Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
Introduction
Testing mobile apps on different devices can be tricky. Every app must run well on Android. It should also perform smoothly on iOS. However, achieving this is not always easy. This is where Appium testing can help. Appium is a free tool that lets you test mobile apps without needing to rewrite your tests for each platform. It works for native apps, mobile websites, and even hybrid apps.
The best part? It also supports many programming languages. This gives you the freedom to test in the way you like. Appium works across platforms and fits into most test setups without much trouble.
This article explains what Appium is, how it operates behind the scenes, and offers a few easy tips to improve your Appium testing skills.
Overview
What is Appium?
Appium extends Selenium WebDriver for mobile, enabling testing of native, hybrid, and web apps. It supports real devices, emulators, desktops, and even smart TV platforms.
History of Appium
Starting as “iOS Auto” in 2011, Appium grew to support Android and beyond. Appium 2.0 now enables custom drivers, plugins, and an active open-source ecosystem.
How Appium Testing Works
Appium uses a client-server model where test scripts send commands via WebDriver. These are translated into native actions on devices or emulators for realistic app interactions.
Appium Architecture
The framework includes a client, server, and end device. Commands flow from scripts → Appium server → platform drivers → device, with results returned to the client.
Best Practices
Keep test names simple, code modular, and reduce flaky tests with waits. Use CI/CD integration, parallel execution, and detailed reporting to ensure reliability and speed.
Limitations of Appium
Appium has slower execution, tricky parallelization, and complex setup. It also lacks strong support for gestures, image comparison, and some hybrid app testing.
Why Choose Testsigma Over Appium
Testsigma offers no-code, AI-driven automation with plain English test creation, 3000+ real devices, auto-healing, parallel execution, and deep DevOps integration, making testing more accessible.
What is Appium?
Appium is an open-source mobile testing framework. It lets QAs automate testing on platforms like Android, iOS, and Windows. It is made especially for testing mobile apps. Appium uses the WebDriver protocol, which is popular for web testing. It extends this to work with mobile apps.
Appium provides APIs and a server. This connects your test scripts with mobile devices or emulators. If you develop apps for iOS or test on browsers like Chrome, Appium supports that. Its reach goes beyond mobile. It also works on desktops like macOS and Windows. It supports TV platforms too, such as Roku, tvOS, Android TV, and Samsung.
Appium capabilities:
- Appium supports many programming languages. This gives you the freedom to write tests in the language you like.
- With Appium, you can test:
- Native mobile apps installed on devices, built using Android, iOS, or Windows SDKs.
- Mobile web apps accessed through browsers like Chrome and Safari. You can also test apps in Android and iOS in in-app browsers.
- Hybrid apps, which have a wrapper around a “webview.” This lets you interact with web content inside a native app. You can test these on real devices or through browser URLs.
- Appium uses native automation APIs. For Android, it uses UI Automator or Espresso. To test iOS Appium, it uses XCUITest. This helps it interact with apps like a real user—tapping, typing, scrolling.
- It does not need any changes in your app code. No extra libraries are required for Appium testing. This makes Appium non-intrusive and easy to use with your existing app.
- It works across platforms. You can run Appium mobile testing on real devices. You can also use emulators for Appium UI testing. This makes Appium a popular and flexible choice for testing mobile apps.
History of Appium
Appium is a strong automation framework. It makes UI testing easier across many app platforms. It started in 2011 as “iOS Auto,” a tool just for iOS testing. Later, it grew to include Android as well. Dan Cuellar, inspired by Selenium WebDriver, introduced “Appium” in 2012. It brought WebDriver ideas to mobile app testing that support popular programming languages.
At first, Appium focused on iOS automation. It used the WebDriver protocol and Apple’s UI Automation library. Soon, it added support for Android. In 2013, the project got a big funding boost. This helped rewrite Appium fully in Node.js. Jonathan Lipps led this rewrite. The new version had many added features.
Appium 2.0 aims to build a flexible automation ecosystem. It helps adapt to fast changes in app development. The 2023 release lets developers create Appium drivers for new platforms. It encourages teamwork through third-party plugins. The Appium CLI tool makes it easy to install these drivers and plugins. Today, Appium is a lively open-source project. It keeps evolving to meet software testing needs. It has become a trusted choice for UI automation.
How Does Appium Testing Work?
Appium testing automates checking if a mobile app works well. It tests apps on different devices and platforms. It controls the app from outside, as a real user does. You don’t need to change the app. This is why Appium is a popular mobile automation framework.
Here is how it works:
How to Install and Configure Appium?
Installing and setting up Appium takes a few steps. These depend on the platform you want to test.
- Install Node.js and npm first. Appium server runs on Node.js.
- Install the Appium Server. You can do this using npm or by downloading Appium Desktop.
Run this command to install via npm:
npm install -g appium - Set up the platform SDKs. For Android, install Android SDK. For iOS, install Xcode and its command line tools.
- Install the Appium client libraries for your programming language. For Python, use:
pip install Appium-Python-Client - Configure environment variables like ANDROID_HOME. This helps Appium find SDKs.
How to Get Started with Appium
Begin by installing the required tools. Make sure all prerequisites are ready.
Prerequisites for Appium Testing on Android
- Appium jar files for Java
- Latest Appium client library
- Appium server
- Java installed on your system
- TestNG
Don’t forget to set Java environment variables. Enable Developer Mode on your test device to allow debugging.
Steps for Appium Testing
Step 1: Writing Test Scripts for Appium UI Testing
You start by writing test scripts that tell the mobile app what to do. You can write these test scripts in many languages, like Java. This flexibility is one of Appium test automation’s strengths. Your scripts tell the app what to do. They include actions like opening the app, tapping buttons, and checking if things show up.
Step 2: Starting the Appium Server
Appium uses a client-server system. The client is where you write tests. The server is where commands run on the device. This setup manages communication between your test scripts and the mobile device. This is key for mobile test automation with Appium.
Before you run tests, start the Appium server. The server acts as a bridge between your scripts and the device.
Here’s how it works:
- Your test scripts stay on the client side. You write them in the language you like.
- When you run tests, the scripts send commands to the server. These commands say things like “tap this” or “enter that.”
- The server listens and turns these commands into actions the device can perform.
This setup makes Appium flexible. You can write tests in different languages and run them on many devices without changing your setup. This is why Appium handles complex tests well.
Step 3: Test Execution on Devices or Emulators
You can run tests on two types of devices:
- Real devices: These are actual phones or tablets. Testing here shows real results. You can find device-specific issues like bugs or performance problems.
- Emulators or simulators: These run on your computer and mimic real devices. They are quick to set up and good for early testing. However, they don’t always match real-world use exactly.
Appium communicates with these devices using native frameworks. This lets your tests run anywhere. You can run tests on your computer or in the cloud.
Step 4: Using Native Frameworks to Interact
Once Appium connects to a device or emulator, it needs a way to work with the app. Instead of controlling the app directly, Appium uses native automation frameworks built into mobile platforms. Android and iOS created these frameworks to help automate UI testing reliably. This is a key part of Appium testing and one of the best mobile testing tools Appium offers.
On Android, Appium uses UI Automator or Espresso. This is part of Appium Android testing.
On iOS, Appium uses XCUITest.
These frameworks understand the app’s UI elements. They can tap buttons, type text, scroll lists, or swipe screens. This makes Appium testing more accurate and realistic.
Example to Understand This Better:
Imagine testing a mobile banking app where the user needs to:
- Open the app
- Tap the “Login” button
- Enter username and password
- Swipe to check recent transactions
Here’s how Appium uses native frameworks to do this:
- Your test script tells Appium to “tap the Login button.”
- The Appium server sends this command to the device’s native framework—UI Automator on Android or XCUITest on iOS.
- The native framework finds the “Login” button by its label or ID.
- It taps the button just like a real user would.
- When the script tells Appium to enter text, the native framework focuses on the username and password fields. It then types on the keyboard.
- When the script commands a swipe, the native framework swipes on the screen to scroll through transactions.
Because Appium uses these trusted native tools, your tests act like real users. This gives you more reliable and realistic Appium testing results. This is why Appium’s automated mobile testing is trusted by many.
Step 5: Executing Test Commands via WebDriver Protocol
Your test scripts communicate with the Appium server using the WebDriver protocol. This sends commands like “click this” or “check this text.” The Appium server passes these commands to the native frameworks on the device. The frameworks then run the commands on the app. This is a core part of Appium testing.
Step 6: Receiving Feedback and Validating Results
After each command runs, the device sends feedback back through the Appium server to your test scripts. For example, if a button is tapped or some text is visible, the framework confirms it.
Your tests use this feedback to check if the app is working or has bugs. This step is important for effective Appium testing.
Step 7: Running Tests Across Platforms with Mobile Test Automation with Appium
Appium supports both Android and iOS. You can often use the same test scripts for both platforms with small changes. This saves time and effort. It makes mobile test automation with Appium more efficient and easier to scale.
Step 8: Integrating Appium with Other Mobile Testing Tools Appium Offers
Appium works well with other tools for reporting, continuous integration, or test management.
This helps teams build full automated testing pipelines. It improves the overall quality of the mobile app.
Architectural Framework of Appium Testing
Appium’s architecture uses a client/server model. The server runs on Node.js. It has a REST API and uses Selenium WebDriver. The framework connects your test script to a mobile app running on a real device, an emulator, or a simulator.
The Appium Server takes commands from the test script via the REST API. It uses WebDriver to turn these commands into automation actions for the mobile platform.
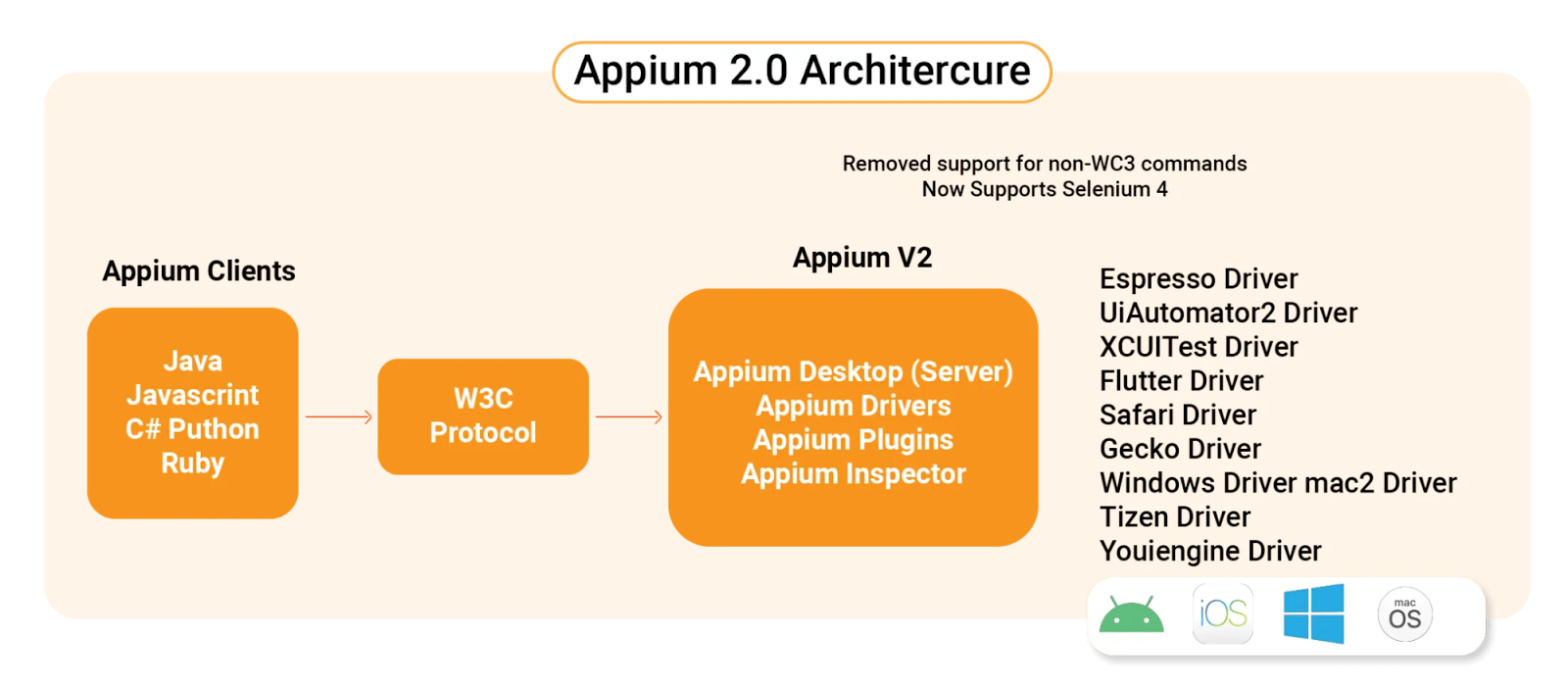
There are three main parts: Appium Client, Appium Server, and End Device.
Appium 2.0 Architecture
Appium Client:
The client includes language-specific libraries or SDKs. These let developers write test scripts for mobile apps using Appium. The client libraries work with many programming languages. They help find elements, interact with UI parts, perform gestures, and check expected behavior. Testers can also set desired capabilities to configure the test environment.
Appium Server:
The server is a key middleman. It connects the test script and the mobile app. The app may run on a real device or emulator/simulator. The server gets commands from the test script via REST API. It changes these commands into platform-specific automation steps. Using Selenium WebDriver, the server talks to the app. It can identify elements, interact with the UI, simulate gestures, and check behaviors. The server gives a unified way to test across platforms. Test scripts can be in different languages and still run on many devices.
End Device:
The end device is an emulator, simulator, or real device connected to the server. Tests run on this device. It is where the app’s functionality and performance are checked. These parts form the base of Appium’s architecture. They help run efficient and reliable mobile testing on many platforms and devices.
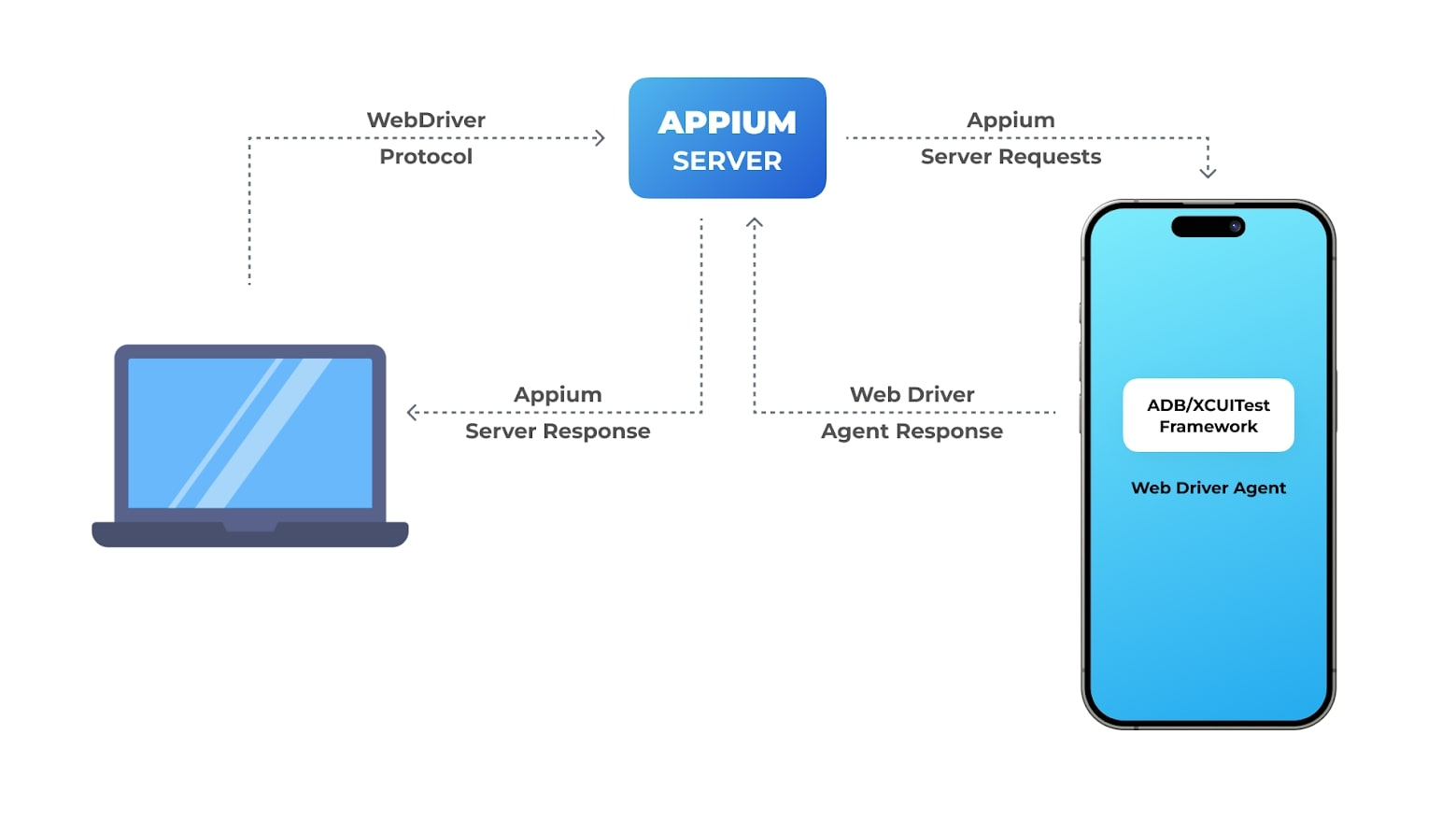
Communication Flow
Here’s how communication works in Appium’s architecture:
- The test script sends a command to the Appium server using the WebDriver protocol.
- The server translates the command into platform-specific actions.
- The server sends these actions to the right device driver (ADB for Android or XCUITest/UIAutomation for iOS).
- The device driver tells the mobile device or emulator/simulator to perform the actions.
- The device driver sends the result back to the Appium server.
- The server changes the result into a WebDriver response and sends it back to the test script.
Best Practices for Appium Testing
Appium is a great tool for mobile test automation. But for good results, you need to follow some smart Appium testing practices. These make your tests reliable, easy to manage, and faster to run. Here are some that you can follow:
- Use simple and consistent names for your tests. It helps others read and understand them.
- Try to keep your code modular. This makes it easy to reuse and update.
- You can add comments to explain the steps for Appium testing. It helps others follow the logic.
- Some Appium tests pass sometimes and fail other times and these are flaky tests. You can reduce flakiness with waits. For this, you have to use WebDriverWait or custom wait methods. This helps avoid timing issues.
- Running tests in parallel can save execution time. However, you have to make sure the tests do not depend on each other. So, you should keep each test separate to avoid failures.
- Good logs and reports are important in your test framework. They help you understand what happened during the test. You can use screenshots, logs, and reports to find issues quickly.
- Add your Appium tests to your CI/CD setup. This gives quick feedback when code changes. Use tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Travis CI to do this.
Limitations of Appium Testing
Some of the common limitations of Appium testing are:
- Appium cannot test Android versions below 4.2.
- It has limited support for hybrid mobile apps.
- Test execution using Appium is slower than other tools.
- Running tests in parallel on multiple devices is not easy with Appium.
- Appium setup requires many dependencies and configurations.
- It does not have built-in support for image comparison.
- Appium has limited support for gestures like double-tap and pinch.
- Debugging test failures in Appium can be difficult.
- Tests may fail due to unstable network or device connection issues.
- Automation support for some mobile browsers is limited in Appium.
Why Choose Testsigma over Appium for Mobile Testing
Testsigma is a no-code AI-driven test automation platform that supports testing native, hybrid, and cross-platform mobile apps for Android and iOS. It lets you create, run, and manage tests using plain English powered by Agentic AI. It also supports testing web, API, SAP, Salesforce, and desktop apps. Testsigma also offers a cloud-based device lab with thousands of real devices. It has AI features that help speed up test automation. You don’t need coding skills to use it.
Here is why Testsigma is different from Appium for mobile testing:
- No Coding Needed
Testsigma lets you write tests in natural language. This makes it easy for non technical team members to help. Appium needs coding knowledge in languages like Java or Python.
- Easy for Everyone
Testers, business analysts, and QA people can all create and update tests in Testsigma. This removes delays caused by waiting for developers.
- All-in-One Tool
Testsigma supports mobile, API, Salesforce, SAP, web, and desktop testing in one platform. Appium mainly focuses on mobile testing.
- Access to 3000+ Real Devices
Testsigma’s cloud lab gives instant access to many real Android and iOS devices. You don’t have to manage physical devices or complex setups like in Appium.
- AI-Powered Auto-Healing
Testsigma finds and fixes broken app elements automatically when the UI changes. This cuts down flaky tests and saves maintenance time. In Appium, you have to fix these manually.
- Easy Data-Driven Testing
You can run tests with many data sets easily in Testsigma. Appium users must set this up themselves with code.
- Smart Test Case Generation
Testsigma’s AI Agents powered by Atto and Copilot allows users to create test cases from Jira stories, Figma designs, videos, PDF, images, etc. This saves time and improves test coverage.
- Works Well with DevOps
It integrates smoothly with tools like Jira and Azure DevOps. This supports continuous testing and faster releases.
- Runs Tests in Parallel
You can run hundreds of tests at the same time on many devices and browsers in the cloud. This speeds up feedback and test coverage.
When you compare Appium vs Detox and LambdaTest vs Appium, Testsigma stands out among Appium alternatives. It offers a no-code and all in one solution. This makes mobile test automation easier. It is also more accessible for teams that don’t have deep coding skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Appium has a flexible architecture. It supports automated testing on many platforms and device types. This makes it a popular choice for mobile test automation. To get the best results, follow good practices. Write clear and maintainable test scripts. Use reliable locators to find elements. Manage your device settings well. Doing this helps you get the most from Appium. It also keeps your tests stable and efficient. Knowing how Appium works and using its strengths helps teams. It lets them deliver better mobile apps faster. It also builds more confidence in the app’s quality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Appium is popular because it works on both Android and iOS. You can test native, hybrid, and mobile web apps. It does not need changes in the app code.
Appium supports many languages. These include Java, Python, JavaScript, Ruby, C#, and PHP.
Appium is for mobile app testing. Selenium is for automating web browsers.
Appium Inspector helps you see the app’s UI elements. It makes creating and fixing tests easier.



