Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Testing often feels overwhelming; apps can accept hundreds or even thousands of possible inputs, and trying to cover them all quickly becomes unmanageable.
Miss the wrong case, and a simple bug can slip into production, costing both time and money (in fact, studies show fixing a defect after release can cost up to 100x more than during development).
This is where Equivalence partitioning (also known as Equivalence class partitioning) provides a clear solution.
By dividing input data into equivalence classes, groups of values that are expected to behave the same, you only need to test one representative from each group. The technique cuts out redundant work while ensuring meaningful coverage.
Understanding and applying this method is crucial for efficient testing. In this guide, we’ll explore the importance of equivalence partitioning, its types, and a step-by-step process you can use to apply it effectively with examples.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What Is Equivalence Partitioning?
- 2 Importance Of Equivalence Partitioning In Software Testing
- 3 Types Of Equivalence Classes: Valid Vs. Invalid
- 4 Step-by-Step Process To Apply Equivalence Partitioning
- 5 Equivalence Partitioning And Boundary Value Analysis: How They Work Together
- 6 Equivalence Class Testing In Test Automation
- 7 4 Key Benefits Of Equivalence Partitioning
- 8 3 Limitations Of Equivalence Partitioning
- 9 Building Stronger QA With Equivalence Class Partitioning
- 10 Frequently asked questions
What is Equivalence Partitioning?
When writing tests, the real challenge isn’t just finding bugs; it’s figuring out which inputs actually matter. Testing every possible value isn’t realistic, but skipping too many can leave critical gaps. Equivalence Partitioning (also called Equivalence Class Partitioning) is a structured way to solve that problem.
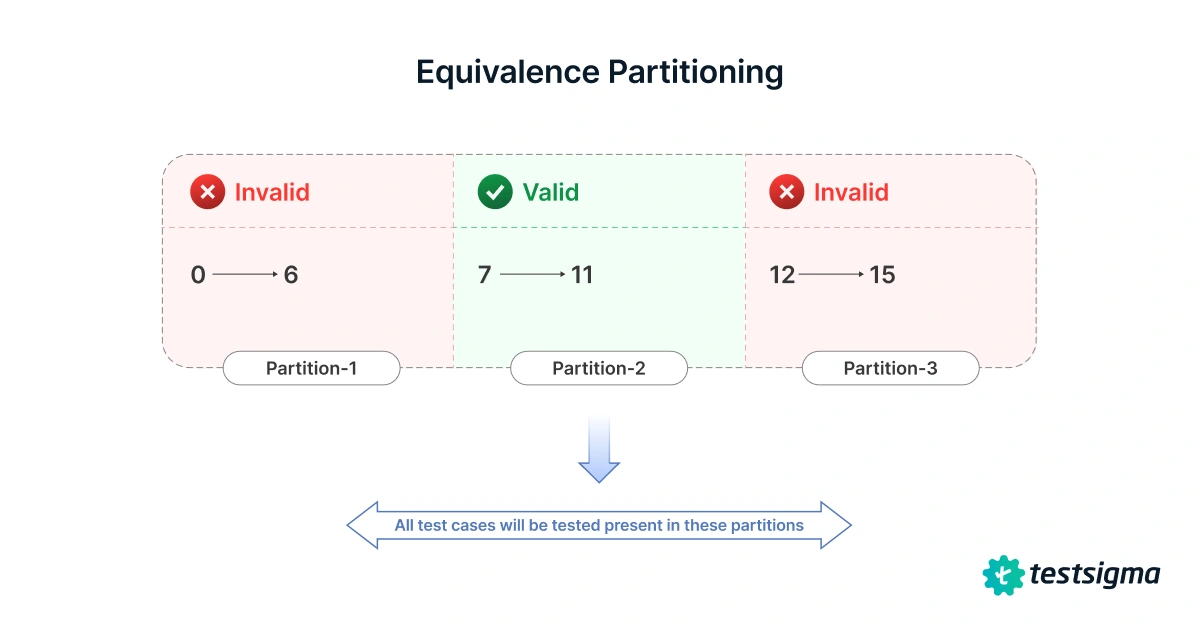
The idea is simple: instead of drowning in countless inputs, you focus on categories that matter. Each class acts like a bucket holding values that should trigger the same outcome in your program.
By selecting just one or two from each bucket, you cut down the noise while still exposing edge cases and potential bugs.
Take a case like age validation, where inputs must be between 18 and 60. Rather than checking every possible number, you can group them into classes: below 18, between 18–60, and above 60. This small shift makes testing faster, more organized, and far less repetitive, making equivalence partitioning one of the most practical techniques in software testing.
Importance of Equivalence Partitioning in Software Testing
By now, it’s clear that equivalence partitioning simplifies test design. But its value goes well beyond convenience. This approach provides concrete benefits that strengthen test coverage, efficiency, and adaptability.
Here’s how:
- Reduces test case volume: By dividing inputs into equivalence classes, testers only need a few representative values instead of hundreds of repetitive cases.
- Increases test coverage: Even with fewer test cases, partitioning ensures all major input categories are validated, minimizing the risk of missed defects.
- Boosts efficiency: Teams can achieve more with less, streamlining test design, execution, and maintenance.
- Streamlines black-box testing: Equivalence partitioning aligns perfectly with black-box testing, where understanding system behavior matters more than code structure.
- Fits agile QA challenges: In fast-moving environments, this approach makes test design quicker, leaner, and easier to adapt to changing requirements.
Used consistently, equivalence partitioning becomes a cornerstone of effective software testing, balancing speed with reliable coverage.
Types of Equivalence Classes: Valid Vs. Invalid
When applying equivalence partitioning in software testing, inputs are generally divided into two main categories. Understanding these types makes it easier to design test cases that balance coverage and efficiency.
Let’s take a look at them.
Valid Equivalence Partitions
A valid equivalence class contains input values that the system should accept as correct. Testing these ensures the software behaves as expected when given proper input.
For example, a valid date like “2024-08-15” should pass in a date field, or a strong password meeting all rules should be accepted during signup. These partitions confirm that normal, acceptable inputs are handled correctly.
Invalid Equivalence Partitions
An invalid equivalence class contains inputs that the system should reject. Testing these helps verify that proper validations and error messages are in place.
Examples include entering “2024-13-45” as a date, or using a password with only two characters when the minimum requirement is eight. These partitions are critical to prevent bad data from slipping through.
To see how valid and invalid equivalence partitions look side by side, check out the table below:
| Input field | Valid partition example | Invalid partition example |
| Date | 2024-08-15 | 2024-13-45 |
| Age | 25 (between 18–60) | 75 (above allowed range) |
| Password | Test@1234 (meets rules) | ab12 (too short) |
Step-by-step Process to Apply Equivalence Partitioning
Knowing the equivalence partitioning process turns a good idea into repeatable, scalable testing. Follow these steps to keep test coverage strong while your suite stays lean. Here are the steps you can apply to any form, API, or workflow:
1. Identify Input Fields and Conditions
List every input and its rules: ranges, formats, required/optional, business constraints, and preconditions. Note boundaries (e.g., min/max, allowed sets). This clarifies the scope and surfaces hidden assumptions early in software testing.
2. Define Equivalence Classes for Each Input
After identifying the input rules, the next move is to split values into logical groups. Think of these as buckets where every item inside should trigger the same behavior.
For instance, if a login form requires a password of at least eight characters, you can form two classes: valid passwords (≥ 8 chars, meeting rules) and invalid passwords (<8 chars or missing complexity). This step sets the stage for focused testing.
3. Select Representative (Test) Values
With your classes in place, the goal now is to pick specific examples that speak for the whole group. Instead of testing dozens of passwords, you might choose Abc123!@ for the valid class and abc1 for the invalid class.
These values become the “voices” of their partitions: small samples that still cover the full range of behavior.
4. Design and Document Test Cases
Turn those representative values into clear test cases with steps and expected outcomes. Use a simple matrix linking inputs → classes → tests. Documentation keeps black-box test design consistent across sprints.
5. Execute and Review Results
Run tests, log outcomes, and compare behavior to expectations. Adjust partitions if failures reveal new behaviors, then update the suite. Continuous refinement keeps coverage tight and maintenance low.
Equivalence Partitioning and Boundary Value Analysis: How They Work Together
Both equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis are popular black-box techniques, but they serve slightly different purposes. Think of them as two sides of the same coin.
Equivalence partitioning helps reduce the number of test cases by grouping inputs into valid and invalid classes. It’s about cutting through noise and making testing manageable.
While boundary value analysis zooms in on the edges of those classes such as minimums, maximums, and just outside the limits, because that’s where defects often show up.
For better comparison, here’s a quick table:
| Aspect | Equivalence partitioning | Boundary value analysis |
| Focus | Groups of valid/invalid inputs | Edge values of input ranges |
| Goal | Fewer representative test cases | Catch defects at boundaries |
| Example (Age 18–60) | Test 25 (valid), 10 (invalid), 75 (invalid) | Test 18, 60, 17, 61 |
| Strength | Reduces redundant cases | Finds edge-case bugs |
When combined, equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis give the best of both worlds: efficient coverage of input groups and sharp focus on boundary conditions. This mix maximizes defect detection while keeping testing costs low: a practical win for any QA team.
Want a deeper dive? Check out our detailed blog on Boundary Value Analysis vs. Equivalence Class Partitioning to see how the two techniques stack up side by side
Equivalence Class Testing in Test Automation
Equivalence class testing is effective when done manually, but it becomes far more powerful once connected to automation. Mapping equivalence classes to automated scripts helps teams cut redundancy, maintain coverage, and adapt quickly in agile environments.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Automated script generation: Tools like Testsigma allow testers to define equivalence classes (valid and invalid inputs) and generate scripts that cover only the representative values. This keeps the test suite lean while still comprehensive.
- Easy maintenance: Plugins and built-in templates let you update equivalence classes once, with linked test scripts adjusting automatically. This reduces rework when requirements evolve.
- CI/CD integration: Equivalence-based tests plug directly into pipelines such as Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI, ensuring they run on every commit or deployment for rapid feedback.
- Scalable coverage: Executing representative values from each class through automation ensures broad coverage with minimal effort, ideal for large, fast-moving projects.
When combined with automation, equivalence partitioning delivers both: smarter test design paired with consistent, pipeline-driven execution.
4 Key Benefits of Equivalence Partitioning
Equivalence partitioning brings real advantages to everyday testing work. It helps teams move faster, stay organized, and catch problems before they slip into production. Some of the biggest benefits include:
1. Faster Testing
Instead of exhaustively testing every possible input, you only run cases that represent each group. This trims down redundant checks without losing accuracy, so test cycles are faster, yet still meaningful.
2. Better Coverage
Equivalence partitioning forces you to think about all possible input categories upfront. That structure ensures you don’t overlook critical scenarios, even when the total number of test cases is smaller.
3. Catches Bugs Earlier
Mixing valid and invalid classes means edge cases get tested up front, instead of showing up later when they’re more expensive to fix.
4. Reusable Approach
Once partitions are defined, they become templates you can apply across similar features. This reusability keeps testing consistent, reduces setup time, and builds a library of logic, testers can lean on repeatedly.
Put simply, equivalence partitioning speeds things up, keeps coverage strong, and makes your tests easier to manage long term.
3 Limitations of Equivalence Partitioning
Like any technique, equivalence partitioning testing has its trade-offs. While it improves efficiency, there are situations where it may leave gaps or depend heavily on the tester’s judgment.
To apply it effectively, it helps to be aware of these limitations:
1. Possible Missed Edge Cases
Equivalence class testing groups inputs into buckets, but values sitting right at the boundaries can still behave differently. For example, if an age field allows 18–60, testing only 25 might miss defects that appear at the edges, like 18 or 60, or just outside at 17 and 61.
2. Reliance on Tester Skill
With equivalence class partitioning, the quality of results depends on how well testers define the classes. Poorly chosen partitions can lead to over-simplified tests that miss important scenarios. Skill and domain knowledge are essential for designing accurate groups.
3. Limited Use for Complex Logic
Equivalence partitioning testing works best for inputs with clear rules, like ranges or formats. For highly complex business logic or workflows with many interdependent conditions, it may not capture all variations on its own.
In these cases, it should be combined with other techniques like boundary value analysis to ensure completeness.
Building Stronger QA with Equivalence Class Partitioning
When you’ve got endless inputs to test, it’s easy to lose track of what really matters. Exactly, where equivalence class partitioning earns its place, helping you stop chasing every possible value and start testing with purpose.
By grouping inputs into meaningful classes, you can run fewer cases while still gaining confidence that your system works as expected.
Of course, no single technique solves everything. Pairing equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis gives you both the broad coverage and the sharp focus on edges where bugs like to hide. Together, they form a practical foundation for black-box testing that fits right into fast-moving projects.
If you’re looking to bring equivalence partitioning testing into your day-to-day workflow, tools like Testsigma make it straightforward. Define your partitions once, automate them, and keep pace with modern development without drowning in test cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
The main purpose of equivalence partitioning is to reduce redundant test cases while still covering all important input conditions. By dividing inputs into valid and invalid classes, testers achieve broader coverage with fewer tests.
Equivalence partitioning testing is a black-box technique. It focuses on system behavior by testing inputs and outputs, without needing to know the internal code structure. This makes it especially useful for functional testing.
Using equivalence partitioning and boundary value analysis together ensures strong coverage. Partitioning checks broad input groups, while BVA validates the exact edge values (like min/max or just outside the range) where defects often appear.
With equivalence class testing, typically one or two representative values are chosen from each partition. The exact number depends on input complexity, but the goal is lean, efficient coverage instead of exhaustive testing.
Yes, equivalence partitioning testing can be automated with modern tools. Platforms like Testsigma support defining equivalence classes and generating scripts, making it easier to maintain tests in CI/CD pipelines.



