Noticing a small button out of place right before a launch can prevent a lot of last-minute chaos and extra work. Every tester has faced those frustrating moments when tiny user interface glitches spoil what could have been a smooth release. This is why UI testing, or user interface testing, is essential for any team aiming to deliver a flawless digital experience that keeps both users and stakeholders satisfied.
Table Of Contents
What is UI Testing?
UI testing (user interface testing) is the process of checking whether the visual and interactive elements of a software application function as intended. It ensures the look, feel, and behavior match design specifications. For example, an online booking site might lose customers if search fields or buttons do not respond, highlighting how crucial UI tests are to a business.
Commonly Tested UI Elements
| Element | Description |
| Button | Triggers actions when clicked; should have proper placement and functions. |
| Text Field | Allows users to input data, such as usernames or emails. |
| Checkbox | Let users select or deselect options. |
| Dropdown Menu | Offers a list of choices from which users select one. |
| Modal/Popup | Overlays that seek user action or display important information. |
| Navigation Bar | Guides users through various sections of an application. |
| Slider | Enables users to select a value from a range visually. |
Benefits of UI Testing
- Prevents Costly Errors: UI testing identifies visual and interactive issues before the software reaches users. Catching these problems early reduces expensive fixes and emergency patches after release.
- Enhances User Satisfaction: A thoroughly tested UI ensures smooth and intuitive interactions, minimizing user frustration. This leads to higher engagement and positive feedback from users.
- Protects Brand Reputation: By eliminating bugs before launch, UI testing helps maintain a polished and professional image. Consistently delivering a stable interface builds user trust and confidence.
- Improves Accessibility: UI tests verify that accessibility features like keyboard navigation and screen readers function properly. This makes the application usable for people with disabilities, broadening its reach and inclusivity.
Effective UI testing tools are essential for delivering reliable, user-friendly interfaces quickly and consistently, as manual testing alone cannot keep pace with modern software releases. For a curated overview of the best options available, explore a comprehensive list of user interface testing tools.
UI Testing Vs. UX Testing
UI/UX testing is often confused with each other. Here’s a clear distinction between them:
| Aspect | UI Testing | UX Testing |
| Focus | Screens, buttons, visual layout | Overall user experience, emotions |
| Goal | Ensure interface works as designed | Ensure users achieve goals comfortably |
| Methods | Functional checks, visual validation | Surveys, usability tests, user feedback |
| Tools Examples | Selenium, Testsigma | Hotjar, UserTesting.com |
Types of UI Testing
- Manual UI Testing
Manual UI testing is the traditional approach to user interface validation, where testers interact with the application personally to uncover issues. It relies on human intuition and exploration to ensure each visual and interactive element behaves as expected. This approach is ideal for early-stage projects, prototypes, or situations where nuanced observation is required.
What Manual UI Testing Does:
- Testers actively click, type, and navigate through the UI as end users would, checking buttons, forms, menus, and links for correct operation.
- They visually inspect screens for layout consistency, color schemes, text alignment, and readability.
- Manual checks help catch usability and accessibility problems that automated scripts may miss.
- Feedback is usually immediate, enabling quick fixes or design tweaks.
- Benefits: Easily adapts to new designs, helps catch complex visual/UX issues, and does not require scripting skills.
- Cons: Time-consuming for large projects, challenges in scaling, prone to human error, and hard to repeat tests consistently.
- Automated UI Testing
Automated UI testing uses specialized software to execute pre-defined scripts that mimic user interactions on the interface. This approach increases efficiency by running comprehensive checks quickly and repeatedly, particularly valuable for regression testing in large or frequently updated applications.
What Automated UI Testing Does:
- Scripts simulate user actions like clicks, text entries, form submissions, and navigation across multiple UI components and user flows.
- Automated tools can run these tests across browsers, devices, and platforms, increasing coverage.
- Easily integrates with CI/CD pipelines for rapid, continuous feedback after every code change.
- Detects issues early in the development cycle, reducing cost and effort in later stages.
- Benefits: Saves time, enables repetitive and large-scale checks, and improves reliability of UI validation.
- Cons: Initial setup can be lengthy, scripts may need frequent updates due to UI changes, and visual or subjective flaws may go undetected.
- Mobile UI Testing
Mobile UI testing focuses on verifying interfaces in mobile applications across devices, screen sizes, and operating systems. It addresses unique challenges such as touch gestures, device orientation, and mobile-specific behaviors.
What Mobile UI Testing Does:
- Tests mobile-specific interactions: taps, swipes, pinches, and hardware integrations like camera or GPS.
- Checks app appearance and behavior on different device brands, screen resolutions, and OS versions.
- Validates responsiveness, performance, and stability under various network and device conditions.
- Ensures usability for accessibility features like voice commands and screen readers.
- Benefits: Helps guarantee a consistent experience for all users regardless of device, catches device-specific bugs, and improves brand reputation on app stores.
- Cons: Devices and OS fragmentation can make coverage complex and resource-intensive, and real device testing can be costly.
Also Read: automated mobile app testing!
- Web UI Testing
Web UI testing ensures that websites work flawlessly for users regardless of their browser, device, or environment. It covers both the visual rendering and the interactive functionality of web applications.
What Web UI Testing Does:
- Executes cross-browser checks to ensure UI stability and fidelity in Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari, etc.
- Validates responsive design, confirming that layouts and elements adjust smoothly across desktops, tablets, and phones.
- Verifies navigation, dynamic elements, pop-ups, forms, and integration points work as intended.
- Tests for accessibility standards, such as keyboard navigation and screen reader compatibility.
- Benefits: Delivers a reliable, consistent web experience, reduces user frustration, and boosts conversion and engagement.
- Cons: Can require maintenance as browsers and devices evolve, and handling dynamic content can sometimes make automation brittle.
UI Testing Process
1. Requirement Analysis
- Review annotation, wireframes, and design documents to identify UI features needing validation.
- Collaborate with developers/designers to clarify functional and visual expectations.
2. Identify Test Scenarios
- List all actionable elements (forms, buttons, navigations).
- Consider common user journeys, edge cases, and integration points.
- Prioritize scenarios based on business and user impact.
3. Prepare Test DATA
- Create sample inputs covering typical, boundary, and negative cases (e.g., valid/invalid email addresses, long strings).
- Validate against multilingual, special characters, and other localization needs.
4. Write Test Cases OR Scripts
- Document manual test steps in detail, clear actions and expected outcomes.
- For automation, code scripts reflecting user behavior with assertions for both functionality and visuals.
- Link cases to requirements for traceability.
5. Execute Tests
- Perform manual UI checks or run automated scripts across target platforms and browsers.
- Note down observed defects, even minor misalignments or inconsistencies.
6. Log and Track Defects
- Use a defect tracking tool to record bugs, with screenshots and steps to reproduce.
- Categorize issues by severity or impact.
7. Re-Test and Review
- After fixes, repeat affected UI tests to ensure defects no longer exist.
- Compare test results with baseline/success criteria.
8. Regression Testing
- Re-run complete or critical UI test suites after UI changes to ensure no previous functionality breaks.
- Regularly update regression tests to include new features or changes.
9. Reporting and Feedback
- Summarize results, what passed, what failed, what needs attention.
- Share actionable feedback with development and design teams.
10. Continuous Improvement
- Refine test cases based on bugs found and new features added.
- Review process regularly for gaps and optimize coverage.
Challenges in UI Testing
- Frequent UI Changes: Agile development often brings design tweaks that break test scripts.
- Cross-platform Complexity: Ensuring uniformity across devices and browsers adds layers of difficulty.
- Dynamic Content: Content that loads dynamically can make web UI testing brittle.
- Test Maintenance: Updating UI tests after interface updates can be tedious without robust automation.
- Human Bias: Manual testing may miss subtle visual regressions.
Best Practices of UI Testing
- Automate Early and Often: Start with automation for stable UI elements to reduce manual effort.
- Focus on Critical Paths: Prioritize tests for features impacting the most users.
- Use Data-Driven Tests: Test UI behavior with diverse data for realistic coverage.
- Leverage Visual Validation Tools: Compare screenshots to catch minor visual discrepancies.
- Regularly Update Tests: Review scripts after UI updates to avoid outdated checks.
How Testsigma Can Help with UI Testing
Testsigma is an AI-powered, codeless test automation platform that lets you automate your entire testing workflow using specialized AI Agents, without writing a single line of code. As a unified platform, Testsigma supports testing across mobile, web, desktop, APIs, SAP, and Salesforce applications, so you don’t need to switch between multiple tools.
UI testing is critical because visual and functional consistency directly impact user satisfaction and business success. With Testsigma’s AI Agents running tests autonomously, you can complete your UI test cycles up to 10 times faster while reducing manual effort.
Here’s how Testsigma makes UI testing more efficient:
- Autonomous Testing: AI Agents intelligently execute tests on your behalf, managing complexities like dynamic controls and UI changes with minimal human intervention. This ensures faster, more reliable test execution.
- Easy Test Creation: Whether you prefer writing test steps in plain English using the Natural Language Processing (NLP) engine in Testsigma or generating tests automatically with the Generator Agent, Testsigma simplifies creating UI test cases, making it accessible for both technical and non-technical team members.
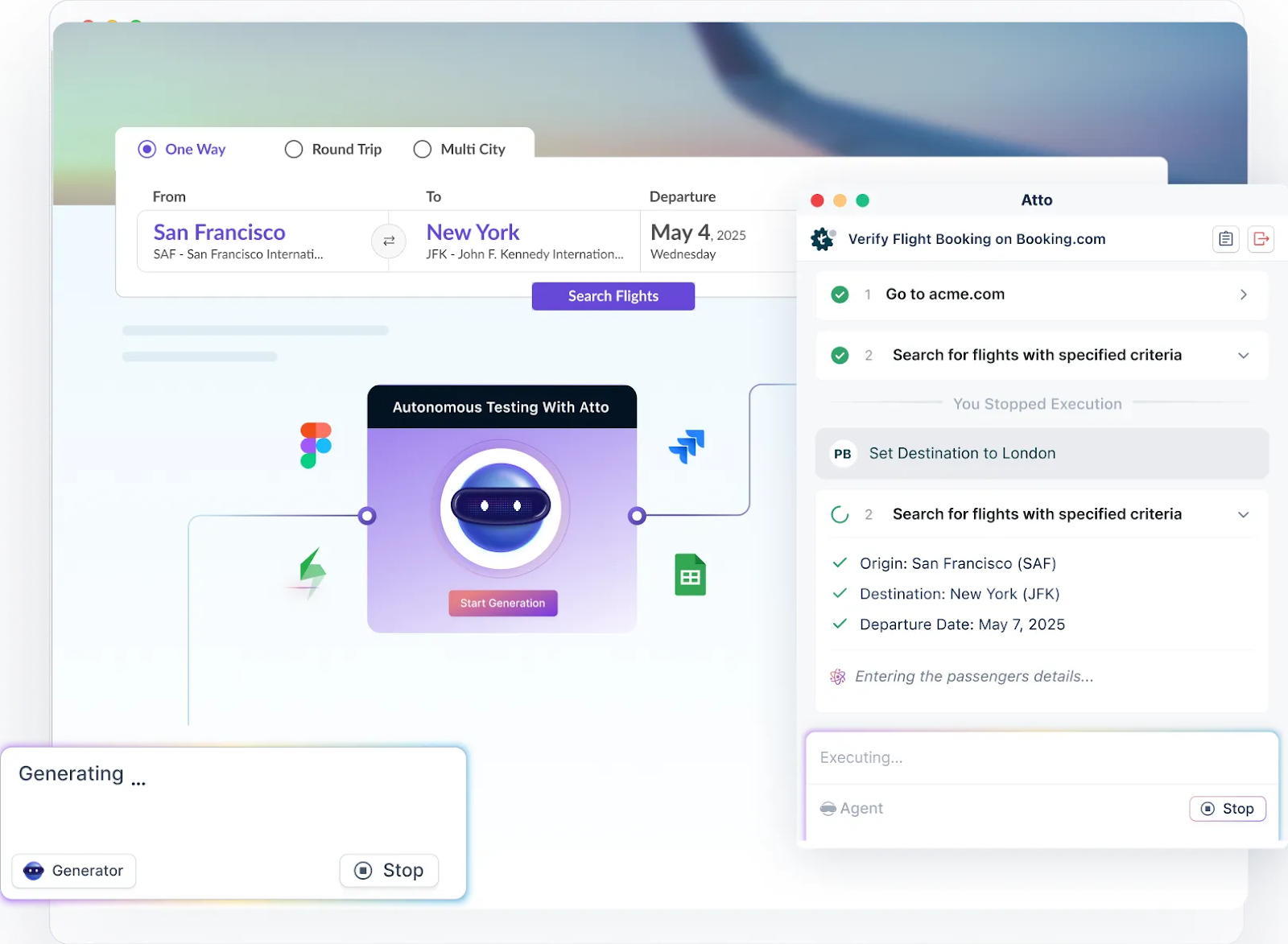
- Unified Platform: Testsigma enables seamless testing across mobile, web, desktop, APIs, SAP, and Salesforce without switching tools. In addition, manage your entire UI test lifecycle on one platform using the test management tool from Testsigma that supports manual, automated, and exploratory tests.
- Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing: Access over 3000 real browser, device, and OS combinations in the cloud, eliminating the need to maintain expensive physical device labs. This guarantees your UI works consistently across environments.
- Parallel Execution: Run multiple UI tests simultaneously to accelerate feedback and reduce overall testing time, helping you meet tight release deadlines.
- Self-Healing Tests: Powered by AI, Testsigma automatically detects changes in UI elements and updates your test scripts accordingly, minimizing test failures caused by UI modifications.
- 30+ Integrations: Easily connect with popular tools like JIRA, Jenkins, Azure DevOps, GitHub, and Bamboo to enable continuous testing and fast feedback loops within your DevOps pipelines.
- High Scalability: Testsigma’s cloud-based platform offers agentic autonomous test automation that scales from small teams to large enterprises, ensuring performance and reliability as your testing needs grow.
Conclusion
Every interaction your users have with a product leaves a mark on your brand. Solid UI testing practices catch scattered visual issues and prevent the kind of slip-ups that lose customers. The right tools and approach mean fewer surprises on release day, a win for any tester.
FAQs
UI testing in the context of API testing means validating the application’s user interface, often by ensuring that data provided by APIs is presented and functions correctly on the front end. While API testing focuses on the backend logic and data flow, UI testing checks that these backend results appear and operate as intended for the end user.
UI testing is a broader term covering all types of interfaces, including graphical interfaces (GUI), command-line interfaces, and more, while GUI testing focuses specifically on the visual elements like windows, buttons, and menus. In short, all GUI tests are UI tests, but not all UI tests are GUI tests.
UI testing is primarily a type of functional testing, as it validates whether the application’s user interface meets specified requirements and works as intended.
Manual UI testing does not require coding, but automated UI testing usually does, as it involves writing test scripts. However, codeless automation tools allow users to automate UI tests without coding knowledge.
