In the realm of software development, ensuring that an application performs as expected is paramount. That is where functional testing steps in. Functional testing stands as a cornerstone in this pursuit, serving as a critical step in the quality assurance process. It empowers software teams to build robust, reliable software that stands the test of time.
In this guide, we will discuss everything about functional testing. But, before we dive into the ‘how-to’ of functional testing, let’s talk about the ‘what’ and ‘why.’
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Functional Testing?
- 2 Why Functional Testing Matters
- 3 Types of Functional Testing
- 4 What is Functional Test Planning
- 5 Functional Testing Process: Step-by-Step Guide
- 6 Functional Testing Techniques
- 7 Manual vs Automated Functional Testing
- 8 Testsigma For 10X Faster Automated Functional Testing
- 9 Real-World Example: End-to-End Functional Test Case
- 10 Functional vs Non-Functional Testing: Key Differences
- 11 Best Practices for Modern Functional Testing
- 12 Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- 13 Advanced Functional Testing: Trends and Innovations
- 14 Functional Testing Metrics: What to Measure
- 15 Conclusion
- 16 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Functional Testing?
Functional testing is a type of software testing that verifies a system’s features and workflows work according to business requirements by checking inputs, outputs, and behavior. In simple terms, it answers the question: “Does the software do what it’s supposed to do?”
Its scope includes validating individual functions, integrated modules, and complete user journeys. It helps detect bugs early, supports smooth releases, and builds confidence in product quality.
Why Functional Testing Matters
Functional testing is important because it helps verify whether your application is working as intended or not. Even if an application passes non-functional tests and performs well, it has to deliver the expected results to be considered functional for end users.

(This is what happens when you plan everything well but fail to execute correctly. That’s exactly the case with functional testing, in the end, output matters)
The goal of functional testing is to ensure that a software application works as expected and meets the business requirements. Here are some of the objectives of functional testing,
Identifies Functional Defects: Aims to identify any discrepancies or defects in the software’s functionality.
Tests the Business Logic: Checks if the underlying business logic of the software is implemented correctly. It involves testing how the software handles different scenarios, inputs, and business rules.
Validate every functionality: Involves examining each function and feature of an application. It is done by providing the relevant input and confirming that the output aligns with the requirements.
Test the UI flow: Evaluates the flow of the UI to confirm that users can smoothly navigate through the application.
Types of Functional Testing
Now, let’s discuss the different functional testing types that are used to ensure the quality of software and deliver a flawless product to the end-users.
Unit Testing
Unit testing is a vital type of functional testing that involves testing the smallest functional and testable unit of code. It is typically performed by developers.
Integration Testing
Integration testing helps validate the interaction between two or more unit-tested software components.
Interface Testing
Interface testing checks the correctness of data exchange, data transfer, messages, calls, and commands between two integrated components. In simple words, interface testing focuses on testing the communication between different interfaces.
System Testing
System testing ensures that all system components are seamlessly integrated and working together as per the requirements specifications. It validates the integrated system against the predefined requirements. It is performed in an almost real-life environment and according to real-life usage.
Regression Testing
After developers make UI enhancements or code fixes, running regression testing is important to ensure that the changes haven’t impacted existing functionalities or introduced new defects.
Smoke Testing
After an application is developed, it is essential to ensure that all major functionalities work seamlessly. Smoke testing is performed for the newly released build to ensure that the application is ready for the next level of testing.
If any major functionality is not working, that particular build is rejected, sent back to developers, and retested after fixes.
Sanity Testing
Sanity testing is performed on a new build created by developers for a relatively stable application. The aim is to verify whether the application is working as expected or not.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance testing is performed by real users to ensure that the application meets their needs and expectations. It is also called beta testing and is performed by real users in a real-world environment.
What is Functional Test Planning
Functional test planning is the process of defining what to test, how to test, and when to test so QA teams can ensure all business requirements are validated before release. It covers scope, test strategy, environment setup, test data needs, resources, timelines, and risk areas.
A solid test plan helps QAs align with stakeholders, avoid coverage gaps, and execute testing efficiently with measurable outcomes.
Functional Testing Process: Step-by-step Guide
Functional testing involves testing the application’s UI, APIs, databases, and functionality. The below steps depict how testers usually perform functional testing manually or using automated functional testing tools. Though, these steps may vary from project to project. Let’s dive in.
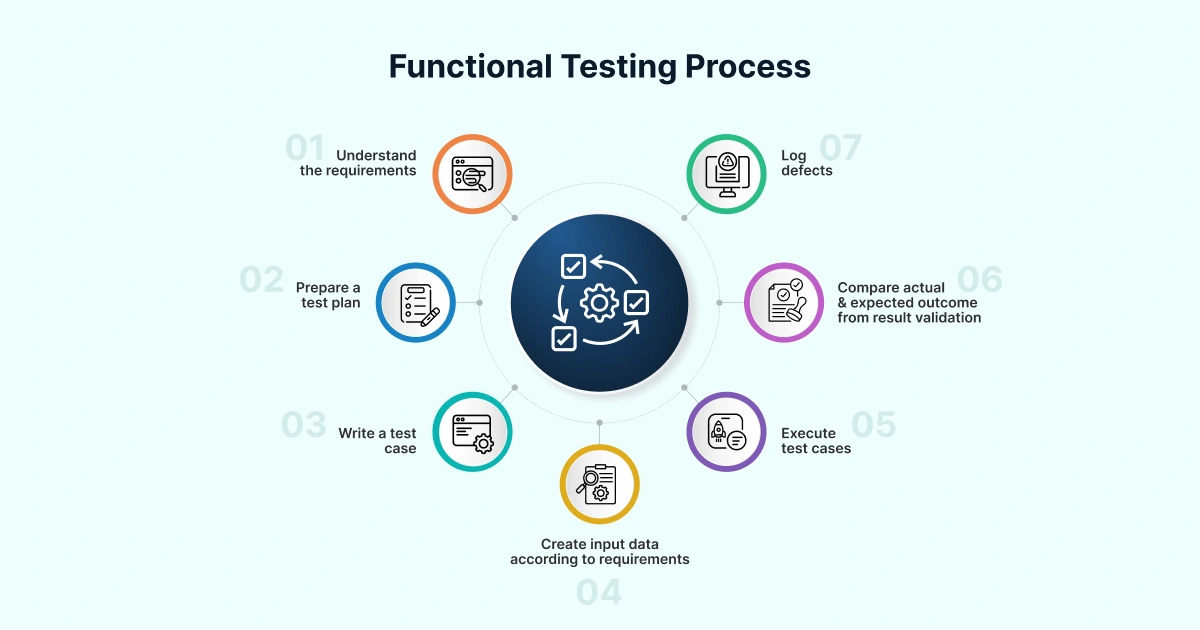
Step 1 – Requirements Analysis
Understand and analyze the functional requirements of the software.
Step 2 – Test Planning
Create a detailed test plan based on these requirements. Identify the functionalities that need to be tested. Define the testing environments and tools required. Select a perfect test automation platform that fits your development pipeline.
Step 3 – Test Case Design
Write detailed test cases that cover all the functional aspects of the software.
Step 4 – Test Environment Setup
Prepare a stable test environment that mirrors production conditions. Integrate real device clouds and CI/CD pipelines for continuous, scalable testing.
Step 5 – Test Case Development
Write detailed test cases covering valid, invalid, and boundary conditions. Use test automation platforms like Testsigma to generate test cases faster, significantly reducing test authoring time.
Step 4 – Test DATA Preparation
Create test data that will be used for testing. It should include valid and invalid input data for negative and positive testing.
Step 5 – Test Execution
Run the test cases either manually or on automated testing platforms, like Testsigma.
Step 6 – Bug Reporting and Retesting
Log the actual results, including any deviations from the expected results. Once the developers fix the reported defects, perform regression testing to avoid new bugs.
Step 7 – Test Reporting
After the entire test execution is complete, create a detailed test report outlining the test results, metrics, etc.
Functional Testing Techniques
Testing techniques are methods that help validate that a software application behaves as expected. The following are some functional testing techniques you can use to test your application,
- Equivalence Class Partitioning
- Boundary Value Analysis
- Decision-Based Testing
- State Transition Testing
- End-user tests/System tests
- Alternate Path Tests
- Ad hoc Tests
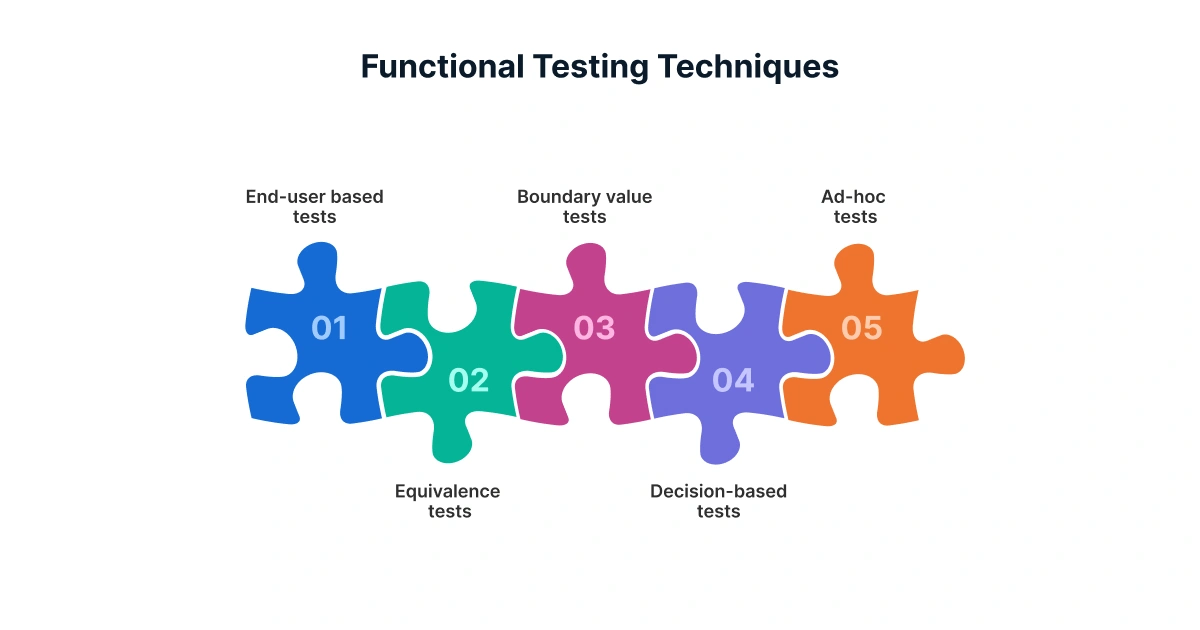
These techniques vary slightly in the way they divide test data/inputs. Let’s see how they help create test cases.
Equivalence Class Partitioning
In equivalence partitioning, the testers will divide the inputs into classes or groups of data that are expected to produce similar results. It helps reduce the number of test cases and provides a high test coverage.
For example, if an application accepts numerical inputs from 1 to 10, you might choose test cases from three classes: less than 1, between 1 and 10, and greater than 10.

Boundary Value Analysis
Boundary value analysis focuses on testing the boundary values between equivalence classes. It includes testing both the minimum and maximum values, along with values just inside those boundaries.
For example, if the application accepts passwords of lengths 8 to 14, then you would test with values like 7,8,14, or 15.

Decision-Based Testing
The decision-based testing technique involves creating test cases based on the decision points or conditions in the code.
That is, you would create test cases to cover every user condition. For example, consider the following scenario,
- If the user enters the wrong credentials to log in to the application, then the system should throw an error.
- If the user enters the correct credentials, then the application should redirect the user to the home page.
State Transition Testing
The state transition testing technique helps test systems that can be in different states and can transition from one state to another based on certain conditions. Let’s take the simplest example to understand this: an ATM. It can be in states like “idle,” “card inserted,” “PIN entered,” and so on. And the test cases would cover the transitions between these states.
End-to-end and User Journey Testing
End-to-End testing checks the entire workflow of an application from start to finish to ensure all integrated components work together. User Journey testing focuses on validating the specific paths a real user would take to achieve a goal, ensuring a smooth and correct experience.
Alternate Path Tests
In the alternate path testing technique, the testers will test all the possible scenarios or ways to use the application. They help cover the not-so-used flows or edge cases.
Ad Hoc Tests
Ad hoc tests are unplanned tests that are performed without using a specific test case or script. Testers use domain knowledge, intuition, and experience to explore the application to find hidden bugs.
Use testing techniques in various combinations, depending on the nature of the application and its requirements to ensure that software is thoroughly tested and reliable before its release.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing is about experience, product knowledge, and intuition to navigate the app in unpredictable ways. This helps uncover hidden issues by exploring like a real user would, adapting your approach as you go.
Manual Vs Automated Functional Testing
You can perform functional testing using two approaches: Manual and Automated. Let’s take a look at both of these approaches:
| Criteria | Manual Functional Testing | Automated Functional Testing |
| Test Frequency | Low or one-time tests | High frequency, like regression tests |
| Test Complexity | Highly subjective, visual, or UX-based | Stable, repetitive, and well-defined |
| Exploration Needed | High | Low |
| Test Stability | Unstable requirements or changing UI | Stable features and UI |
| Speed Requirement | Slower | Fast |
| Initial Setup Cost | Low but expensive in the long run | High initially |
| Maintenance Effort | Low upfront, but repetitive | Higher, but less repetitive work |
| Best Use Cases | Usability testing, ad-hoc checks, exploratory testing | Regression, UI, smoke tests, data-driven tests |
| ROI Potential | Low to Medium | High |
Testsigma for 10x Faster Automated Functional Testing
Testsigma is a cloud-based, codeless, agentic AI-driven test automation platform that allows testers to automate web, mobile, SAP, API, Salesforce, desktop app, and ERP testing.
At the core of Testsigma are Testsigma Copilot and Atto, an AI coworker for QA teams that mobilizes a crew of AI agents to autonomously plan, design, develop, execute, maintain, and optimize tests. It works along with QA teams in every phase of the testing lifecycle, from test creation and optimization to execution and maintenance, making testing faster, smarter, and more intuitive.
Key Features
Codeless Automation: It simplifies the test creation by allowing testers to create automated tests in plain English without requiring any coding. This makes the platform accessible for both technical and non-technical team members.
AI-Powered Capabilities: Leverage GenAI for test generation and self-healing tests. Testsigma’s AI agents detect UI changes, update tests automatically, and optimize which browsers/devices to run tests on, keeping maintenance low and reliability high.
Cross-Browser Testing: You can run your tests over 3000+ real devices, platforms, and versions on the cloud.
Unified Automation: Automate testing for web, mobile, desktop, Salesforce, SAP, and API applications in one place.
Auto-Healing Tests: Automatically fix broken locators when the UI changes, reducing maintenance overhead.
Test Management: Built-in test management using Test Management by Testsigma.
Parallel Testing: You can run parallel tests simultaneously, speeding up the testing execution.
30+ Integrations: Integrates with 30+ CI/CD tools, collaboration, product management, and bug-tracking tools for seamless automation within your development pipeline.
Zero Setup: Simply sign in, create, and run tests instantly. No coding or setup required.
Custom Test Reporting: Generates automated test reports, allowing you to track the progress and results of your tests.
24×5 Support: It provides extended support for customers via chat, phone, email, and community.
With plain English test scripts, self-healing capabilities, real-device cloud execution, and seamless CI/CD integration, QA teams can release faster, cut maintenance costs, and improve product quality, all without heavy coding or complex frameworks.
Real-World Example: End-to-end Functional Test Case
An example of an end-to-end functional test case using Uber. What do testers validate when they test the Uber app? Consider the tester has to check the user flow when a user tries to book a ride from point A to point B. To do that, the QA team will start creating test cases. Here are the sample test cases.
1. Log in to the application
2. Select the drop location
3. Then, select the pickup location or move the map pointer to the correct pickup location.
4. Select the preferred ride.
5. Uber will start looking for nearby rides. Once an Uber driver accepts your request, the app will display details like driver details, bill, pickup time, driver location, vehicle details, driver rating, etc
6. Once Uber confirms the ride details, the booking is successful.
In the below sections, we will discuss how this can be automated with the help of a test automation tool.
Functional Vs Non-Functional Testing: Key Differences
In simple terms, functional testing checks “Does the app work?” while non-functional testing checks “How well does the app work?”. Other core differences include:
| Feature | Functional Testing | Non-Functional Testing |
| Purpose | Checks if the system’s functions and features work as expected. | Validates how well the system performs |
| Focus | Validates the system in terms of business logic | How the system works in terms of performance, stability, usability, security, etc. |
| Type of Tests | Smoke, sanity, regression, integration, system | Performance, scalability, load, stress, security, compatibility |
| Techniques Used | Black box, white box, manual, automated | Mostly black box, specialized tools |
| Impact | Directly affects functionality | Affects speed, stability, and user experience |
| Examples | Login, search, add-to-cart, payments | Load testing, stress testing, security, accessibility |
| Tools | Selenium, Cypress, Testsigma, etc | JMeter, LoadRunner, etc |
| Phase | Generally performed before non-functional tests | Usually, after functional tests and before production |
| Outcome | Pass/fail based on feature implementation | Metrics such as response time, throughput, error rate, etc. |
Best Practices for Modern Functional Testing
Proven strategies and practical tips to ensure your functional tests are efficient, reliable, and future-ready:
Automate Repetitive Tests
Automate tests whenever possible to save time, costs, and effort. This speeds up the feedback and release cycles.
Choose Test Cases to Automate Wisely
Do not automate every test case. Choose test cases wisely:
- Frequently run test cases
- Repetitive tests, such as regression tests
- High-priority test cases (P1, P2) that are time-consuming.
- Tests with varying data sets or inputs.
- Cross-browser, cross-platform tests, and such
- Tests that are prone to human error.
Shift-Left and Continuous Testing
Move testing earlier in the development lifecycle to catch bugs sooner and reduce rework costs. Test continuously by integrating your tests into CI/CD pipelines for faster feedback and ongoing quality checks.
DATA-Driven Testing
Use varied datasets to validate functionality under multiple scenarios without duplicating scripts. Testsigma supports data-driven testing, so leverage AI-driven test automation for faster yet efficient testing.
Cross-Platform Testing
Run tests across different platforms, browsers, and devices to ensure a consistent user experience.
Testing on Real Devices and Browsers
Simulate actual user environments by testing on real devices and browsers, not just emulators. This helps uncover performance and UI issues that appear only in real-world conditions.
Test on 3000+ real devices and browsers in the cloud: Start Testing
Test Case Reusability and Maintenance
Design modular, reusable test cases to reduce duplication and ease updates when UI changes. Keep automation tests maintainable by following clean coding practices or use AI-powered auto-healing for easy maintenance.
Prioritizing Critical Workflows
Focus testing on the most business-critical and high-risk scenarios first. Use risk-based prioritization to balance coverage with time constraints.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Some of the typical challenges faced by testers and practical strategies to tackle them effectively:
Missed Edge Cases
Challenge: Uncovered scenarios slip through when only happy paths are tested.
Impact: Defects appear in production under rare or extreme conditions.
Solution: Use exploratory testing, boundary value analysis, and pair testing to uncover hidden paths.
Test DATA Problems
Challenge: Inconsistent, stale, or missing data causes false failures or blocked tests.
Impact: Reduces test accuracy and slows execution.
Solution: Maintain versioned, reusable test datasets and use data generation tools or mocks where possible.
Integration Debts
Challenge: Delayed or incomplete integration testing leaves critical API and service defects undetected. API functional testing ensures your APIs perform flawlessly.
Impact: Causes cascading failures when systems go live.
Solution: Test early with stubs/mocks, run continuous integration tests, and schedule regular full-stack integration runs.
Advanced Functional Testing: Trends and Innovations
How AI in software testing is driving new trends and innovations:
Gen-AI for QA
- Automates test case generation with natural language, speeding up test authoring.
- Analyzes test outcomes and learns from defects to optimize future test execution.
- Drives intelligent recommendations for test prioritization and maintenance.
Self-Healing Tests
- Detects UI changes and automatically updates scripts, reducing manual maintenance.
- Minimizes flaky test failures by intelligently mapping elements.
Cut Test Maintenance with Self-Healing Automation: Start Testing
Smart Object Recognition
- Uses AI-powered algorithms to identify and interact with dynamic UI components.
- Improves automation reliability across frequent UI changes or responsive apps.
- Reduces element locator errors, streamlining test creation and execution.
Cloud Scalability
- Runs tests simultaneously across global infrastructures, maximizing coverage.
- Supports real-time scaling resources for unpredictable test workloads.
Integrations with CI/CD and Devops
- Seamlessly triggers automated functional tests within deployment pipelines.
- Delivers instant feedback to developers, promoting rapid iteration.
- Fosters a culture of continuous testing, aligning QA with agile practices.
Functional Testing Metrics: What to Measure
Some of the key metrics to track in functional testing to ensure quality, efficiency, and continuous improvement throughout the software lifecycle:
- Test Coverage = (Number of covered requirements/Total number of requirements) x 100
- Defect Density = Defect Density = Total Defects / Size of the Software
- Test Effectiveness = (Number of valid defects fixed / (Number of defects injected + Number of defects escaped)) x 100
Conclusion
Functional testing is essential to ensure that software applications perform their intended functions correctly, delivering reliable and seamless user experiences. Automating functional testing with Testsigma accelerates this process by enabling fast, accurate, and scalable test creation and execution without complex coding. It boosts test coverage, helping teams quickly and confidently ship high-quality software.
Frequently Asked Questions
Validating business requirements, ensuring correct outputs for given inputs, verifying workflows, and focusing on end-user functionality.
Unit testing, integration testing, system testing, regression testing, smoke testing, sanity testing, and UAT.

