APIs are the digital connectors of today’s software ecosystem. Whether using a food delivery app, making a payment, or simply browsing a website, APIs are behind the scenes, handling data requests, user authentication, and seamless app integration. That’s why API testing has become a crucial part of the QA lifecycle.
This guide’ll explain API testing, its definition, key testing methods, real-world examples, common pitfalls, and why tools like Testsigma make it easier than ever.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What Is API Testing?
- 3 Why Is API Testing Important?
- 4 What Are The Different Types Of API Testing?
- 5 What Are API Testing Methods?
- 6 What Is An Example Of API Testing?
- 7 What Are Some Common Bugs Found In API Testing?
- 8 How To Perform API Testing?
- 9 What Are The Benefits Of API Testing?
- 10 What Are Some API Testing Best Practices?
- 11 What Is The Relationship Between API Testing And API Monitoring?
- 12 What Is The Future Of API Testing?
- 13 Why Use Testsigma For API Testing?
- 14 Frequently Asked Questions
Overview
What Is API Testing?
API testing ensures that an API works according to specifications, ensuring smooth communication among various software systems.
Types of API Testing
- Functional Testing: Verifying that API is providing appropriate responses for specific requests.
- Performance Evaluation: Analyses an API’s capacity to handle high traffic volumes and large data sets.
- Security Testing: Testing an API’s protection from unintended access is crucial to its viability.
- Testing API Documentation: Testing to make sure the API reflects what’s described in its documentation.
- Regression Testing: Regression testing ensures that changes do not create new errors.
- Fault Tolerance Testing: Assesses how well an API handles unexpected failures or issues.
What is API Testing?
API testing is a type of software testing that validates whether an Application Programming Interface (API) behaves as expected. Instead of focusing on how a user interacts with the UI, API testing focuses on how different software systems communicate through requests and responses.
APIs are messengers between components, transmitting data, commands, and services. Ensuring their reliability, speed, and security is critical, especially in microservices, cloud-based, and mobile applications.
Why is API Testing Important?
APIs are the backbone of modern software applications. Here’s why testing them matters:
- Catch bugs early: Validate data integrity and system logic before UI development begins.
- Ensure reliability: Prevent failures in integration points between services.
- Improve security: Detect vulnerabilities like broken authentication or data leaks.
- Boost performance: Identify bottlenecks that impact speed and scalability.
- Accelerate development: Automate testing in CI/CD pipelines for faster releases.
What Are the Different Types of API Testing?
When it comes to this testing, the main focus is on verifying the API’s functionality and performance. Basic assertions start by validating the response body, schema, and response codes.
However, other tests, such as security and performance testing of APIs, need to be performed.
Contract Testing
- Verifies that the API adheres to its defined contract or specification like OpenAPI/Swagger.
- Ensures that data formats, required fields, and response structures match what consumers expect.
- Detects breaking changes early when APIs evolve.
Unit Testing
- Focuses on testing individual endpoints or functions in isolation.
- Ensures that each endpoint returns the correct response for given inputs, catching issues at a granular level.
End-to-end Testing
- Simulates real user workflows involving multiple APIs and external systems.
- Validates that business processes function correctly from start to finish, ensuring overall system integrity.
Load Testing
- Measures API speed, scalability, and stability under expected and peak workloads.
- Identifies bottlenecks by simulating large numbers of requests or users.
Security Testing
- Ensures that the API is protected against unauthorized access and threats.
- Detects vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), improper authentication/authorization, data leakage, use of default credentials, and insecure data transfers.
- Includes testing for encrypted data, password policies, network security, and more.
Integration Testing
- Examines how different modules or services interact via APIs.
- Validates data flow and correct functioning of multiple components working together.
Functional Testing
- Tests specific functions or use cases of the API, such as submitting a form or retrieving data.
- Checks for expected outputs, correct data manipulations, and proper handling of errors for various inputs.
What Are API Testing Methods?
APIs primarily use the HTTP protocol for communication. The four core HTTP methods are:
- GET – Retrieves data from the server.
- Example: Fetching user profile data from a social media platform.
- POST – Submits new data to the server.
- Example: Registering a user or submitting a support ticket.
- PUT – Updates or creates a resource.
- Example: Editing product details in an inventory system.
- DELETE – Deletes a resource.
- Example: Removing a user’s account or deleting old records.
What is an Example of API Testing?
Imagine you’re logging into a mobile app like your favorite shopping or banking app. The moment you enter your username and password and hit “Login,” an API call is triggered in the background to check your credentials.
Here’s where API testing comes in. An API test in this case would verify whether:
- The app successfully logs you in when you enter the correct details
- It shows an appropriate error when you enter the wrong password
- It protects your data from suspicious or malicious login attempts like a hacker trying to break in.
In this example, testers don’t look at how the screen behaves, they check whether the communication between the app and the server is working correctly.
They test:
- Did the server respond with the right message?
- Was the response fast enough?
- Was your login info handled securely?
- Did it behave the same way when the same request was sent twice?
API testing ensures that this “behind-the-scenes” interaction is reliable, secure, and consistent without needing to rely on the app’s interface.
So while the user sees a simple “Welcome back!” message, a lot of complex testing has already happened to make that moment seamless. That’s the power and purpose of API testing.
Manual Ways to Test APIs
When manually testing APIs, you directly interact with the API endpoints to verify their behavior. This typically involves:
- Sending Requests with Different Inputs – Manually construct API requests using various combinations of parameters, headers, and body data to see how the API responds under different conditions.
- Validating Status Codes – Check whether the API returns the correct HTTP status codes (like 200 for success, 400 for bad requests, 401 for unauthorized access, etc.) based on your request.
- Reviewing the Response Body – Carefully inspect the returned data to ensure it matches what’s expected in structure, fields, values, and format.
What Are Some Common Bugs Found in API Testing?
- Incorrect HTTP status codes – Returning a 200 OK or 201 Created status for error scenarios (e.g., authentication failed or resource not found) instead of using proper codes like 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized, or 404 Not Found. Using the wrong status code can confuse clients and obscure actual problems.
- Broken authentication or authorization – Endpoints allow access without proper credentials or do not enforce expected user roles. Sensitive operations can be performed without authentication, or users can access another user’s data.
- Response structure/schema mismatches – The returned response does not match the API’s contract or documentation. Missing required fields, extra/unexpected fields, or incorrect nesting of objects.
- Null or incorrect field values – Fields in the response are null when data is expected, or contain incorrect values due to backend bugs or data mapping issues.
- Inconsistent data formats – Some endpoints return JSON, while others return XML or plain text inconsistently. Fields like dates, numbers, or booleans are formatted differently across responses.
- Timeout or performance bottlenecks – API calls are slow or time out under normal or expected load, making the service unreliable. Inefficient queries or code cause the API to slow down as data or user load increases.
How to Perform API Testing?
API testing follows a structured process to validate that APIs function as intended, ensuring correct responses, security, and performance under varying conditions. Here’s how to perform it effectively:
1. Understand API Requirements and Specifications
Before testing, carefully study the API documentation. Identify:
- Endpoints and their purposes (e.g., /login, /users)
- Request methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
- Required parameters, headers, and authentication
- Expected responses and error codes
Tools like Swagger or Postman collections make this exploration easier by providing interactive documentation.
2. Set up the Testing Environment
Prepare a controlled testing setup:
- Define the base URL (e.g., staging or QA environment)
- Configure authentication tokens (API key, OAuth, JWT)
- Set up the necessary test data and variables for the request bodies
- Ensure dependencies like databases or mock services are accessible
3. Design Comprehensive Test Scenarios
Create test scenarios that cover all aspects of API behavior:
- Positive Tests: Verify valid inputs return correct responses.
- Negative Tests: Use invalid or missing data to ensure proper error handling.
- Boundary Tests: Check edge conditions like large payloads or extreme parameter values.
- Security Tests: Validate authentication, authorization, and encryption.
- Performance Tests: Assess how the API performs under load or concurrent requests.
4. Write and Execute Test Cases
Use tools to send requests and validate responses:
- Manual Testing: With tools like Postman or cURL, send requests and analyze responses.
- Automated Testing: With platforms like Testsigma, you can create and run no-code API tests quickly.
- Define request type, headers, body, and assertions.
- Validate status codes, response body, and response time.
- Schedule and execute tests across environments.
5. Validate Responses and Results
After execution, verify:
- HTTP Status Codes: Ensure correct responses (e.g., 200 OK, 400 Bad Request, 401 Unauthorized).
- Response Body: Check structure, schema, and field values.
- Headers: Validate content type, caching, or authentication-related headers.
- Response Time: Ensure performance is within acceptable thresholds.
6. Automate and Integrate with CI/CD
To maintain efficiency and scalability:
- Integrate API tests into CI/CD pipelines (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions).
- Automate test runs after every code push or deployment.
- Generate reports and logs for continuous feedback to developers.
- Use AI-powered tools like Testsigma for self-healing tests and reduced maintenance.
7. Monitor and Maintain Test Suites
APIs evolve, new endpoints are added, parameters change, and old ones are deprecated. Maintain your test suites by:
- Updating test cases alongside API changes.
- Revalidating API documentation.
- Reviewing failures to identify regressions or performance drops.
- Using API monitoring tools to track production performance continuously.
What Are the Benefits of API Testing?
- Faster Feedback Loop in Development – API tests run faster than UI tests, enabling teams to spot issues early, often within seconds after a code commit.
- Better Test Coverage for Business Logic – API tests directly target the application’s core logic and data processing, allowing comprehensive verification of complex rules, workflows, and data transformations.
- Reduced UI Dependency for Test Execution – API tests don’t rely on the application’s interface, allowing testing to start even before the front end is built or finalized.
- Reusability and Easy Automation – API test scripts and setups can often be reused across different environments and projects.
- Easier Debugging and Maintenance – Since APIs expose precise endpoints, issues are easier to pinpoint no need to sift through layers of GUI or user flows.
What Are Some API Testing Best Practices?
- Understand API Requirements and Specifications – Thoroughly review API documentation and clarify the expected inputs, outputs, authentication, and error handling before designing test cases.
- Automate Your API Tests – Automate regression and critical-path tests using reliable tools to ensure scalability, repeatability, and more frequent execution, especially as part of CI/CD pipelines.
- Use the Right API Testing Tools – Select tools matching your tech stack and project needs (e.g., Postman, REST-assured, SoapUI, JMeter) for functional, security, and load testing.
- Create Comprehensive and Structured Test Cases – Include positive, negative, boundary, and edge-case scenarios. Structure tests by categories, e.g., authentication, data processing, third-party integration to simplify maintenance.
- Validate Both Functional and Non-Functional Aspects – Check response codes, payload formats, schema validity, and data correctness. Test performance by simulating concurrent users and validating response times under load.
- Test Across Multiple Environments – Run tests in environments mirroring production such as dev, staging, and prod to catch environment-specific issues early.
- Use Realistic Test Data – Employ valid, varied, and production-like data to detect unexpected behaviors and data handling issues.
- Prioritize Security Testing – Regularly test for vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, XSS, and broken authentication. Validate user inputs, check for error leaks, and enforce proper access controls.
What is the Relationship between API Testing and API Monitoring?
- API testing is performed during pre-production (development and staging phases) to verify that APIs function correctly, securely, and efficiently before software releases. It focuses on validating all possible scenarios positive, negative, edge cases, security checks, and performance, under controlled conditions to prevent defects from reaching live environments.
- In contrast, API monitoring is a continuous, automated process carried out in production. Its purpose is to track API health, availability, performance, and errors in real time as end users interact with the service. Monitoring detects malfunctions, latency spikes, outages, or security threats immediately and alerts teams for quick remediation.
- Both are needed for a complete API quality strategy: testing ensures software stability before release, and monitoring safeguards user experience and reliability in production.
What is the Future of API Testing?
1. AI and Machine Learning Revolutionizing Testing
- Automated Test Creation: AI analyzes API specifications and user behavior to generate comprehensive test suites, drastically reducing manual effort and time-to-coverage.
- Self-healing Tests: As APIs evolve, AI adapts existing test cases automatically, fixing broken tests and minimizing maintenance costs.
- Intelligent Test Execution: AI prioritizes and selects tests most likely to catch issues, improving efficiency and speed rather than blindly running every test.
- Natural Language Test Authoring: Teams can describe required testing in plain language (e.g., “Test payment gateway with invalid cards”), and AI turns it into executable tests.
2. Shift-Left Testing and CI/CD Integration
- Early Validation: Testing is increasingly moving to the earliest phases of development (shift-left), embedded directly in CI/CD pipelines. This ensures that issues are caught and fixed before they reach production.
- Continuous Testing: Every code commit triggers automated API tests, giving rapid feedback to developers and reducing post-release defects.
3. Advanced Security Testing
- Zero Trust Models: Security testing is adapting to “never trust, always verify” approaches, with automated vulnerability scans and “fuzzing” (randomized attacks) integrated into routine testing.
- AI-driven Security: AI will detect and even predict new attack vectors faster than traditional methods, helping to keep APIs safe as threats evolve.
4. Adapting to Modern API Architectures
- Event-Driven & Asynchronous APIs: API testing tools are being upgraded to validate streaming, GraphQL, and event-driven APIs (like Kafka, gRPC, WebSockets), supporting real-time and microservices-based software.
- API Virtualization: Simulated APIs (virtual APIs) let teams test integrations even if downstream services aren’t ready, speeding up parallel development.
5. Comprehensive Monitoring and Observability
- Testing meets Monitoring: Real-time performance and health analytics are becoming as essential as API functional tests, providing deep insight into API usage, latency, and failures, both in dev and production.
- Proactive Issue Detection: Modern platforms can flag risky code or suspicious behavior before it impacts users, blurring the line between traditional testing and operational monitoring.
6. Expansion to New Frontiers
- IoT & Blockchain: Specialized API testing is being developed for domains like IoT and blockchain, addressing unique challenges beyond REST API testing.
- Low-Code and No-Code Testing: User-friendly tools are democratizing API quality by enabling testers and business users not just developers to design and run tests.
7. Unified Tool Ecosystems
- End-to-end Quality Platforms: API test automation, security, monitoring, and lifecycle management are integrating into unified platforms, giving teams everything needed for robust quality at scale.
Why Use Testsigma for API Testing?
Testsigma is an Agentic AI-powered test automation platform that simplifies API testing for QA teams of all sizes. Here’s how it helps:
- Create and run API tests without writing code.
- Supports all HTTP methods, headers, and payloads.
- Easily assert status codes, response times, and schema validations
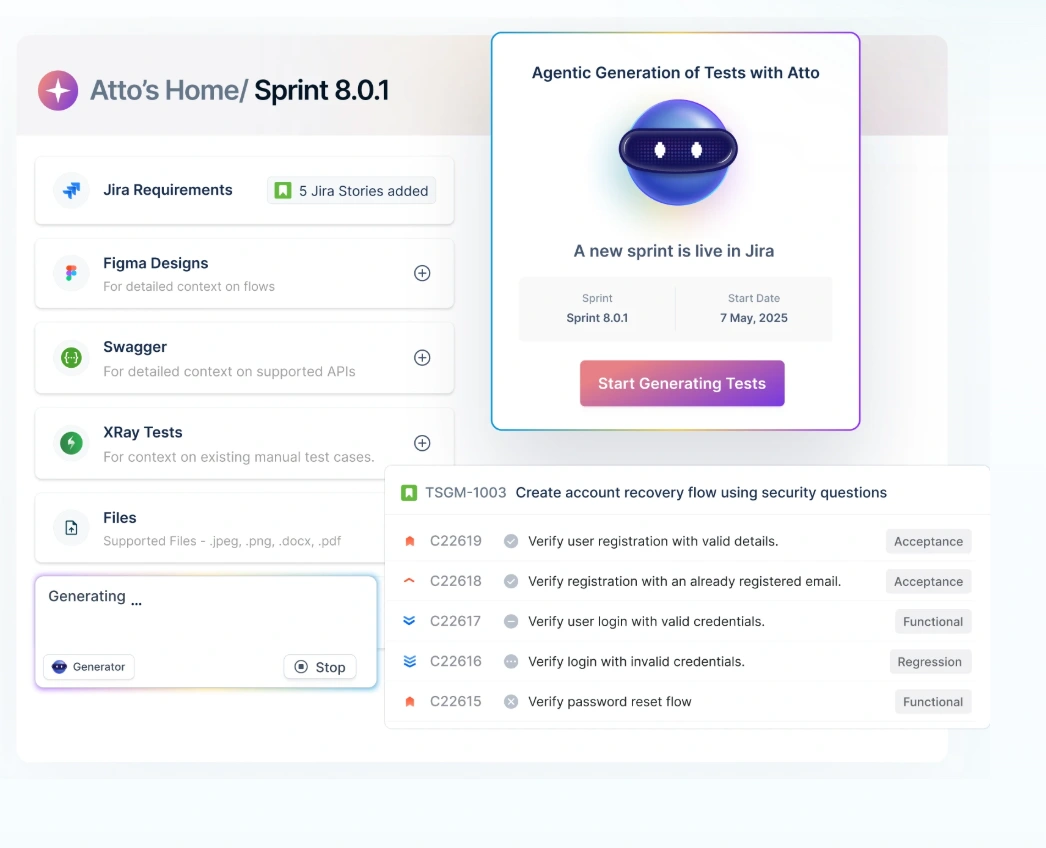
Testsigma offers numerous benefits that support testing, such as web, app, mobile, desktop, browser, Salesforce, and ERP applications. Self-healing tests, AI-powered test creation, maintenance, reduced flakiness, rich device lab, and cross-platform support are some of the novel features of Testsigma. They have launched their intelligent agent, Atto. Atto and its suite of specialized agents help in smarter testing. These agents help plan, organize, execute, and even report bugs efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
API documentation (Swagger/OpenAPI)
Access credentials or API key
API testing Tools like Testsigma
It enables fast, repeatable, and scalable testing critical for CI/CD pipelines and agile teams.
For API testing, manual testers often rely on tools like Postman, Swagger UI, or cURL to send requests and analyze responses. For automation, popular choices include RestAssured, SoapUI, and Karate. However, Testsigma stands out as the best option for both beginners and advanced teams, it offers a no-code, AI-powered platform that simplifies API test creation, execution, and maintenance.
Choose tools aligned with your tech stack
Integrate tests into the CI/CD process
