Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
qTest by Tricentis is a comprehensive test management platform used by teams across industries to plan, organize, execute, and analyze testing. In this blog, we’ll explore what qTest is, its features, benefits, and limitations, and how to work with it.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is qTest?
- 2 Features of qTest
- 3 Benefits of qTest
- 4 Limitations of qTest
- 5 How to Create & Manage Tests in qTest
- 6 Why are Teams Switching to AI-Based Test Management Tools?
- 7 Test Management by Testsigma: The Best AI‑Powered Alternative to qTest
- 8 AI Capabilities in Test Management by Testsigma
- 9 Features of Test Management by Testsigma
- 10 Conclusion
What is qTest?

qTest is a unified test management solution by Tricentis that supports manual, automated, and exploratory testing in a single platform. It offers complete traceability from requirements through execution to defects, integrating with tools like Jira and Jenkins. According to Devzery Latest, qTest holds a roughly 9% share in the test‑management market.
Features of qTest
qTest offers several core capabilities to support the full testing lifecycle:
Centralized Test Case and Requirement Management
qTest allows teams to organize test cases and requirements in a structured, hierarchical format. Requirements can be linked to test cases with full version control for traceability and change tracking.
Test Planning and Execution with Releases, Cycles, and Builds
Teams can define releases, builds, and test cycles to structure execution across different testing phases. This enables better tracking, environment-based execution, and alignment with sprint goals.
Automation Framework Integration
Execution results from frameworks like Selenium, TestNG, and Cucumber can be integrated via APIs or qTest Launch. Automated and manual test results are unified within the platform for streamlined reporting.
Defect Tracking
Defects can be logged directly from failed tests or specific steps and linked to test cases. Integration with tools like Jira ensures faster issue triaging and resolution.
Customizable Dashboards and Reporting
qTest offers real-time dashboards and reports with charts, heatmaps, and coverage metrics. These can be tailored by release or module to monitor progress and quality trends.
Role-Based Access and Audit Logs
Custom roles and permissions control who can create, edit, or approve test artifacts. All changes are logged for auditability, supporting compliance in regulated environments.
Import/export and Bulk Operations
Test cases and requirements can be imported or exported in bulk via Excel. Users can also clone or reuse artifacts across projects to reduce manual work.
Benefits of qTest
qTest delivers several advantages for QA teams:
Improved Collaboration and Visibility
qTest acts as a central workspace for QA, development, and product teams. All stakeholders can view the current status of test cases, execution progress, and defect details in real time. This transparency supports faster decision-making and keeps teams aligned throughout the testing lifecycle.
Flexible Methodology Support
Whether teams follow Agile, Scrum, Waterfall, or hybrid methodologies, qTest offers flexible configuration. Releases, iterations, and test cycles can be defined based on the team’s workflow, and reporting can be adjusted to reflect sprint-level or release-level metrics. This adaptability makes it easier to fit qTest into varied SDLC models.
Scalable for Enterprise Use
qTest is designed to support large-scale projects with thousands of test cases and multiple concurrent users. The platform provides strong performance, version control, and organizational features that allow it to scale effectively across teams and departments in enterprise environments.
Traceability and Compliance Readiness
By linking requirements to test cases and tracking execution results and defects, qTest ensures end-to-end traceability. Approval workflows, change logs, and audit trails support compliance with industry regulations, making qTest suitable for use in highly regulated domains such as healthcare, finance, and aviation.
Limitations of qTest
While powerful, qTest also comes with some drawbacks:
Steep Learning Curve and Complexity
qTest offers a wide array of features, but that also means it can be overwhelming for new users. Configuring projects, setting up hierarchies, and understanding all the modules may take time, especially without prior experience with enterprise-grade test management tools.
Costlier for Smaller Teams
While qTest is well-suited for enterprises, its licensing and infrastructure costs may be prohibitive for startups or small QA teams. The investment may not justify the benefits for teams that need only basic test case management.
Interface Usability Issues
Some users report that the interface is less intuitive than expected. Navigating between modules, creating test plans, or setting up integrations may involve multiple steps, which can slow down onboarding and reduce productivity for teams under tight deadlines.
Limited Customization in Reporting
Although qTest offers several default reports and dashboards, advanced customizations often require manual configuration. Users looking for deeply tailored views or combining data across multiple projects may find the reporting capabilities restrictive without additional setup.
Performance Concerns at Scale
As test case volume and execution data grow, some users experience slow performance or lag, especially during dashboard rendering or when switching between modules. Large-scale projects with complex hierarchies may require additional optimization or infrastructure support.
How to Create & Manage Tests in qTest
Teams typically follow these steps to build and run tests in qTest:
Step 1: Create a Project
Start by creating a project and defining its basic settings such as name, domain, and team members. You can import requirements or test cases from external tools or Excel sheets to speed up the setup.
Step 2: Define Requirements and Test Cases
In the Requirements module, you can create or import business requirements. These can then be linked to corresponding test cases within the Test Design module, ensuring traceability. Test cases are organized in folders and can include steps, expected results, and attachments.
Step 3: Plan Releases and Test Cycles
Use the Test Plan module to define release timelines, objectives, and associated builds. Under each release, you can create test cycles to structure execution for different environments or test phases like smoke, regression, or UAT.
Step 4: Execute Tests
Navigate to the Test Execution module to assign test cases to test cycles. From here, testers can begin execution using the TestPad, record results as passed, failed, or blocked, and link any defects discovered during execution.
Step 5: Report Defects
If a test fails, a defect can be logged directly from the test run or step level. These defects are automatically linked to the execution context and can be synced with external tools like Jira, making it easier to triage and resolve issues.
Step 6: Track Progress and Quality
Dashboards and the Insights module help track overall progress, defect trends, and test coverage. These visualizations assist managers and leads in evaluating release readiness and identifying bottlenecks early in the cycle.
Why Are Teams Switching to AI-Based Test Management Tools?
Here’s why teams are switching to AI-powered qTest alternatives:
AI tools can reduce manual test creation, increasing coverage without extra effort by converting user stories, requirement documents, and even design files into executable test cases automatically. This speeds up the test creation process and ensures broader test coverage without scaling team size.
Codeless workflows and autonomous agents reduce reliance on technical expertise allowing even non-technical users to create, manage, and execute test cases using plain language or visual interfaces. Autonomous agents can plan sprints, execute tests, and report bugs without requiring scripting knowledge.
Real-time collaborative features and intelligent dashboards help non-technical users participate by including shared dashboards, live status updates, and inline comments to keep cross-functional teams aligned. Product managers, business analysts, and support teams can actively contribute to the QA process without needing specialized tools.
Automation and AI capabilities accelerate feedback loops and defect resolution. When tests fail, AI can instantly generate detailed bug reports with logs, reproduction steps, and screenshots. These reports can be sent to issue trackers with one click, helping developers act on feedback faster.
Cloud-native AI platforms reduce setup and maintenance overhead compared to traditional automation testing tools as these tools doesn’t require manual installation, upgrades, or server maintenance. Teams can scale usage easily and stay updated with new features automatically.
Test Management by Testsigma: The Best AI‑Powered Alternative to qTest
Test Management by Testsigma is an Agentic AI-powered test management platform built for modern Agile and DevOps workflows. It allows QA teams to manage manual, automated, and exploratory tests in a single space, without needing to write or maintain scripts. Designed to reduce tool fragmentation, it brings together test planning, execution, and bug reporting in one interface.
Unlike traditional tools like qTest, which rely on external automation setups and limited AI functionality, Test Management by Testsigma introduces agentic AI to support test creation, execution, and reporting. It minimizes manual effort and makes test management accessible to non-technical users as well.
AI Capabilities in Test Management by Testsigma
- Atto, the AI coworker in Testsigma, supports everyday testing tasks like writing test cases, assigning ownership, and tracking execution. It helps testers work faster without removing human oversight.
- The Sprint Planner detects new Jira sprints, pulls in associated user stories, and generates relevant test cases, enabling testers to start validating features as soon as development begins.
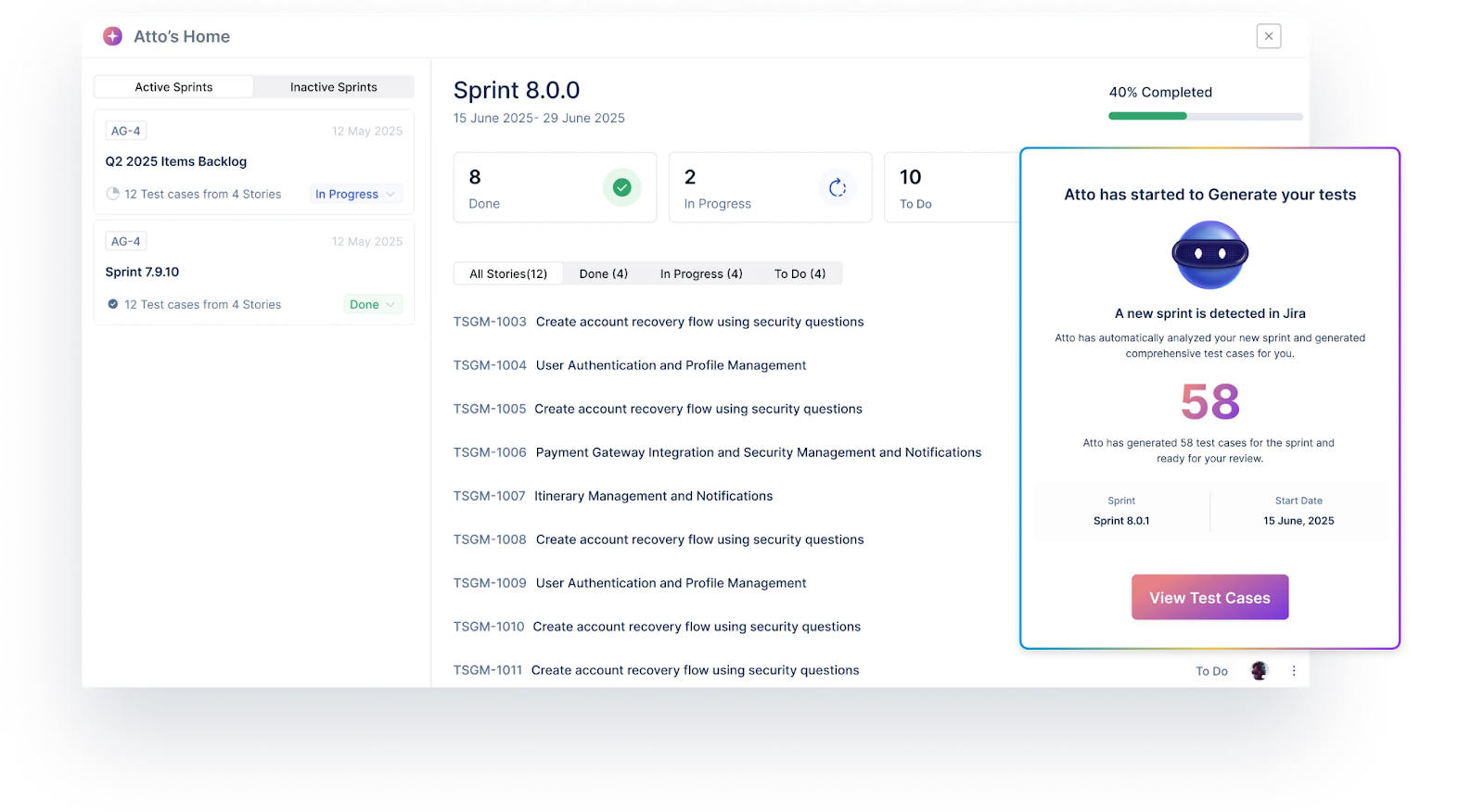
- The Generator instantly creates test cases from product inputs such as user stories, UI designs, videos, or live application walkthroughs, reducing dependency on manual documentation.
- The Runner executes tests directly in the browser, automatically logs results, and syncs execution data without any additional setup, reducing the time spent managing environments.
- The Bug Reporter creates detailed defect reports with reproduction steps, console logs, and screenshots, and allows one-click logging to issue trackers like Jira.
Features of Test Management by Testsigma
- Auto-generate test cases by pulling data from Jira sprints and user stories without needing manual entry.
- Manage all test cases, manual, automated, and exploratory, from a single unified interface.
- Use shared steps to avoid duplicating common actions across multiple test cases.
- Track changes in test cases with versioning and compare edits across different iterations.
- Assign ownership by allocating test cases, executions, or reviews to team members directly in the tool.
- Monitor execution status in real time and respond quickly to test failures or delays.
- Collaborate in real time using comments, status updates, and shared visibility across the platform.
- Supports native integration with Jira
- Log bugs in one click by capturing all necessary context during test failure and sending it to your issue tracker.
Conclusion
qTest is a robust test management tool that offers end-to-end traceability, automation integration, and structured test planning suited for enterprise-scale QA operations. While it provides strong support for Agile and hybrid methodologies, challenges like steep learning curves, high cost, and limited flexibility in customization make it less ideal for fast-moving or smaller teams. As testing grows more collaborative and AI-driven, teams are increasingly moving toward intelligent alternatives that simplify test creation and accelerate delivery. For those seeking a more scalable, user-friendly, and AI-powered approach, platforms like Test Management by Testsigma offer a compelling modern solution.