You can’t inspect every line of code in a complex application – nor should you have to. What if you could simply test how users will actually experience your software without diving into its inner workings?
That’s what black box testing is all about. It highlights the issues that truly impact user experience while ignoring technical details that users never get a chance to see. As development cycles accelerate and user expectations rise, this approach offers an efficient way to verify software quality without slowing down releases.
In this guide, we’ll explore what black box testing is, what it matters and essential techniques and best practices for effectively implementing these tests in your workflow.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What Is Black Box Testing?
- 2 The Black Box Approach: How Exactly Do The Tests Work?
- 3 Black Box Testing In The Software Development Lifecycle
- 4 6 Types Of Black Box Testing Methods To Improve User Experience
- 5 Advantages Of The Black Box Testing Approach
- 6 Disadvantages Of Black Box Testing
- 7 5 Black Box Testing Techniques That Find Issues Real Users Care About
- 8 6 Best Practices For Effectively Using Black Box Testing
- 9 Testsigma: Automate Black Box Testing 10x Faster
- 10 Final thoughts
- 11 FAQs
What is Black Box Testing?
Black box testing examines software functionality without examining its internal code structure. In this approach, testers interact with applications just as end users would, verifying that the system behaves according to requirements.
Also known as closed-box testing, this technique ensures applications fulfill their functional expectations regardless of how they’re coded.
Consider a simple login page black box testing example:
- You enter a username and password, then click the login button
- You then see what happens next
- If credentials are correct, the system should grant access and display the dashboard
- If details are incorrect, it should present an appropriate error message (like “Invalid credentials”)
Throughout this process, testers never examine the underlying authentication code or password verification logic.
Instead, they focus exclusively on what goes in (input) and what comes out (output). This forms the essence of black box testing: treat the application as a sealed box, provide various inputs, and assess whether the outputs align with expected results.
The Black Box Approach: How Exactly Do the Tests Work?
Unlike other software testing methods, this technique deliberately avoids examining source code, focusing instead on the user’s perspective and expected behaviors. Here’s a black box testing diagram to help you understand better:
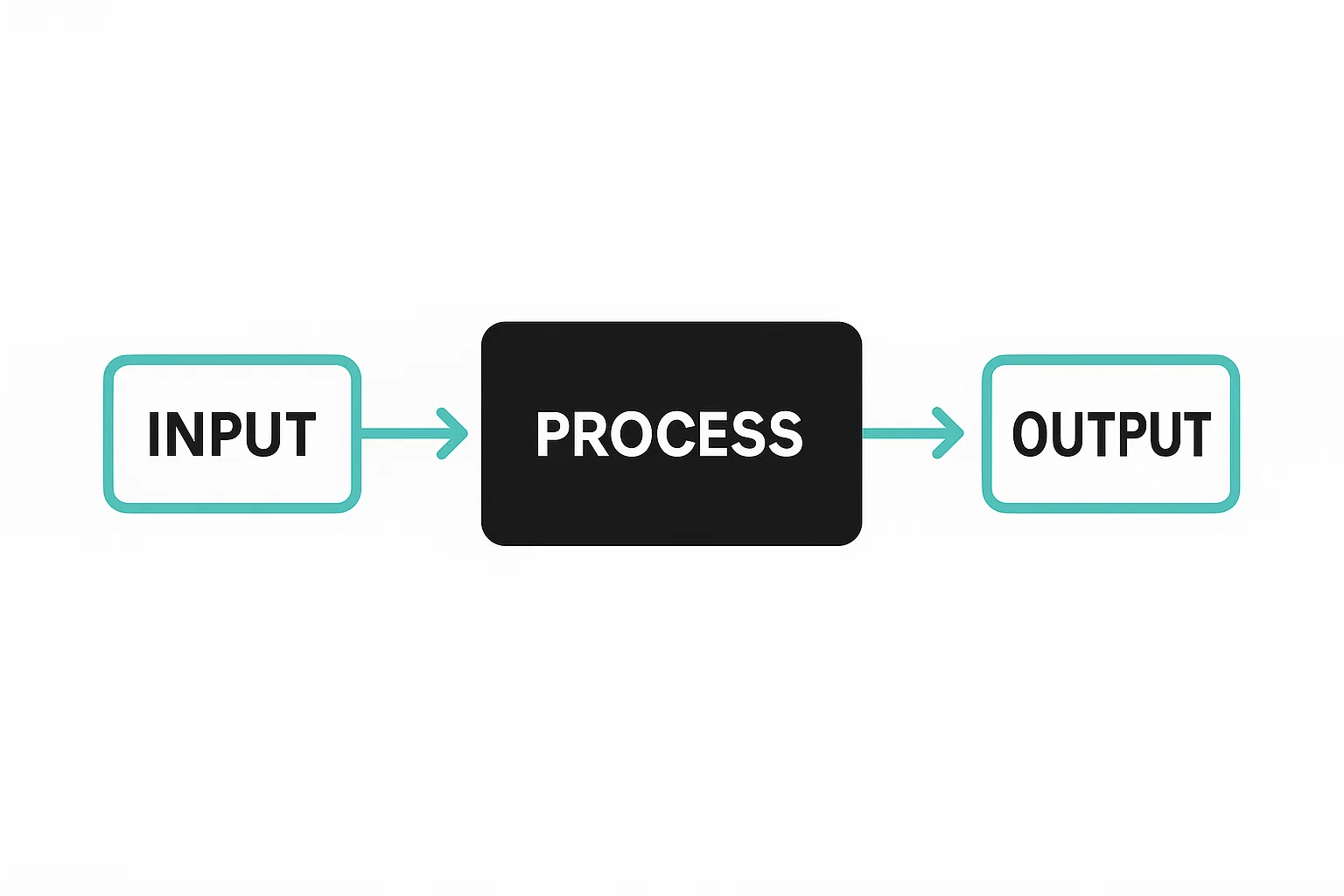
When implementing the black box method, here’s what testers do:
- First, they analyze requirements and specifications to understand what the software role is
- Next, they develop test cases covering various input scenarios and their expected outcomes
- Then, they execute these tests while documenting any discrepancies between actual and expected results
What makes this black box approach unique is its focus on functional validation rather than development details. Testers ask: “Does this feature work correctly?” instead of “How is this feature built?”
With that said, this approach is different from white box testing, where testers examine the internal code structure and execution of the tool.
But it is slightly related to grey box testing, which combines limited knowledge of internal architecture with black box techniques. Grey box testing allows you to test functionality from the user’s perspective while also getting partial visibility into the system’s structure.
Black Box Testing in the Software Development Lifecycle
The black box testing approach can be applied to different stages of software development. But mostly it is used in system testing, since it directly focuses on user-facing behavior.
In the system testing phase, testers validate complete workflows and scenarios against business requirements without concerning themselves with code implementation. They verify that the application functions correctly as a whole, just as users would experience it.
Besides this phase, black box testing in software engineering also works with:
- Requirement analysis: Testers create test cases based on specifications upfront, often identifying ambiguities or contradictions that might cause problems later in development.
- Development phase: As features are completed, developers and testers perform initial black box testing to verify that each component meets its functional requirements before integration.
- Maintenance phase: Black box regression testing ensures new changes don’t break existing functionality, with tests remaining valid even when internal implementations change.
6 Types of Black Box Testing Methods to Improve User Experience
Black box testing covers various approaches, each designed to validate different aspects of software functionality. These testing types can be used individually or combined to create comprehensive test coverage for applications.
Here’s a look at the different types of black box testing:
- Functional testing
Functional testing evaluates the features and functions of the software, making sure they perform as per requirements.
For an e-commerce website, this can involve checking if products can be easily searched, added to the cart, and purchased successfully. It can focus on the most crucial aspects of the software, integration between key components or the system as a whole.
- Non-functional testing
One of the important types of black box testing, it goes beyond functional testing to evaluate aspects such as performance, usability, and security.
Rather than asking “Does it work?” non-functional testing asks “How well does it work?” These tests measure quality attributes that impact user satisfaction and system reliability.
- Regression testing
This kind of testing ensures that new code changes don’t negatively impact your existing functionality. After modifications or updates to the software, regression test suites verify that previously working features still function correctly.
Many teams automate these tests to run whenever code changes are made, catching unexpected side effects before they reach production.
- User acceptance testing (UAT)
UAT involves actual end users checking that the software meets their needs and expectations. It typically occurs in the final stages before release when stakeholders and customer representatives test the application in scenarios that mimic real-world usage.
Their feedback helps determine if the software is ready for deployment or needs further refinement.
- Smoke testing
A preliminary check to verify that the most critical functions work properly. Before conducting more extensive testing, teams run these smoke tests to ensure the application doesn’t “catch fire” when started.
These quick tests check if users can log in, navigate basic screens, and perform essential operations without encountering major failures.
- Integration testing
As its name suggests, it checks whether the different components or systems are working together as expected. When multiple modules are combined, integration testing confirms they communicate and exchange data correctly.
For example, testing might verify that a payment processing service properly integrates with a shopping cart system, maintaining data consistency throughout the transaction process.
Advantages of the Black Box Testing Approach
This method has become the backbone of quality assurance at companies from startups to tech giants. Here are the key advantages of black box testing that make it worth considering:

- Unbiased testing
As part of the test, testers approach the software objectively with an unbiased view. This helps catch issues that developers might miss due to their familiarity with the system.
- User-centric validation
By focusing on functionality from the user’s perspective, teams can identify usability issues and functional problems that directly impact customer experience.
- Early-stage defect detection
When used from the requirements phase, this testing method catches misunderstandings before they become coding mistakes. By creating test cases early, you can identify potential issues before development even begins.
- Wide test coverage
The black box method encourages exploring various input combinations and scenarios. This comprehensive coverage helps spot unexpected behaviors and edge cases that might be missed otherwise.
- Large-scale testing
The approach scales well to complex systems and works perfectly for regression testing. Test cases remain valid even when internal code changes, making this method valuable throughout product evolution.
Disadvantages of Black Box Testing
While black box testing offers many benefits, it also comes with certain limitations that teams should consider. With that knowledge, they can complement this approach with other testing methods to secure comprehensive quality assurance.
Here are the key limitations of the black box testing method:
- Limited insight into code quality
Black box testing can’t assess the quality of the underlying internal code. So, issues like memory leaks, poor algorithm choices, or unnecessarily complex implementations may go undetected despite passing functional tests.
- Possible test coverage gaps
Without knowledge of internal paths and conditions, testers might miss testing certain code branches. This can lead to untested scenarios in the app that could potentially contain defects.
- Inefficient for complex logic testing
When testing applications with complex business rules or calculations, black box testing may require numerous test cases to achieve adequate coverage. This approach becomes less efficient compared to white box methods for such scenarios.
- Difficult to pinpoint defect locations
When defects are found, black box testing identifies that a problem exists but provides limited information about where in the code the issue resides. This limitation can increase debugging time for developers.
- Risk of redundant test cases
Without visibility into code structure, testers might unknowingly create multiple test cases that exercise the same code paths. This redundancy can waste testing resources without improving quality.
5 Black Box Testing Techniques That Find Issues Real Users Care about
The black box testing approach relies on several techniques that offer a structured way to explore application behavior across different scenarios. Let’s look at the main techniques that testing professionals use to catch defects early.
- Equivalence class partitioning
This technique tests a range of inputs by dividing them into valid and invalid groups. Valid partitions contain acceptable values, while invalid partitions have rejected values. Instead of testing every possible input, you select representative samples from each group.
For example, when testing a field that accepts ages 18-65, you might just test with 25 (valid), 15 (too young), and 70 (too old) rather than all possible ages. Testers love this approach because it dramatically reduces test cases while maintaining good coverage.
- Boundary value analysis
Most times, bugs often lurk at the edges. This method focuses on testing values present at the boundaries of valid and invalid ranges.
Say you’re testing that password length field requiring 8-16 characters. You’d specifically check passwords with 7, 8, 16, and 17 characters. It’s believed these points are particularly error-prone in code, making boundary testing a highly effective technique for finding defects.
- Decision table testing
When your application has complex business rules with multiple conditions? That’s where decision tables are perfect.
Consider a health insurance application that calculates premiums based on age, pre-existing conditions, and coverage level. A decision table maps all these input combinations to expected outputs in an organized format. This visual approach helps ensure you’ve covered all possible scenarios and their correct outcomes.
- State transition testing
Many applications behave differently depending on their current state. This technique helps verify those state-dependent behaviors.
Consider a document editing app. The “Save” button should be disabled when no changes exist, but enabled after modifications.
So, state transition testing would verify correct behavior as the document moves between “unchanged,” “modified,” and “saved” states. It’s particularly valuable for catching sequence-dependent bugs.
- Error guessing
This method relies on the tester’s intuition to predict where problems might hide based on common mistakes, past experiences, and known problem areas.
An experienced tester might try entering emojis into a username field or uploading a 0KB file because they’ve seen similar inputs cause problems before.
While less structured than other techniques, error guessing often finds issues that more formal methods miss.
6 Best Practices for Effectively Using Black Box Testing
While the black box testing method seems like a straightforward technique, it does require careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices that can help you improve its effectiveness and reduce the effort involved.
- Start with clear requirements
Always start by understanding the specifications and user requirements. Well-defined requirements make it easier for you to determine expected behaviors and create comprehensive test cases.
Plus, note down any ambiguities you find and get them clarified before testing begins.
- Design test cases methodically
Create test cases that cover both valid and invalid inputs to maximize defect detection. Plus, use established techniques like equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis to ensure efficient coverage. Remember that quality matters more than quantity when it comes to test cases.
- Prioritize based on risk and impact
Start your testing by focusing on high-risk features and critical user journeys. You should identify which functions would cause the most damage if they failed, and test those thoroughly before moving to less critical areas. This approach ensures you catch the most important issues even with limited time.
- Document expected results clearly
Clearly specify what accounts as a pass or fail for each test case. With vague expectations like “the system should respond appropriately, ” it can be difficult to verify test cases.
Instead, document specific expected behaviors like “system should display error message X when input Y is provided.”
- Focus on automation
Find test cases that run repeatedly and automate them to save time. While not all black box tests can be automated, regression tests and smoke tests make for excellent candidates. With automation, you can easily free up time to focus on exploratory testing and complex scenarios.
- Make tests scenario-based
Create test cases that follow complete workflows as users would experience them. For example, instead of just testing a login feature, test the entire sequence from login to completing a purchase and receiving confirmation.
This approach helps uncover integration issues and usability problems that might be missed when testing individual components.
Testsigma: Automate Black Box Testing 10x Faster
If you want to make black box testing easier and more effective, Testsigma is the perfect solution. The platform combines AI-powered test automation with a codeless approach, making testing accessible to everyone on your team without requiring programming skills.
Here are its key features that make it worth an investment:
- Natural language test creation: Write test cases in plain English without coding knowledge, and convert them into executable test cases without any effort.
- AI-powered testing agents: Let intelligent AI agents explore your application like human testers would, identifying elements and suggesting test steps automatically.
- Cross-browser and cross-device testing: With one click, run tests across multiple browsers and real devices simultaneously.
- Test data management: Create profiles for various test conditions and apply them to your tests without complex configurations or script changes.
- Continuous integration support: Make testing an integral part of your development process by connecting Testsigma to your CI/CD pipeline.
Final Thoughts
As applications grow more complex with microservices and multiple integrations, the black box testing method offers the most realistic view of the actual user experience. This approach gives teams confidence in their software without wasting time examining every line of code inside.
With AI and machine learning, black box testing has become significantly more powerful. These technologies automatically generate test cases and identify potential issues before they reach users, improving both speed and reliability without requiring technical expertise.
What’s even better, Testsigma brings these benefits directly to your team with an easy-to-use platform. Our codeless solution helps you keep up with fast development cycles while still testing thoroughly across all browsers and devices.
So, ready to make testing easier? Sign up for free today and see the difference for yourself.
FAQs
It can be both. Black box testing focuses on inputs and outputs, so tests may be done manually or automated with tools.
You can perform black-box testing to validate functionality against requirements, especially from an end-user perspective, without needing knowledge of the code.
Black box: No knowledge of internal code. Tests focus on behavior.
White box: Full knowledge of code. Tests focus on internal logic/paths.
Gray box: Partial knowledge of code. It combines both approaches.
