Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
The shift left approach is a methodology that enables organizations to test earlier in the development process. By doing so, organizations can detect and fix issues much earlier in the development process, resulting in higher-quality software at a lower cost. It’s also regarded as a culture, as it allows businesses to instill collaborative work efforts and launch products into the market faster.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Shift Left Testing?
- 2 Example of Shift Left Testing
- 3 Benefits of the Shift Left Approach
- 4 Types of Shift-Left Testing
- 5 What are Shift Left Testing Principles?
- 6 How to Implement the Shift Left Testing Approach?
- 7 Challenges of Shift-Left Testing & Their Solutions
- 8 Best Practices for Shift-Left Testing in Agile
- 9 5 Best Tools for Shift Left Testing
- 10 The Role of Real Devices in Shift Left Testing
- 11 Shift Left Testing with Testsigma
- 12 Conclusion
What is Shift Left Testing?
Shift-left testing is a proactive software testing approach that involves performing testing activities earlier in the software development lifecycle (SDLC), shifting them “left” on the project timeline.
Unlike traditional testing, which happens after development, the shift left approach starts testing from the very beginning, during the requirements gathering, design, or even planning stages. This helps identify defects, ambiguities, or performance bottlenecks early, when they are cheaper and easier to fix.
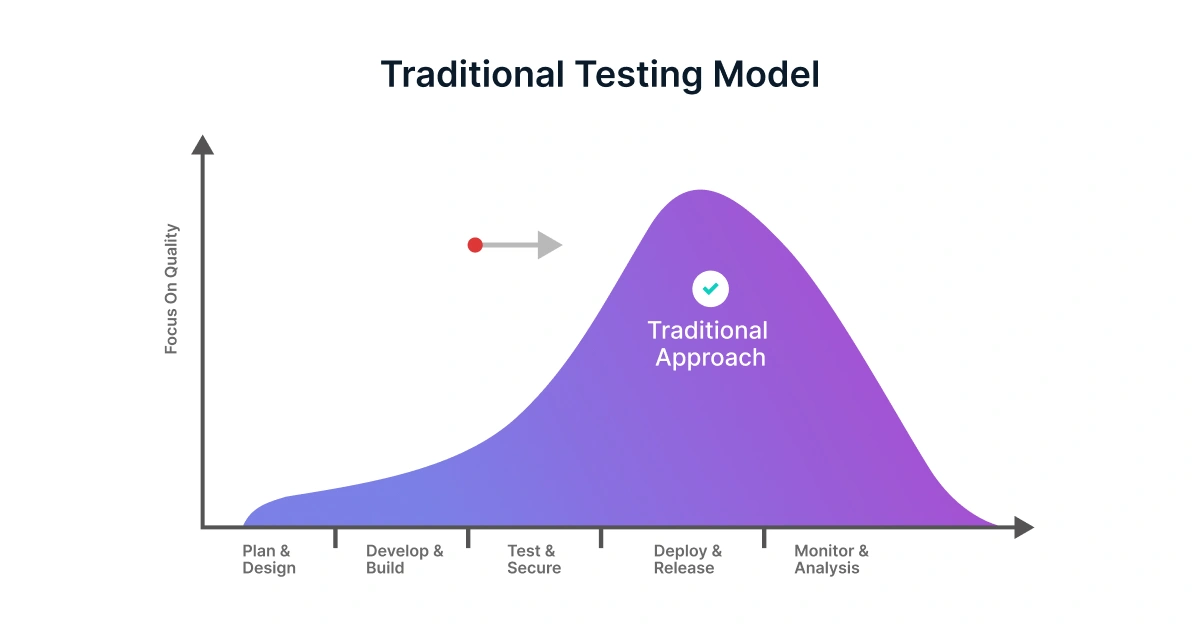
The core idea behind the shift left methodology is to integrate testing closely with development and encourage early collaboration between testers, developers, and business teams. This results in faster feedback, improved software quality, and reduced rework. By testing early and often, teams can avoid late-stage surprises, shorten release cycles, and achieve higher confidence in every deployment.
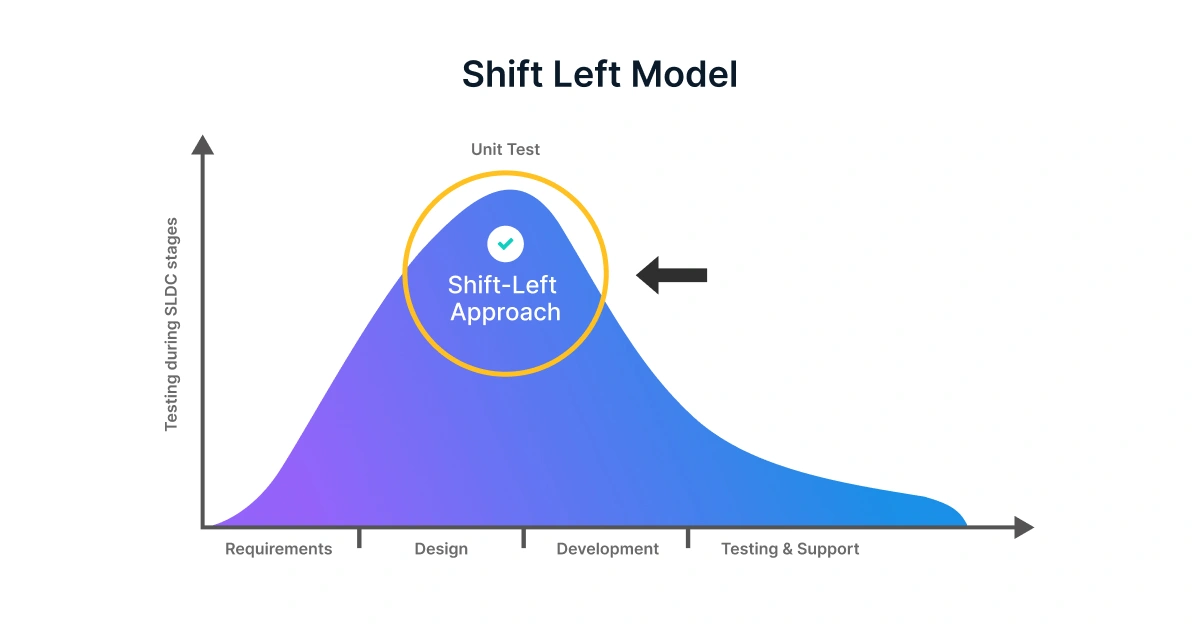
Example of Shift Left Testing
When you’re using a shift left strategy, the testers and developers will start testing at a very early stage of SDLC. That is, they will start creating test cases based on requirements gathering, do early unit testing when the initial code is written, review the design, and so on.
A glimpse of what happens in traditional testing methods vs shift left testing,
Traditional approach: No testing activities are involved until the development phase is completed,
Shift-left approach: Testers are involved right from the requirements gathering phase to understand the project in detail. Also, they will start creating test cases concurrently with the developers in the development phase.
Benefits of the Shift Left Approach
Testing early can help you avoid costly and time-consuming fixes later! With the shift left approach, you don’t have to worry about expensive rework during development. Here are some of the benefits of this method.
- Early defect detection: Shift left testing is a way of finding problems in the software development process sooner. Instead of waiting until the end to test, testers look for issues earlier on. This helps them spot and fix problems before they become too expensive or take too long.
- Faster feedback loops: Shift left testing helps detect and fix problems faster. It creates shorter and more frequent feedback loops, so any issues are spotted quickly and don’t take much time or energy to fix.
- Reduced costs: Finding problems early on saves money in fixing, checking, and making the product. Doing tests earlier also means you don’t have to spend as much money fixing things later.
- Improved collaboration: Shift left testing involves getting everyone involved early in the development process. That means developers, testers, and others interested in the project come together to work on it from the beginning. This makes it easier to spot problems and fix them before the product is finished, so you have a better result.
- Improved quality: Shift left testing can help ensure the final product is high quality. It does this by spotting and fixing problems early in the development process. This makes customers happier with what they get, with fewer mistakes and less money spent on repairs.
- Agile development support: Shift left testing is helpful for businesses that use the agile development process. It helps them spot and fix problems quickly to deliver high-quality software quickly.
Types of Shift-Left Testing

There are four types or methods of shift-left testing, as follows,
- Traditional Shift Left Testing
- Incremental Shift Left Testing
- Agile/DevOps Shift Left Testing
- Model-Based Shift Left Testing
What Are Shift Left Testing Principles?
The shift left testing principles revolve around moving testing activities earlier in the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to detect and fix defects before they escalate. This helps reduce cost, complexity, and delays typically associated with late-stage testing. These are the key principles of shift left testing:
1. Test Early and Continuously
Testing begins at the initial stages of SDLC and continues throughout. This ensures faster feedback and early detection of defects.
2. Developer Involvement in Testing
Developers play a more active role in maintaining quality. They write and run unit tests, adopt Test-Driven Development (TDD), and use automation tools for early validation.
3. Collaborative Quality Ownership
Testers, developers, and stakeholders work together from the start. Quality is not the sole responsibility of the QA team.
4. Automation across the Pipeline
Shift left methodology often includes automation tools that support early test creation, such as tools for unit testing, API testing, or automated regression testing.
5. Reduce Feedback Loops
By identifying bugs sooner, teams minimize the time spent on rework and avoid delays caused by back-and-forth between dev and test teams.
Also Read: Shift Left Vs Shift Right
How to Implement the Shift Left Testing Approach?
Implementing the shift left testing approach requires changes in mindset, process, and tooling. Here’s how to adopt the shift left methodology effectively:
1. Define Scope and Objectives
- Identify which testing activities should shift earlier in the software development lifecycle, such as unit testing, integration testing, or requirement validation.
- Align the entire team on the goals of shift left in testing, such as faster feedback, early bug detection, or reduced rework.
- Ensure clarity on how this approach contributes to project quality, timelines, and cost.
2. Use the Right Testing Tools and Practices
- Adopt tools that support early and continuous testing, including unit test frameworks, API testing tools, and codeless automation testing tools.
- Implement automated testing, continuous integration, and continuous testing to run tests with every code commit and catch issues early.
- Consider techniques like exploratory testing and risk-based testing to uncover issues that scripted tests may miss.
3. Foster Team Collaboration and Communication
- Encourage tight collaboration between developers, testers, business analysts, and product managers from day one.
- Set up regular syncs like daily standups, and use shared documentation to ensure visibility into testing progress and blockers.
- Promote a shared responsibility model where everyone contributes to software quality, not just the QA team.
4. Monitor and Optimize
- Continuously review testing practices, tooling, and communication workflows.
- Track metrics for testing, such as defect leakage, test coverage, and feedback cycle times, to measure the impact of the shift left approach.
- Iterate and refine your software testing strategy based on results and team feedback.
Challenges of Shift-Left Testing & Their Solutions
Adopting the shift-left testing approach can significantly improve software quality, but it also introduces certain challenges. Here are the most common ones, and how to overcome them:
1. Organizational Resistance and Cultural Shift
The shift-left methodology requires developers, testers, and stakeholders to work together from the start. This can disrupt traditional workflows and meet resistance from teams used to working in silos.
Solution: Promote awareness about the benefits of shift-left testing through training and leadership support. Start small with pilot projects to build trust and demonstrate value.
2. Defect Management at Early Stages
Catching bugs early is a strength of shift-left in testing, but managing these defects quickly without stalling development can be difficult.
Solution: Set up clear workflows for early defect triaging, assign responsibilities, and use tools that integrate testing with version control and CI/CD pipelines.
3. Lack of Collaboration between Teams
Poor communication between developers and QA can lead to misaligned expectations, missed defects, and slow feedback cycles.
Solution: Establish cross-functional teams, adopt agile practices like daily standups, and use collaboration tools that provide real-time visibility into testing progress.
4. Test DATA Availability for Early Testing
Creating realistic and usable test data at the beginning of the SDLC is often complex and time-consuming.
Solution: Use synthetic data generation tools or anonymized production data sets to support early-stage testing without violating data compliance rules.
Best Practices for Shift-Left Testing in Agile
- Set up regular check-ins and open communication channels to foster close collaboration between developers, testers, and stakeholders. This will align everyone on quality goals and support effective shift-left testing.
- Automate testing wherever possible to accelerate feedback loops and improve accuracy. Use tools like Selenium, Appium, or JUnit to integrate automation into early stages of development.
- Implement continuous testing to validate software at every phase of the Agile cycle. This ensures early detection of defects and supports the core principles of shift left in Agile.
- Incorporate exploratory testing throughout the development process to uncover unexpected issues that scripted tests might miss.
- Apply risk-based testing to prioritize test coverage on high-impact features or modules. This helps catch critical defects early, aligning with shift-left testing best practices.
- Monitor metrics such as defect detection rate, coverage, and execution time. Use insights to refine testing strategies and continuously improve product quality.
5 Best Tools for Shift Left Testing
| Tool | Description | Key Features |
| Testsigma | A cloud-based, AI-powered test automation platform that supports the shift-left approach by allowing test creation from the design phase itself. | Codeless testing using NLP (write tests in plain English)- In-sprint automation and parallel execution- Real-time device lab with multiple OS-browser combinations- CI/CD integrations with Jenkins, GitLab, Bamboo, etc.- Custom reports and collaborative dashboards |
| Sauce Labs | A cloud-based, test automation platform that supports shift-left testing with integrated visual testing and early-stage UI component testing. | Visual testing via Screener- In-sprint and parallel test execution- Frontend performance insights pre-deployment- Real devices, emulators, and simulators on the cloud- Advanced reporting and analytics dashboard |
| TestLeft | A SmartBear tool built specifically for shift left testing, enabling developers to automate tests directly from IDEs like Visual Studio and IntelliJ. | Test automation directly within developer IDEs- Supports BDD and CI/CD integrations- Parallel execution with full-page snapshots and logs- Rich performance analytics and report sharing |
| Ranorex Studio | A codeless automation tool ideal for both beginners and experienced testers, supporting the shift-left methodology with DevOps integrations. | Supports multiple tech stacks: .NET, Java, HTML5- In-sprint testing and parallel execution on VMs, servers, or Selenium grids- UI error detection via screenshot comparison- Remote execution via Ranorex Remote- XML-based test run reports and dashboards |
| Katalon Studio | A low-code to advanced automation solution tailored for continuous and shift-left testing with out-of-the-box test libraries and CI/CD compatibility. | Built-in templates, test cases, keywords, and repositories- Beginner-friendly with advanced scripting flexibility- Seamless Jira-BDD integration- Cloud/local execution with comprehensive analytics- Debugger for fast bug identification |
The Role of Real Devices in Shift Left Testing
- Shift left testing is most effective when conducted on real devices from the early development stages, as it ensures accurate results under real user conditions.
- Emulators and simulators often miss device-specific issues; relying on them alone can lead to incomplete defect detection and lower software quality.
- Testing on real devices, both manually and through automation, helps identify UI, performance, and compatibility issues early, improving overall test coverage.
- Setting up an in-house device lab is costly and hard to maintain; using a cloud-based real device lab like Testsigma enables anytime, anywhere testing on 3000+ devices and browser-OS combos.
- Early testing on a real device cloud speeds up bug resolution, reduces rework, and supports faster, more reliable releases with fewer post-deployment issues.
Shift Left Testing with Testsigma
Testsigma is a codeless, Agentic AI-driven test automation platform designed to support shift-left testing from the very beginning of the software development lifecycle. It allows teams to start testing alongside development without writing code and enables fast, collaborative, and scalable test execution across web, mobile, desktop, APIs, and enterprise apps.
By offering a codeless experience, real device testing, and support for modern DevOps workflows, Testsigma helps teams catch defects early, reduce rework, and accelerate releases, all key goals of the shift left approach.
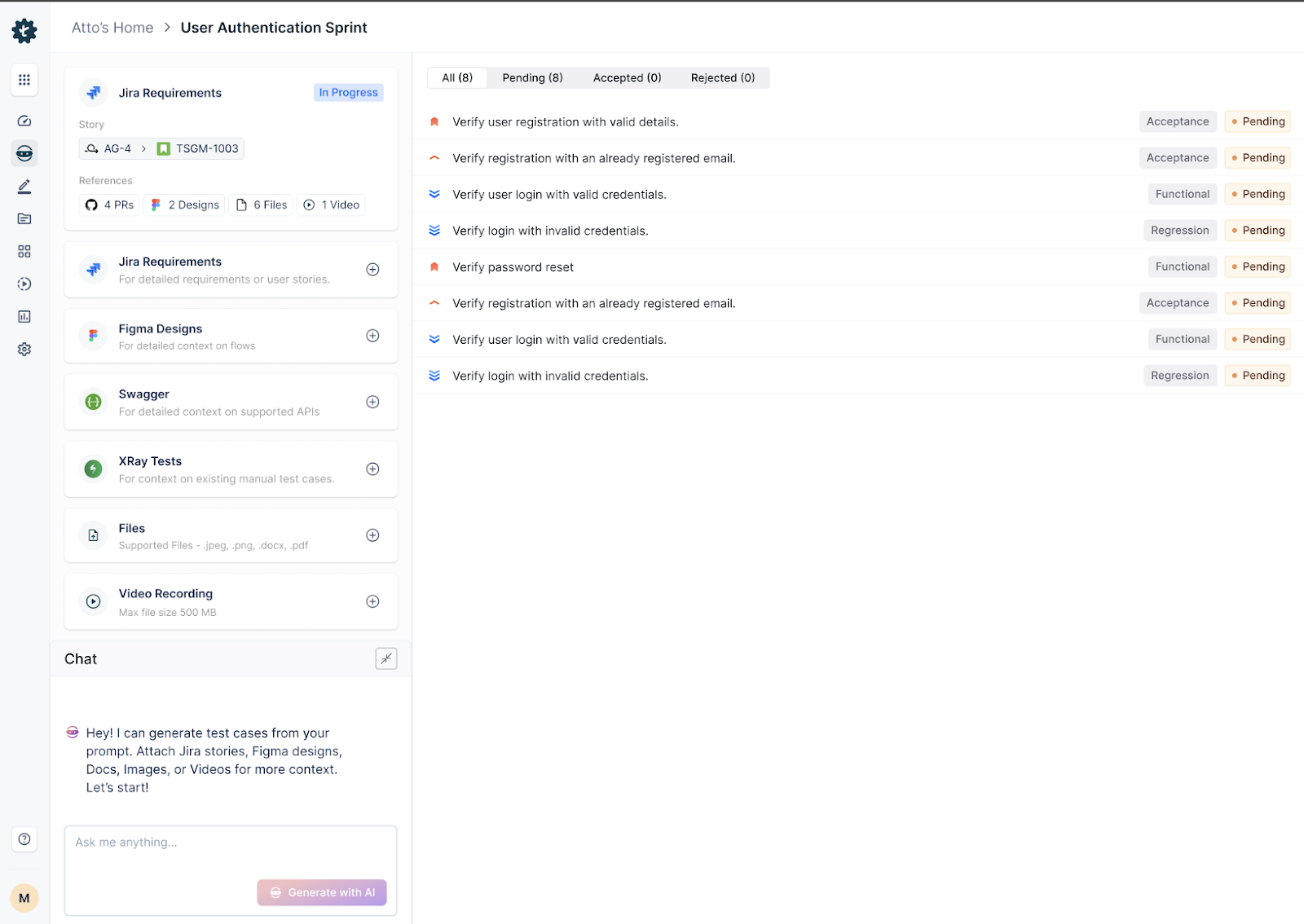
Features of Testsigma
- Codeless Test Automation: Author test cases in plain English using NLP-based scripting. No programming knowledge is needed, making it accessible for QA, product, and business teams.
- Cross-Browser and Real Device Testing: Run tests across 3000+ real mobile devices and browser-OS combinations in the cloud, ensuring accurate and reliable results under real-world conditions.
- Parallel Testing: Execute multiple tests simultaneously across environments to speed up feedback cycles and reduce test execution time. This is critical for shift-left testing in agile and CI/CD workflows.
- Unified Platform Support: Create and manage tests for APIs, mobile apps, desktop applications, and web platforms, including Salesforce and SAP. Conduct accessibility and visual testing from a single interface, enabling a consistent test strategy across the stack.
Conclusion
The days of development first and testing later are over. Today, organizations follow continuous development and continuous testing. DevOps is making it possible with CI/CD approach. But the overall idea can only thrive if automation comes into the picture.
Shift-left testing ensures that testing moves closer to development and helps introduce automation into the entire process. We discuss all the possible options and choices so you understand shift left testing and implement it to improve the software quality.



