite, and automate them.
Testsigma offers Agentic AI capabilities using different AI agents powered by Atto. These agents help with test creation, optimization, maintenance, execution, and reporting.
Features of Testsigma
Testsigma comes packed with additional features that help you scale your automated script testing and integrate it with your existing testing cycles. Here are a few features of Testsigma that make your testing life easier.
- Codeless Test Automation: Automate tests in simple English without coding knowledge, making it accessible for non-technical team members.
- Unified Testing: Automate tests for web, mobile, API, and desktop applications from one platform.
- AI-Supported Features: AI-powered features aid in test maintenance, bug reporting, and test optimization.
- Cloud Execution: Execute tests on the cloud from anywhere, connecting to preferred cloud device labs for scalability.
- Debugging Made Easy: Capture screenshots, videos, and logs during test runs, and use the built-in debugger for issue identification.
- Customizable Reports: Tailor reports to specific needs with real-time reporting capabilities.
- Continuous Testing: Facilitate team collaboration and integrate with popular CI/CD tools.
- Parallel Testing: Run multiple tests simultaneously to reduce testing time and speed up time-to-market.
- Testing on Local Devices: Test apps on local devices for more accurate real-world scenario testing.
- Image Recognition: Identify visual changes with image recognition capabilities.
- 24/7 Support: Round-the-clock support available for prompt issue resolution.
Selenium

Selenium is a widely used open-source tool for automating web browser testing. It provides a programming interface to interact directly with web elements on web pages, enabling testers to replicate user interactions. Testers can use various programming languages like Java, Python, and C# to write test scripts that navigate through web pages, click buttons, fill forms, and perform verifications.
Features of Selenium
- Supports multiple programming languages such as Java, Python, and C#.
- Allows direct browser interaction for precise control over testing scenarios.
- Offers compatibility with various browsers, ensuring cross-browser testing capabilities.
Appium

Appium is an open-source tool specifically designed for automating testing of mobile applications on Android and iOS platforms. It utilizes the WebDriver protocol to interact with the mobile application’s user interface. Testers can use a range of programming languages to write test scripts that simulate interactions with mobile app elements, such as tapping buttons, entering text, and verifying content.
Features of Appium
- Supports mobile testing on both Android and iOS devices.
- Allows test script development in various languages such as Java, JavaScript, Python, and Ruby.
- Provides seamless integration with Selenium WebDriver, enabling a consistent testing experience.
TestComplete

TestComplete offers a versatile approach to automating test scripts for web, desktop, and mobile applications. It provides multiple methods for test case creation, including scriptless test automation, keyword-driven testing, and record-and-playback. Testers can create test scripts by simply dragging and dropping test elements, setting verification points, and defining test data.
Features of TestComplete
- Facilitates scriptless test automation with keyword-driven or record-and-playback methods.
- Provides built-in support for multiple scripting languages, including JavaScript, Python, and VBScript.
- Offers cross-platform testing capabilities for web, desktop, and mobile applications.
Ranorex

Ranorex specializes in automating test scripts for desktop applications. It offers a user-friendly and codeless approach to creating test scripts through drag-and-drop and modular action table features. Testers can interact with desktop applications by simply recording interactions and using these recordings as the basis for automated test scripts.
Features of Ranorex
- Offers a codeless test automation approach with drag-and-drop and modular action table features.
- Supports C# and VB.NET scripting for advanced customization and integration.
- Provides dedicated tools for desktop application testing, ensuring efficient and reliable execution.
Cypress

Cypress focuses on automating test scripts for web applications. Its unique architecture allows it to run directly in the browser, providing real-time debugging and fast test execution. Testers can write test scripts using JavaScript, leveraging Cypress’s seamless integration with modern web development frameworks like React and Angular.
Features of Cypress
- Runs directly in the browser, providing real-time debugging capabilities.
- Offers fast test execution for quick feedback on web application testing.
- Integrates smoothly with modern web development frameworks, simplifying test script development.
Robot Framework

Robot Framework is a versatile test automation tool supporting both web and mobile application testing. It employs a keyword-driven approach, allowing testers to write test scripts in a simple tabular syntax using plain English keywords. Testers can easily define test steps, expected outcomes, and test data in a human-readable format.
Features of Robot Framework
- Employs a simple tabular syntax for easy-to-read and write test scripts.
- Supports multiple test libraries and allows custom keyword extensions in Python or Java.
- Suitable for web and mobile application testing, providing a comprehensive testing solution.
How to Run the Automated Test Script in Testsigma?
Running an automated test script in Testsigma is as simple as writing steps in plain English, as it supports AI-powered codeless testing. Unlike many tools that require complex scripting or steep learning curves, Testsigma allows testers of all skill levels to create, schedule, and execute tests directly on the cloud with minimal setup. Its AI-driven capabilities, parallel execution, and seamless integrations with CI/CD pipelines make it faster and more collaborative, helping teams move from script design to real results much more efficiently than traditional automation tools.
A step-by-step guide to run automated tests using Testsigma

- Log in to your Testsigma account.
- Navigate to your project and open the test case you want to run.
- Select the test environment for execution.
- Choose between local execution, cloud devices, or integrated platforms.
- Click “Run” to start the execution.
- View results in the Reports section for logs, screenshots, and insights.
Conclusion
Automated test scripting has emerged as a game-changer in the world of software testing, offering efficiency, accuracy, and accelerated feedback to development teams.
Selecting the right test automation tool is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the success of your testing efforts. Each tool comes with its own set of features catering to specific use cases. As you venture into the world of automated test scripting, explore various tools, conduct trials, and take advantage of free evaluations to make an informed decision.
As a first step, sign up for a free trial of Testsigma – an AI-driven, scriptless test automation platform. Embrace the power of natural language processing, cloud-based parallel test execution, and seamless collaboration to accelerate your testing efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Example of an Automation Test Script for a Login Page?
This is an example of a login test script using Selenium WebDriver in Java
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class LoginTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Set up WebDriver
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://example.com/login");
// Enter username
WebElement username = driver.findElement(By.id("username"));
username.sendKeys("testuser");
// Enter password
WebElement password = driver.findElement(By.id("password"));
password.sendKeys("testpass");
// Click Login
driver.findElement(By.id("loginBtn")).click();
// Verify successful login
if (driver.getCurrentUrl().contains("dashboard")) {
System.out.println("Login Test Passed!");
} else {
System.out.println("Login Test Failed!");
}
driver.quit();
}
}How to Write Test Scripts for API?
Writing test scripts for API testing requires a solid understanding of the API endpoints, data formats, and expected responses. Define the endpoint and request method, set input parameters, send the request, validate the response status and data, and add assertions for expected outcomes.
Which Tools Make it Easy to Write Automated Test Scripts?
Tools like Testsigma, TestComplete, and TestRigor provide scriptless test automation capabilities, allowing testers to create test cases with no or minimal coding.
Testing frameworks like Cypress and Selenium WebDriver offer extensive support for web application testing, but require strong coding knowledge for scripting.
Difference between Simulation vs Validation in Test Scripts
Simulation in test scripts refers to mimicking real user actions or system behavior to test how an application responds under certain conditions, often without needing actual data or environments. In contrast, validation focuses on verifying that the application’s outputs or behavior match expected results after actions are performed.
What are the Problems with Automated Test Scripts
Automated test scripts offer speed and efficiency but also come with challenges like
- Flakiness due to timing or sync issues
- High maintenance from frequent UI changes
- Complex initial setup
- Strong coding skills required



