Behind every flawless website is a tester armed with the right tools. Website testing tools help crush bugs, prevent crashes, and keep users happy. Ready to find the best ones? Explore our top picks for smarter, faster, and more reliable testing.
Website testing tools ensure websites function correctly, look consistent across browsers and devices, and deliver a smooth user experience. They help testers and developers detect bugs, broken links, performance bottlenecks, and security vulnerabilities before users ever encounter them. From automation frameworks to cross-browser testing platforms, these tools streamline the testing process, save time, and improve product quality. By using the right website testing tools, teams can release faster, minimize risks, and deliver reliable digital experiences.
Summarize this article with AI:
Table Of Contents
- 1 Comparison of the 5 Best Website Testing Tools
- 2 18 Best Website Testing Tools in 2025
- 3 Factors to Consider while choosing the Best Website Testing Tool
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Comparison of the 5 Best Website Testing Tools
Features | Testsigma | DogQ | Mocha | LoadRunner | Jest |
| Ease of Use | Low-code/codeless; very beginner-friendly UI | Yes | No, requires JavaScript knowledge and is CLI-driven | No | Yes |
| Cross-Browser & Cross-Device Support | Built-in web + mobile cloud devices & browsers | Only browser-based functional testing | No | Yes | No, focused on JS unit/UI tests, not browser testing |
| Automation Capabilities | Functional, regression, API, mobile, cross-browser automation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| AI-Powered Test Creation | Yes, NLP Engine and AI agents. | No | No | No | No |
| Self-Healing | Auto-healing tests | No | No | No | No |
| Integration support | CI/CD integrations like Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab, Azure, Jira, Slack, etc. | Very limited, basic workflow export only | Can integrate with Chai, Sinon, and Cypress for richer setup | Enterprise tool integrations (CI/CD, monitoring, cloud apps) | Integrates well with React, Babel, TypeScript, and Cypress |
| Flakiness reduction | self-healing, and retry mechanisms | No advanced handling | Manual handling by the developer | Stable under heavy load, but functional test flakiness is not covered | Flakiness is common; it requires manual test structuring |
18 Best Website Testing Tools in 2025
Here is the list of best web application testing tools in 2025,
Testsigma
Testsigma is an Agentic AI-powered test automation platform that streamlines website testing for QA teams of all sizes. Its no-code approach and intelligent agents allow testers to validate functionality, UI, and performance quickly and efficiently. Beyond web automation, Testsigma also supports API, mobile, desktop, browser, Salesforce, and ERP testing, all in one unified platform. With self-healing tests, AI-powered test creation, reduced flakiness, a rich device/browser lab, and cross-platform support, QA teams can ensure seamless user experiences across environments.
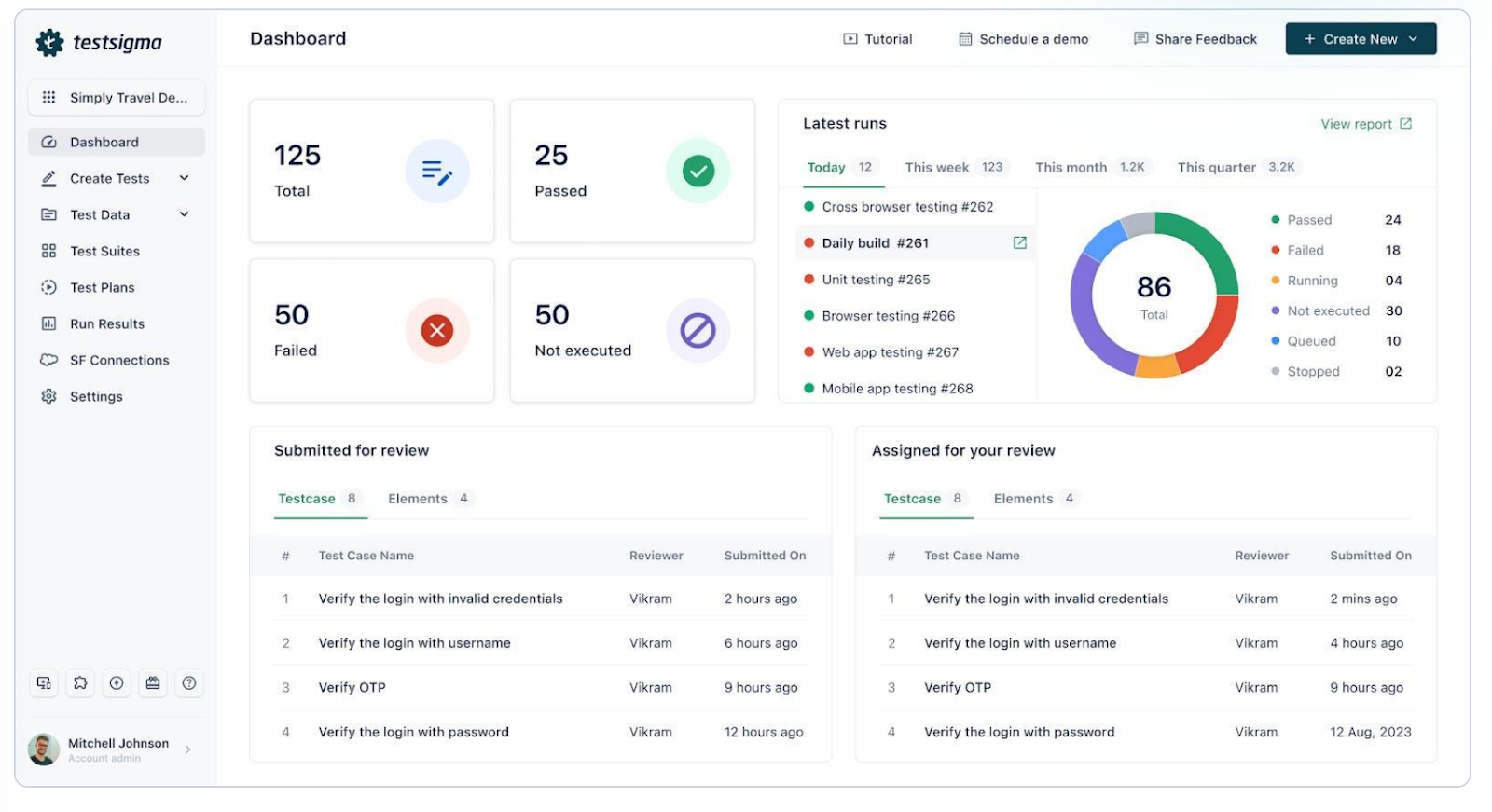
Features of Testsigma
- Create and run tests without code – Write website test cases in plain English without scripting.
- Cross-browser & cross-device testing – Validate websites on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and real devices.
- Device lab – Offers a rich test lab with 3000+ real browsers and devices.
- Functional & regression testing – easily Automate UI, workflows, and business-critical scenarios.
- Visual validations – Detect layout shifts, broken elements, and device rendering issues.
- Data-driven testing – Run the same test with multiple datasets to cover broader user scenarios.
- Self-healing tests – Automatically fix broken locators and stabilize flaky tests.
- Test management – Built-in test management support. Organize, prioritize, and track website test cases in one place.
- Collaboration-ready – Share reports, dashboards, and test results across QA, Dev, and Product teams.
- CI/CD integration – For continuous website testing, plug into Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab, or Azure DevOps.
Dogq
DogQ is a cloud-based, no-code website testing tool designed to make functional and regression testing accessible to teams without deep technical expertise. It allows testers, product managers, and non-technical stakeholders to create and run automated tests through an intuitive UI. DogQ is especially suited for small to mid-sized teams looking for simple, affordable automation without coding complexity.
Features of Dogq
- No-code test creation – Build automated web application testing through an easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface.
- Cross-browser testing – Verify functionality across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
- Reusable components – Modularize tests and reuse steps across multiple workflows.
- Regression testing – Quickly rerun existing test suites to validate updates or bug fixes.
- Collaboration-friendly – Share test cases and results with the entire team for better alignment.
- Cloud-based execution – No setup required; run tests directly from the cloud.
- Reporting & analytics – Provides execution logs, test results, and simple dashboards.
Pros
- No coding skills required, making it easy for non-technical testers.
- Runs on the cloud, so no infrastructure or complex configuration is needed.
- Cost-effective compared to enterprise automation tools.
- Simple workflows that cover basic website validation.
- Multiple team members can participate in testing without steep learning curves.
Cons
- Lacks AI-powered test creation, self-healing, or intelligent wait handling.
- Primarily for web functional testing; no native mobile, desktop, or API testing support.
- Not ideal for enterprise-scale test automation with large, complex test suites.
- Fewer CI/CD and DevOps integrations compared to leading automation platforms.
Mocha
Mocha is a popular open-source JavaScript test framework running on Node.js and in the browser. It’s widely used for unit and integration testing, particularly in JavaScript and full-stack applications. With its flexibility, support for asynchronous testing, and integration with libraries like Chai or Sinon, Mocha is a favorite among developers who prefer a customizable test environment.

Features of Mocha
- Flexible test framework – Works for unit, integration, and end-to-end testing.
- Asynchronous testing support – Handles callbacks, promises, and async/await with ease.
- Customizable reporting – Multiple reporters available, like spec, dot, JSON, etc., for flexible output.
- Broad assertion library support – Integrates seamlessly with Chai, Should.js, Expect, etc.
- Hooks for setup/teardown – Before/after hooks allow structured test workflows.
- Wide ecosystem – Can be paired with Sinon for mocks/spies, Istanbul/NYC for coverage, and Chai.
- Runs in Node.js and browsers – Suitable for both backend and frontend testing.
Pros
- Highly flexible – Doesn’t enforce one style, works with multiple assertion libraries.
- Mature & widely adopted – Stable, well-documented, and supported by a large community.
- Great async support – One of the best frameworks for handling asynchronous testing in JS.
- Rich ecosystem – Can be extended with plugins for coverage, mocking, reporting, and more.
- Open-source & free – No licensing costs, widely accessible for individuals and teams.
Cons
- Steeper learning curve – Requires knowledge of JavaScript and setup with assertion libraries.
- Not codeless – Developers must write test scripts manually (not suitable for non-technical testers).
- Limited out-of-the-box features – Many capabilities, e.g., mocking, assertions, coverage, require third-party libraries.
- No visual testing – Focused purely on logic/unit testing, not UI validation.
Loadrunner
LoadRunner (by Micro Focus, formerly HP) is one of the most established performance, scalability, and load testing tools. It helps QA and DevOps teams simulate thousands of virtual users to test how websites, applications, or systems behave under heavy traffic. With strong protocol support, monitoring, and enterprise-grade integrations, LoadRunner is widely adopted by large organizations that prioritize performance engineering.

Features of Loadrunner
- Scalable load testing – Simulate thousands of virtual users across different geographies.
- Protocol support – Covers 50+ protocols, including HTTP/HTTPS, WebSockets, Oracle, SAP, Citrix, and more.
- Realistic user simulation – Emulates user actions and network conditions for accurate performance insights.
- Detailed performance metrics – Track response times, throughput, resource utilization, and bottlenecks.
- End-to-end monitoring – Integrates with application performance monitoring (APM) tools to correlate server metrics.
- Test scripting with VuGen – Record and customize virtual user behavior with flexibility.
- Continuous testing support – Works with CI/CD pipelines for performance testing in DevOps workflows.
- Cloud execution – Run large-scale tests via LoadRunner Cloud without needing on-premises infrastructure.
Pros
- Can handle massive traffic simulations across multiple protocols.
- Provides deep insights into application and infrastructure performance.
- Supports web, mobile, legacy, ERP, and custom protocols.
- Models real-world user behavior and network conditions.
- Advanced analytics and dashboards help pinpoint bottlenecks quickly.
Cons
- Steeper learning curve, requires technical expertise.
- Licensing and maintenance make it expensive, especially for smaller teams.
- Needs robust infrastructure for large-scale on-premises testing.
- Purely focused on performance/load, not functional or visual QA.
Jest
Jest, maintained by Meta (Facebook), is a widely used JavaScript testing framework, especially popular in the React ecosystem. It provides an all-in-one testing solution with built-in assertions, mocking, and snapshot testing, making it easy to test modern JavaScript applications. Jest is designed for simplicity, speed, and developer productivity, which has led to its adoption across frontend, backend, and full-stack projects.

Features of Jest
- Zero-config setup – Works out of the box with most JavaScript and React projects.
- Snapshot testing – Capture UI component output and detect changes over time.
- Mocking & spies – Built-in support for mocking modules, functions, and timers.
- Parallel test execution – Runs tests concurrently for faster performance.
- Code coverage – Built-in coverage reporting with Istanbul integration.
- Watch mode – Automatically re-runs only affected tests on file changes.
- Rich ecosystem – Works seamlessly with Babel, TypeScript, React, and Node.js.
- Extensible – Can integrate with Enzyme, Cypress, Playwright, or Puppeteer for end-to-end testing.
Pros
- Minimal setup, great for beginners and experienced developers.
- Optimized for component and UI testing in React/Next.js.
- Assertions, mocking, and snapshots built into a single framework.
- Parallelization and smart test selection make it very quick.
Cons
- Primarily focused on JS/TS, not ideal for non-JS tech stacks.
- Best for unit/integration, not performance or functional website validation.
- Snapshots can become bloated or unhelpful if not maintained properly.
Nightwatch.js
Nightwatch.js is an open-source, Node.js-based end-to-end (E2E) testing framework designed for web and mobile applications. It provides an integrated solution for writing, running, and managing automated tests, making it especially useful for teams that want a single framework to handle UI, functional, and API testing. Nightwatch.js is built on Selenium WebDriver and can also integrate with newer frameworks like Playwright for modern browser automation.

Features of Nightwatch.js
- End-to-end testing – Automates functional tests for websites and web application testing across multiple browsers.
- Cross-browser & cross-device support – Works with Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and mobile platforms via Appium.
- Built-in test runner – Includes its own runner with support for parallel test execution.
- BDD-style syntax – Write tests in simple, readable JavaScript with Mocha/Cucumber support.
- Page object model support – Encourages modular, maintainable test design.
- API testing support – Basic API testing capabilities in addition to UI.
- CI/CD friendly – Works well with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI/CD, and other pipelines.
- Playwright & Selenium integration – Choose between traditional Selenium WebDriver or modern Playwright APIs.
- Rich ecosystem – Plugins for reporting, cloud device farms, and custom commands.
Pros
- Covers web, mobile, and API testing under one roof.
- Familiar to frontend developers and full-stack teams.
- Easy to learn with BDD-style test writing.
- Flexibility with Selenium and Playwright.
- Built-in reports and dashboards for test execution results.
Cons
- Slower compared to lightweight frameworks like Playwright or Cypress.
- Requires configuration for parallelism, cloud integrations, and scaling.
- Not as plug-and-play as Jest for new testers.
Postman
Postman is one of the most popular tools for API development and testing. While it’s not a traditional website testing tool that checks UI elements, it plays a critical role in ensuring the backend services that power a website work seamlessly. Since most modern websites depend on APIs for authentication, content, payments, and data exchange, Postman helps QA teams verify that these APIs deliver reliable performance and correct responses, making the overall website experience smoother for end-users.

Features of Postman
- Easy request building – Test APIs with GET, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE methods.
- Automated test scripts – Write JavaScript-based assertions for API responses.
- Collections & workspaces – Organize test cases and share them with team members.
- Environment variables – Switch between dev, staging, and production easily.
- Mock servers – Simulate APIs before the backend is ready.
- API monitoring – Schedule automated checks to ensure website APIs are up and running.
- Collaboration support – Real-time teamwork with shared workspaces and version control.
- CI/CD integration – Run API tests automatically in build pipelines.
Pros
- User-friendly interface, beginner-friendly.
- Covers the entire API lifecycle.
- Strong collaboration features for distributed QA teams.
- Widely adopted with large community support.
Cons
- Not suitable for UI or visual website testing.
- Can feel heavy with very large collections.
- Advanced scripting requires JavaScript knowledge.
- Limited load/performance testing compared to tools like JMeter or LoadRunner.
New Relic
New Relic is a leading observability and performance monitoring platform designed to help QA, DevOps, and engineering teams ensure websites and applications run smoothly. Unlike functional testing tools, New Relic specializes in real-time performance insights, error tracking, and user experience monitoring. It helps teams quickly detect bottlenecks, crashes, or downtime, making it a critical tool for keeping websites fast and reliable at scale.

Features of New Relic
- Real User Monitoring : Track how real visitors experience your website across browsers and devices.
- Synthetic Monitoring: Simulate user journeys (logins, checkouts, searches) to detect issues before they impact users.
- Application Performance Monitoring (APM): Get deep insights into server-side performance, database queries, and API calls.
- Error & Crash Analytics: Identify root causes of slowdowns, memory leaks, or broken dependencies.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Monitor servers, containers, and cloud services alongside website health.
- Custom Dashboards & Alerts: Set thresholds for uptime, latency, and error rates with real-time notifications.
- CI/CD Integration: Catch performance regressions early in the release cycle.
- AI-Powered Insights: Anomaly detection and predictive alerts.
Pros
- Comprehensive observability across frontend, backend, APIs, and infrastructure.
- Strong synthetic testing for simulating end-user journeys.
- Real-time performance monitoring helps detect issues instantly.
- Highly customizable dashboards for team-specific metrics.
Cons
- Steeper learning curve compared to simpler testing tools.
- Can be expensive for small to mid-sized teams.
- Overwhelming amount of data if not configured properly.
- Requires integration and setup effort for full coverage.
Jasmine
Jasmine is a popular open-source behavior-driven development (BDD) testing framework for JavaScript. It’s mainly used for unit and functional testing of web applications, especially in frontend projects. Unlike some test runners that need additional assertion libraries or mocking tools, Jasmine comes as an all-in-one framework with built-in spies, mocks, and assertions, making it easy to get started.

Features of Jasmine
- BDD Syntax: Readable, natural language style for writing tests.
- Built-in Assertions & Spies: No need for external libraries for mocks and stubs.
- Asynchronous Testing Support: Handles async code with callbacks, promises, or async/await.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works with any JavaScript-enabled platform, browsers, or Node.js.
- Zero Dependencies: Simple setup without additional libraries.
- Custom Matchers: Extend assertions with project-specific matchers.
- Integration with CI/CD: Works seamlessly with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and other pipelines.
- Browser & DOM Testing: Useful for verifying UI behavior in client-side applications.
Pros
- Lightweight and easy to set up.
- Clear, human-readable test syntax.
- Provides a complete package (assertions + mocks + spies) out of the box.
- Works in both Node.js and browsers.
Cons
- Not as fast as Jest for large-scale test suites.
- No built-in test runner GUI and relies on command-line.
- Limited debugging support compared to modern frameworks.
- Requires manual configuration for integration with modern build tools.
- Doesn’t focus on performance or end-to-end testing, meant more for unit/functional testing.
Bugzilla
Bugzilla is one of the most established open-source bug tracking systems, originally developed by Mozilla. It has been used for decades by large organizations to manage software defects, issues, and project workflows. Bugzilla helps QA and development teams collaborate effectively by providing advanced search, filtering, and customizable workflows. Though its UI feels dated compared to modern SaaS tools, it remains a reliable, cost-effective solution for teams that want a proven and robust issue-tracking system.

Features of Bugzilla
- Bug and Issue Tracking with Detailed Reporting – Log, track, and manage bugs with robust reporting features for improved visibility.
- Advanced Search and Filtering Options – Quickly find issues using
- customizable queries and filters.
- Role-Based Access Control and Workflow Customization – Assign roles and tailor workflows to match team processes.
- Email Notifications and Automated Updates – Receive real-time alerts on bug status changes.
- Integration with CI/CD Pipelines – Enhance traceability by linking Bugzilla with repositories and pipelines.
Pros
- Free and open-source with strong community support.
- Highly customizable workflows.
- Proven reliability at enterprise scale.
Cons
- Outdated UI and not very user-friendly.
- Limited built-in integrations compared to modern tools.
- Requires manual setup and maintenance.
Ranorex Studio
Ranorex Studio is a commercial automation platform that caters to enterprises needing to automate testing across desktop, mobile, and web applications. Its biggest strength lies in desktop (Windows) testing. Ranorex offers codeless test automation via record-and-replay, but also supports scripting for advanced users in C# and VB.NET. With its strong integration ecosystem and powerful UI object recognition, it’s considered a good fit for teams balancing both technical and non-technical testers.

Features of Ranorex Studio
- Cross-platform functional testing – Supports automation across desktop, web, and mobile applications.
- Low-code/no-code automation – Provides record-and-playback test creation, making it accessible to non-programmers.
- AI-based object recognition – Maintains stable tests even when UI elements change.
- Built-in CI/CD integrations – Connects with Jenkins, GitHub, Jira, and other popular DevOps tools.
- Detailed analytics and reports – Provides error tracking and dashboards to improve test visibility.
Pros
- Great for both beginners and advanced users.
- Strong desktop testing support (Windows apps).
- Professional support and training.
Cons
- High licensing costs.
- Steeper learning curve for scripting.
- Limited support for non-Windows environments.
Selenium
Selenium is the most popular open-source test automation framework in web application testing tools. It allows testers to write robust browser automation scripts in languages like Java, Python, C#, and JavaScript, and execute them across different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge) and platforms. Selenium Grid enables distributed and parallel execution, making it suitable for scaling large test suites. While Selenium offers unmatched flexibility and ecosystem support, it demands strong technical expertise, as it doesn’t come with built-in reporting or test management.

Features of Selenium
- Open-source web automation – A widely adopted framework for automating web application testing.
- Language flexibility – Supports multiple programming languages like Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and more.
- Cross-browser and cross-platform coverage – Works on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and other major browsers.
- Scalable with Selenium Grid – Allows parallel execution to reduce test cycles.
- Rich community and ecosystem – Backed by a strong developer community and third-party integrations.
Pros
- Free and widely adopted.
- Extremely flexible and extensible.
- Works with almost any browser and language.
Cons
- No built-in test reporting or management.
- Requires advanced setup and coding skills.
- Flaky tests if not managed properly.
TestComplete
TestComplete, by SmartBear, is a commercial UI automation tool built for organizations looking to test across web, desktop, and mobile platforms. It features a hybrid approach, allowing codeless test creation for business users and full scripting capabilities (JavaScript, Python, VBScript, DelphiScript) for advanced testers. With its AI-powered object recognition, TestComplete adapts to dynamic UI changes, reducing test flakiness. It is widely chosen by enterprises that want a balance of speed, scalability, and strong reporting, without relying on open-source setups.

Features of TestComplete
- Comprehensive UI test automation – Supports functional, regression, and automated GUI testing for desktop, web, and mobile applications.
- Scripted and no-code testing options – Enables both record-and-playback test creation as well as advanced scripting in languages like Python, JavaScript, and VBScript.
- Cross-browser and cross-device testing – Works across Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari, iOS, and Android platforms.
- AI-powered object recognition – Identifies dynamic UI elements using visual AI, reducing flakiness in test execution.
- Data-driven testing – Allows running the same test with multiple datasets to ensure broader coverage.
- Seamless integrations – Connects with CI/CD tools (Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitHub), defect trackers (Jira, Bugzilla), and test management systems.
- Detailed reporting and dashboards – Provides execution logs, error snapshots, and performance metrics for faster debugging.
Pros
- Easy for beginners with no-code options.
- Strong support for desktop app testing.
- AI-based object recognition improves test stability.
Cons
- Paid tool with high licensing fees.
- Slower test execution at scale.
- Limited flexibility compared to open-source tools.
Bugbug.io
startups, small teams, and non-technical testers. Unlike heavy enterprise tools, BugBug emphasizes simplicity and speed, offering record-and-playback test creation with a visual editor. It requires no installation and supports cloud-based test execution and scheduling. While it doesn’t have the depth of tools like Selenium or Cypress, BugBug’s ease of use and low barrier to entry make it an attractive choice for teams that need quick test coverage without technical overhead.

Features of Bugbug.io
- Lightweight browser-based testing – Designed for simple web automation without heavy setup or complex configuration.
- No-code test creation – Record user actions directly in the browser to build tests quickly, even without programming skills.
- Cloud execution and scheduling – Run tests automatically in the cloud on a schedule, ensuring continuous monitoring.
- Collaboration-friendly – Share tests, results, and reports with team members for transparent QA processes.
- CI/CD support – Integrates with popular CI/CD pipelines like GitHub Actions and GitLab for automated workflows.
- Visual test editor – Provides an intuitive interface for editing and maintaining recorded tests.
- Error reporting and debugging – Offers detailed logs and step-by-step screenshots to help identify failures faster.
Pros
- Very beginner-friendly and intuitive.
- Affordable pricing compared to enterprise tools.
- Quick setup with no coding required.
Cons
- Limited advanced automation capabilities.
- Not ideal for large enterprise-scale projects.
- Fewer integrations compared to bigger players.
Playwright

Playwright, developed by Microsoft, is a fast-growing open-source framework for web automation and end-to-end testing. It’s designed to solve many of Selenium’s limitations by offering auto-waiting, reliable locators, and built-in cross-browser support (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit). Playwright supports multiple languages (JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Java, .NET) and includes advanced features like network mocking, API testing, and parallel execution. Its architecture makes it particularly well-suited for testing modern, dynamic web apps.
Features of Playwright
- Cross-browser automation – Supports testing on Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit with a single API, ensuring wide coverage across browsers.
- Multi-language support – Works with JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, C#, and Java, making it flexible for diverse teams.
- End-to-end web testing – Automates UI workflows, API calls, and network interactions for complete application coverage.
- Auto-waiting and reliability – Waits automatically for elements to be ready before interacting, reducing flaky tests.
- Headless and headed modes – Run tests faster in headless mode or visually debug them in headed browsers.
- Parallel execution and test isolation – Enables faster test runs with multiple browsers, contexts, and tabs in parallel.
- Native mobile emulation – The responsive design testing tools in Playwright simulates iPhones and Android smartphones.
- Built-in tracing and debugging tools – Provides detailed execution traces, screenshots, and videos to speed up debugging.
- CI/CD friendly – Integrates seamlessly with GitHub Actions, Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and other pipelines.
Pros
- Fast, reliable, and less flaky than Selenium.
- Rich API with modern features.
- Strong community and Microsoft backing.
Cons
- Smaller ecosystem compared to Selenium.
- Can be complex for beginners.
- Limited support for legacy browsers.
Cypress

Cypress is a JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework that has become the go-to choice for frontend developers. Unlike Selenium, which works outside the browser, Cypress runs directly inside the browser, giving it deep access to DOM elements, local storage, and network requests. Its real-time reloading, time-travel debugging, and built-in screenshot/video capture make it incredibly developer-friendly. While it shines for modern JavaScript frameworks (React, Angular, Vue), Cypress has limited cross-browser and mobile testing support.
Features of Cypress
- Fast, developer-friendly testing – Built specifically for modern web applications with real-time reloading and debugging.
- JavaScript-based framework – Tests are written in JavaScript, making it easy for frontend developers to adopt.
- End-to-end and integration testing – Supports UI testing, API calls, and component testing within a single framework.
- Automatic waiting – Eliminates the need for explicit waits, reducing flaky tests.
- Time travel debugging – Captures snapshots during execution so you can hover over steps and see what happened.
- Built-in parallelization – Runs tests in parallel across environments for faster execution.
- Rich ecosystem – Offers plugins, community support, and dashboard services for test analytics.
- CI/CD integration – Works seamlessly with Jenkins, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, and GitLab.
Pros
- Extremely developer-friendly.
- Fast and reliable test execution.
- Excellent debugging with real-time runner.
Cons
- Only supports JavaScript/TypeScript.
- Limited cross-browser support (no Safari/IE).
- Not suitable for desktop/mobile native apps.
BrowserStack

BrowserStack is a cloud-based cross-browser and cross-device testing solution trusted by thousands of enterprises worldwide. Instead of maintaining physical devices and virtual machines, teams can test on BrowserStack’s vast cloud infrastructure of 3000+ real devices and browsers. It integrates seamlessly with popular automation frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright, as well as CI/CD tools. BrowserStack’s biggest advantage is eliminating infrastructure costs and ensuring tests run on real user environments, making it ideal for distributed teams and enterprise-scale projects.
Features of BrowserStack
- Cloud-based testing platform – Provides instant access to 3000+ real browsers, devices, and OS combinations.
- Cross-browser and cross-device testing – Ensures websites and apps work seamlessly across all environments.
- Automated and manual testing support – Run Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, or Appium scripts, or conduct live testing sessions.
- Visual testing – Detects UI inconsistencies using automated screenshot comparison and layout validation.
- Real device testing – Test on actual iOS and Android devices for accuracy and performance validation.
- CI/CD integration – Works with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, and more.
- Scalable test execution – Run thousands of automated tests in parallel with enterprise-grade reliability.
- Security and compliance – Enterprise-ready with secure connections, SOC2, GDPR, and ISO certifications.
Pros
- Huge library of real devices and browsers.
- No need to maintain infrastructure.
- Excellent scalability for distributed teams.
Cons
- Paid subscription required which can be costly.
- Internet latency can affect test speed.
- Limited offline/local testing support.
Puppeteer
Puppeteer is a Node.js library developed by Google to provide a high-level API for controlling Chrome or Chromium via the DevTools protocol. While it’s not a full testing framework, Puppeteer is widely used for headless browser automation, scraping, screenshot generation, and performance testing. Developers often pair Puppeteer with Jest or Mocha for building automated test suites. Its speed, lightweight design, and deep browser control make it popular among developers, but its Chromium-only limitation restricts cross-browser testing.

Features of Puppeteer
- Headless browser automation – Provides a Node.js library to control Chrome and Chromium browsers programmatically.
- Web scraping and automation – Ideal for capturing screenshots, generating PDFs, or crawling websites.
- UI and functional testing – Supports automating user interactions to validate workflows.
- Performance monitoring – Collects metrics like page load time, runtime performance, and network activity.
- Cross-browser support – Primarily for Chromium but has growing support for Firefox.
- Debugging-friendly – Offers detailed logs, screenshots, and the option to run in non-headless mode for live debugging.
- CI/CD integration – Fits into Node.js pipelines and tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab.
- Lightweight and flexible – Minimal setup makes it faster than full-scale frameworks for targeted automation tasks.
Pros
- Great for headless testing and scraping.
- Fast and lightweight.
Cons
- Limited to Chromium browsers.
- Requires coding knowledge (Node.js).
Factors to Consider While Choosing the Best Website Testing Tool
Choosing the right website testing tool can make or break your QA strategy. With so many options in the market, it’s important to evaluate tools based on features, scalability, and team needs. Here are the key factors to keep in mind:
1. Ease of Use – A good website testing tool should be beginner-friendly yet powerful enough for advanced testers. Look for no-code or low-code test creation if your team has non-technical members, and ensure there’s comprehensive documentation and community support for developers.
2. Cross-Browser & Cross-Device Coverage – Modern users access websites from multiple browsers and devices. Your tool should provide real device testing (not just emulators) and support all major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge along with iOS and Android devices.
3. Automation Capabilities – Automation is key for faster releases. The tool should support end-to-end automation for web, API, and mobile apps, along with features like parallel execution, scheduling, and reusable test steps.
4. Seamless CI/CD Integration – For continuous testing, integration with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps is essential. Tools with built-in version control support and API access make it easier to fit into your development pipeline.
5. AI & Smart Features – Next-gen QA requires smarter testing. Look for AI-powered test creation, self-healing tests, and flakiness reduction features. Visual AI is especially helpful in catching UI changes that could impact functionality.
6. Reporting & Test Management – Clear insights are critical for debugging. Tools with dashboards, detailed reports, screenshots, video recordings, and error tracking can save hours of manual analysis. Built-in test management features are a plus.
7. Scalability & Performance Testing – Your tool should scale with your team and application growth. Check if it supports load testing, stress testing, and performance benchmarking in addition to functional tests.
8. Collaboration & Team Features – Distributed teams need tools with role-based access control, real-time collaboration, and cloud-based access. Features like email notifications and integrations with Slack or Jira make teamwork smoother.
9. Pricing & Licensing – Consider your budget and compare free, open-source, and enterprise-grade tools. Some platforms offer free tiers for small teams, while others provide advanced enterprise features at a premium.
10. Security & Compliance – If you’re working with sensitive data, security is non-negotiable. Look for tools with secure connections, data encryption, and compliance with SOC2, GDPR, or ISO standards.
Conclusion
Selecting the best website testing tool in 2025 comes down to your team’s needs whether it’s ease of use, automation depth, cross-browser coverage, or scalability. While open-source frameworks and specialized tools have their strengths, managing multiple platforms often adds complexity. If you’re looking for a future-ready testing solution that scales with your business, Testsigma is a strong choice to consider.
Frequently Asked Questions
A website testing tool is a software solution that helps QA teams and developers validate the functionality, performance, security, and user experience of websites. These tools allow you to run tests across different browsers, devices, and environments to ensure that your site works seamlessly for all users. Many modern tools also support automation, AI-powered self-healing, and CI/CD integration, making testing faster and more reliable.
1)Detect bugs and errors before end-users face them.
2)Ensure cross-browser and cross-device compatibility.
3)Improve site speed, performance, and scalability.
4)Validate security and compliance standards.
5)Save time with automation and parallel test execution.
Enable teams to deliver flawless digital experiences consistently.
In short, they help teams ship high-quality websites faster while reducing manual effort and costs.
Testsigma is one of the most comprehensive website testing tools available today. It combines codeless automation, AI-powered test creation, self-healing capabilities, API testing, mobile/web/browser support, and test management into a single platform. Unlike many other tools that focus only on one area, Testsigma offers an all-in-one solution, making it a strong choice for QA teams that want to scale quickly and reduce tool fragmentation.
Testsigma – AI-powered, codeless, all-in-one test automation platform.
Playwright – Open-source framework for reliable end-to-end testing.
Cypress – Fast, developer-friendly tool for frontend testing.
Selenium – Widely used open-source web automation framework.
BrowserStack – Cloud-based platform for real device/browser testing.
LoadRunner – Performance and load testing at enterprise scale.
Mocha & Jest – JavaScript testing frameworks for unit and integration testing.
Yes! Several popular open-source website testing tools are included in the list, such as:
Selenium – The most widely used framework for web automation.
Playwright – Backed by Microsoft, great for cross-browser testing.
Cypress – Open-source and developer-centric for frontend testing.
Mocha and Jest – JavaScript testing frameworks for unit and integration tests.
Puppeteer – Node.js library for automating Chrome/Chromium.
These open-source options are cost-effective, flexible, and highly customizable, though they may require more setup and coding expertise compared to all-in-one platforms like Testsigma.

