Manual testing tools are essential allies for testers who need to validate software through hands-on, exploratory, and flexible testing approaches. These tools help testers organize test cases, track defects, and collaborate efficiently, even when requirements change quickly or projects have tight deadlines. This list highlights the top manual testing tools in 2025, chosen for their ability to support testers in delivering reliable software with features that simplify manual workflows and improve team coordination.
Summarize this page with AI:
Table Of Contents
- 1 Comparing Top 5 Manual Testing Tools
- 2 12 Best Manual Testing Tools of 2025
- 3 Factors to Consider while Choosing the Best Manual Testing Tool
- 4 Conclusion
Comparing Top 5 Manual Testing Tools
| Tool | Description | Key Features That Support Manual Testing |
| Test Management by Testsigma | Agentic AI-powered test management tool combining manual, automated, and exploratory testing with the assistance of an AI coworker called Atto, and various autonomous Agents. | AI-driven test case generation and execution Real-time sprint planningTwo-way Jira syncEasy bug reportingUnified manual and automated test management. |
| TestLink | Open-source test management tool for organizing, executing, and tracking manual and automated tests. | Test case management with detailed stepsReal-time execution tracking Customizable reportsRole-based user managementIntegration with Jira. |
| SpiraTest | Comprehensive QA solution managing requirements, tests, bugs, and exploratory manual testing. | Test execution wizard Exploratory testing mode Requirements traceabilityBug tracking Manual and automated test integration Detailed reporting |
| TestRail | Centralized test case management tool widely used for manual and automated testing coordination. | Manual test case creation and organization Test execution tracking Defect reporting integration Real-time dashboards Customizable reportsCI/CD integrations |
| BugBug | User-friendly codeless test automation tool designed mainly for web apps but supports manual testing workflows. | Intuitive test recorder Unlimited free local runs Cloud execution with CI/CD integrationAutomated alerts Collaborative test managementPDF reporting |
12 Best Manual Testing Tools of 2025
1. Test Management by Testsigma
Test Management by Testsigma is a unified test management tool that uses Agentic AI to handle sprint planning, write detailed test cases, execute tests, and file bug reports automatically, without switching tools or using spreadsheets. Atto, the built-in AI coworker, uses specialized AI agents to plan, write, run, and report on tests, but testers always stay in control of the entire testing process. The tool also syncs with Jira and CI/CD pipelines, and its clean interface makes it easy to get started in minutes with no steep learning curve.
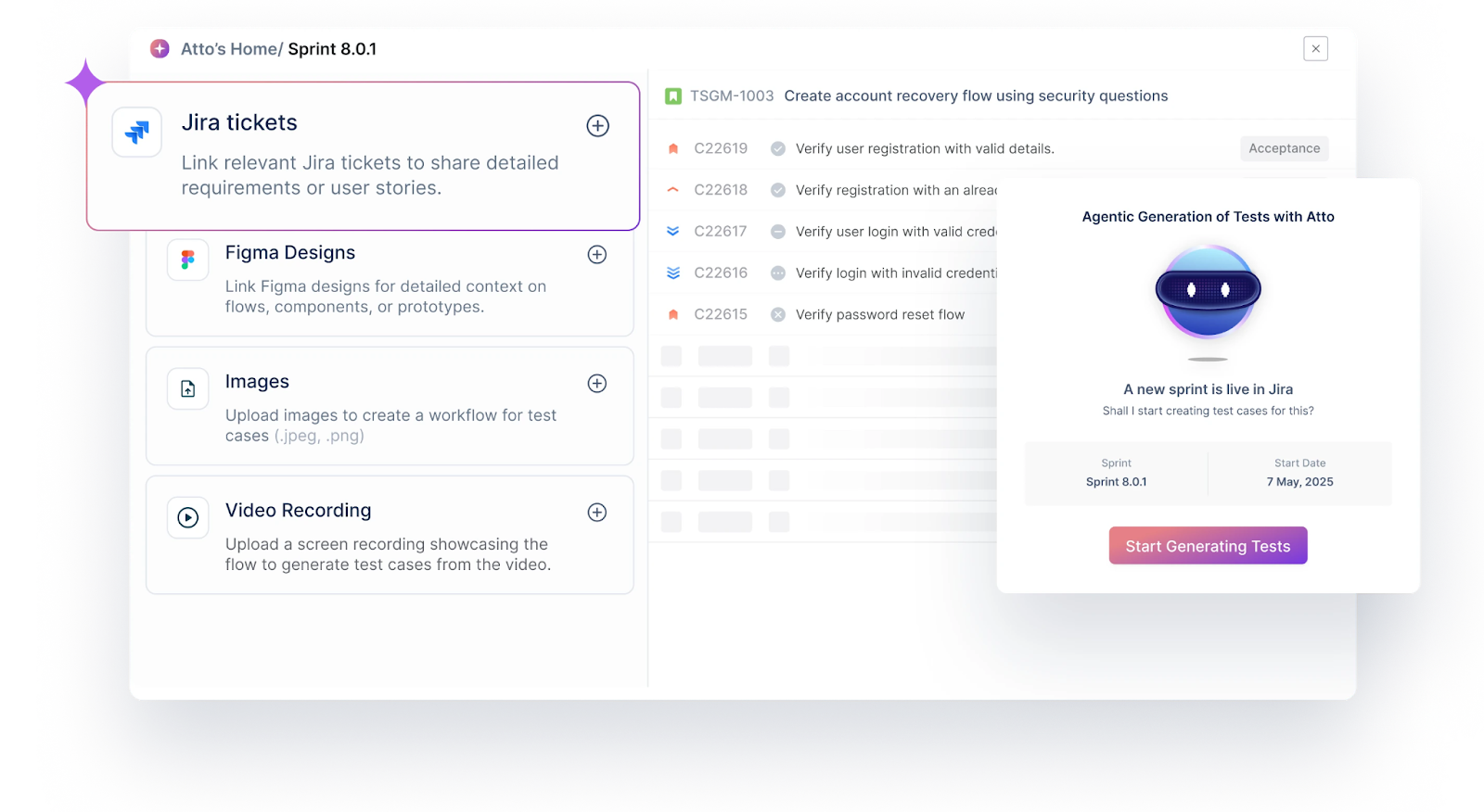
Features
- AI-powered test case generation, execution, and bug reporting
- Unified manual, automated, and exploratory test management in one place
- Real-time visibility and sprint detection as sprints start
- Automated test case writing and execution with AI agents
- Option to pause, refine, or re-run AI-executed tests for realistic results
- Clean UI and intuitive workflows, easy onboarding
- Generates accurate AI-driven test cases quickly for unit, regression, and more
- Two-way Jira sync for requirements traceability
- Integrates with Jira seamlessly
- No tool switching or reliance on spreadsheets
- Fast onboarding; testers can start in minutes without a learning curve
- Flexible plans, including free forever and paid options
Pros
- Moves beyond spreadsheets and outdated tools with a modern, end-to-end test management solution
- Easily import test data in one click from Excel, CSV files, and popular open-source tools
- Builds strong integration networks with widely used development and project management platforms, including two-way Jira sync
- Uses AI agents to execute tests directly in the browser, reducing manual effort and increasing focus on critical issues
- Provides a clean, intuitive interface that simplifies sprint planning, test execution, and bug reporting across the QA lifecycle
Cons
- Requires initial familiarization with AI-driven interface
2. Browserling

Browserling is an interactive cloud platform for real-time manual cross-browser testing. It enables users to test websites across multiple browsers and operating systems without local setup. It allows you to capture, save, and share screenshots of your web pages in all popular browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer.
Features
- Real-time interactive cross-browser testing on multiple browsers and OS
- Instant access to popular browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera, and Internet Explorer
- Live API testing capabilities for JavaScript and web applications
- Custom cross-browser testing solutions for complex environments
- Screenshot capture and sharing during tests
- Cloud-based platform eliminates the need for local virtual machines
- Developer-friendly with quick response and support for JavaScript testing
Pros
- Fast, responsive, and reliable cross-browser testing service
- Saves costs by eliminating the need for multiple VMs and licenses
- Highly praised for solving complex legacy environment challenges
- Provides real-time feedback with live interaction in browser sessions
- User testimonials highlight technical capability and excellent support
Cons
- Limited test management features beyond browser and API testing
- Focuses mainly on web and JavaScript environments, less suitable for full manual test management
- No built-in defect tracking or test case management system
3. JIRA

Jira is a widely used tool for issue and project tracking, popular in Agile testing environments, and not inherently a manual testing tool but it can be extended for manual testing through plugins and integrations with specialized test management tools like Test Management by Testsigma. It helps QA teams manage test defects and organize project workflows with customizable features.
Features
- Agile workflows supporting Scrum and Kanba
- Real-time collaboration and dashboard reports
- Customizable workflows and issue tracking
- Integrations with developer tools and test management tools
Pros
- Strong integration ecosystem
- Provides visibility into project and defect status
- Flexible and scalable for multiple project types
Cons
- Has a steep learning curve for beginners
- Setup and customization can be time-consuming
4. TestLink

TestLink is an open-source test management tool that supports manual test case creation, execution, and reporting. It promotes traceability by linking test cases to requirements and integrates with popular bug trackers like Jira and Bugzilla.
Features
- Test case management with structured steps, expected results, and priorities
- Creation of comprehensive test plans covering multiple test cycles or milestones
- Test execution management with real-time progress tracking and result recording
- Detailed reporting and metrics on test execution, coverage, and pass/fail rates
- Role-based user management with customizable permissions
- Support for custom fields to tailor test cases and plans
- Supports both manual and automated testing workflows
Pros
- Free and cost-effective as an open-source tool
- Centralizes all testing activities in a single platform
- Improves test coverage and ensures traceability with requirement linking
- Flexible and customizable to fit specific project needs
- Enhances collaboration among QA teams and stakeholders
Cons
- User interface can appear outdated and less intuitive
- Requires setup and maintenance since it is self-hosted
- Lacks some advanced automation and modern usability features
- May have a steeper learning curve for new users
5. SpiraTest

SpiraTest is a comprehensive test management tool that includes test case management, defect tracking, and reporting. It supports manual testing workflows with collaborative features.
Features
- Easy-to-use test execution wizard to run groups of test cases, mark each step as pass/fail, and log defects
- Centralized test case management with authoring, organizing, and real-time tracking of test progress
- Requirements management with full traceability from requirements to test cases and defects
- Dedicated exploratory testing mode for on-the-fly test creation and issue tracking
- Customizable bug tracking and issue management with workflows, notifications, and reporting
- Integration with popular automation tools like Rapise, UFT, Selenium, enabling manual and automated tests in one platform
- Detailed reporting and project dashboards for real-time visibility into test execution and quality metrics
- Responsive web interface supporting all devices and platforms for flexible, anywhere testing
Pros
- All-in-one quality assurance platform covering requirements, testing, bugs, and project health
- Robust manual and automated test management integration
- Flexible and customizable to fit varied team workflows and regulatory needs
- Support for regulated industries with electronic signatures and audit compliance
- Easy administration and user management with SSO and delegated roles
- Rich reporting and analytics provide deep insights into project status
Cons
- High feature set may introduce complexity for new users or small teams
- Some advanced features may require configuration effort and learning
- Primarily suited for teams needing full QA lifecycle coverage, may be overkill for smaller projects or simple testing needs
6. Postman

Postman is primarily an API testing tool but it supports manual testing for APIs through an easy-to-use interface. It helps testers create, organize, and execute API test requests manually.
Features
- Unified API test automation for functional, regression, integration, and performance testing
- Automated test coverage with real-time visibility across environments
- Reusable test collections, mocks, and environments to reduce duplication and rework
- CI/CD pipeline integration allowing automated test runs inside build pipelines
- Scheduled monitors to continuously validate API reliability in staging and production
- Test collaboration to accelerate release cycles and improve release confidence
- Comprehensive reporting and insights for faster issue detection and reduced outages
Pros
- Speeds up API release cycles by shifting testing earlier in development
- Reduces manual testing time significantly with automation
- Enhances confidence in releases through continuous validation
- Supports easy integration with existing development and DevOps workflows
Cons
- Primarily focused on API testing, less suited for UI or full manual testing management
- Some initial setup and learning curve for complex test automation scenarios
- May require paid plans to access advanced features and higher testing volumes
7. Bugzilla

Bugzilla is primarily an open-source bug-tracking system, not a dedicated test management tool, though it can be used for managing issues found during testing and integrates with specialized test management tools like Test Management by Testsigma. It is known for its reliability and customization options. It supports issue tracking discovered during manual testing with advanced search and reporting.
Features
- Custom workflows for bug resolution
- Role-based access and email notifications
- Time tracking and audit logs
- Integrations with test case management tools
Pros
- Highly customizable
- Open-source and widely adopted
- Good for detailed bug tracking
Cons
- Lacks built-in test case management
- Interface is not modern
8. Mantis

Mantis is a web-based bug tracking system that is often configured for general issue tracking and project management, but it doesn’t have comprehensive test management features on its own. It helps manage the defect lifecycle and allows testers to report issues.
Features
- User-friendly bug tracking
- Email notifications and role management
- Integration with source control and test tools
- Basic reporting and customizable workflows
Pros
- Simple to use and set up
- Good collaboration and notification system
- Open-source with active community
Cons
- Limited test management features
- Not suitable for large, complex projects
9. TestRail

Testrail is a comprehensive test case management tool supporting manual and automated tests. It offers rich reporting and supports integration with defect trackers and CI/CD tools.
Features
- Centralized test case repository for organizing and managing test suites
- Intuitive UI/UX for faster creation of test cases and test plans
- Real-time tracking of test execution progress and automation coverage
- Deep integrations with various development and testing tools for seamless workflows
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics for insights into testing status and risks
- Supports Agile testing methodologies with frameworks and guides
- Enterprise-grade capabilities for scalability and quality assurance control
Pros
- Boosts productivity by saving time on test creation and management
- Enhances collaboration across QA teams and stakeholders
- Flexible for both small teams and large enterprise environments
Cons
- Advanced features may require onboarding and training for new users
- Some integrations may need configuration effort initially
- May have higher pricing for smaller teams or startups
10. Citrus

Citrus is an open-source testing framework focused on automated integration and manual API testing. It facilitates complex test scenarios and validation for message-based applications.
Features
- Automated integration testing focused on messaging applications and microservices
- Supports a wide range of messaging protocols such as HTTP REST, Kafka, JMS, TCP/IP, SOAP, FTP, and more
- Powerful message validators for various data formats, including XML, JSON, YAML, and plaintext
- Flexible test writing using Java, XML, YAML, or Cucumber BDD Gherkin feature files
- Integrates seamlessly with JUnit Jupiter, Spring Boot, Quarkus, Maven, Gradle, and Cucumber
- Ready-to-use client and server components to simulate service interfaces and third-party apps
- Supports behavior-driven development (BDD) with Cucumber integration using given-when-then syntax
- Facilitates cloud-native testing with Kubernetes, Docker, and Apache Camel integrations
- Provides test container modules for easy test infrastructure setup
- Supports Selenium for browser simulation, combined with integration testing
Pros
- Highly flexible and extensible for different integration test scenarios
- Strong support for automated testing of microservices and messaging protocols
- Enables testing at multiple layers, including UI via Selenium integration
- Open source with an active community and evolving capabilities
- Supports BDD for clear test scenario specifications
Cons
- Requires technical expertise to implement and maintain
- Lacks GUI, mainly code and configuration-driven testing
- Best suited for integration testing, not a full manual test management solution
11. Tessy

Tessy specializes in manual testing for embedded systems and safety-critical software. It supports test case design, execution, and detailed reporting.
Features
- Automates the complete unit test cycle, including regression testing for embedded C/C++ software
- Test project management with customizable project structure, environment variables, and compiler/debugger configurations
- Basic requirements management with import/export support from tools like Polarion, DOORS, Jama Connect, and Visure using CSV, XML, and ReqIF formats
- Support for software variant management, enabling efficient testing of base and derived code variants
- Advanced code coverage features, including Call Pair Coverage, Hyper Coverage, and Code Access Analysis, for detailed test coverage insights
- Comprehensive test result visualization and reporting with plots, flow charts, and detailed coverage views
- Scenario Editor allows setting and checking of component interface variables during tests
- Multiple automated test report types in PDF summarizing execution, coverage, and test status
- Integration via API and command line interface, enabling scripting and automation of testing workflows
Pros
- Highly specialized for embedded software unit testing with strong automation capabilities
- Supports detailed analysis of test coverage with advanced coverage measurement techniques
- User-friendly graphical editors simplify creating complex test cases and scenarios
- Extensive integration options enable automation and customization
Cons
- Primarily focused on embedded C/C++ applications, less suited for general software testing
- Requires technical expertise to set up and use effectively
- Interface and tools may be complex for smaller teams or those new to embedded testing
12. BugBug

BugBug is a relatively new tool focused on manual and exploratory testing with a collaborative approach. It supports bug reporting with detailed insights and integrates with various project management platforms.
Features
- Intuitive codeless test recorder for easy and fast test creation without coding
- Integration with CI/CD pipelines, CLI, API, and scheduled test execution
- Automated alerts and notifications via email, Slack, webhooks, and Zapier
- PDF report generation for stakeholders to review test results
- Test maintenance with Components, allowing bulk edits and re-recording of specific steps
- Unlimited users for collaborative test creation and management
- Cloud-based platform with no infrastructure management required
Pros
- Enables rapid test creation without writing code
- Cost-effective with free unlimited local runs and predictable cloud pricing
- Seamless integration with modern development workflows and communication tools
- Simplifies test maintenance and collaboration across teams
- Positive user feedback highlighting ease of custom logic implementation
Cons
- Focuses primarily on web app testing, with limited support for non-web platforms
- Some advanced customizations require JavaScript knowledge
- May not cover complex scenarios suited for traditional scripted frameworks
Factors to Consider While Choosing the Best Manual Testing Tool
- Ease of use and learning curve
- Integration with existing development and bug tracking tools
- Support for test case management and organization
- Reporting and analytics capabilities
- Collaboration features for team workflows
- Cost and licensing model (open-source vs commercial)
- Scalability for multiple projects and users
- Support for manual, exploratory, and automated testing
- Platform compatibility (web, desktop, embedded, API)
Conclusion
Manual testing tools are essential for organizing, executing, and tracking testing activities efficiently. Tools like Test Management by Testsigma offer AI-powered assistance that reduces manual effort, while others like Jira and Bugzilla excel in issue tracking and project management. Understanding the features and limitations of these tools will help testers choose the best fit to enhance manual testing workflows in 2025.
Ideally testing manually is the one done without the use of tools. But to aid the testing, certain tools like traffic analyser or performance analyser are used at times. This manual can be automated too with the help of tools like Testsigma.
Testsigma is a notable alternative to traditional testing methods, offering a transition towards automated testing. As a scriptless test automation tool, Testsigma allows testers to create and execute tests without extensive coding. This makes it an efficient solution for those seeking an alternative to manual that doesn’t require advanced programming skills. Testsigma’s user-friendly interface and cloud-based platform contribute to its appeal, facilitating collaborative testing efforts. While the “best” alternative depends on specific project requirements, Testsigma is a compelling option for organizations aiming to enhance testing efficiency and move toward automation

