Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What is Manual Mobile App Testing?
- 3 Key Characteristics of Manual Mobile App Testing?
- 4 How to Perform Manual Mobile Testing Effectively?
- 5 Checklist for Manual Mobile App Testing
- 6 Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them in Manual Mobile Testing
- 7 Best Practices for Testing Mobile Apps
- 8 When Should You Choose Manual Mobile Testing for Mobile Apps Over Automation?
- 9 Why Use Testsigma for Mobile Testing?
Overview
What is Manual Mobile App Testing?
Manual mobile app testing is the process of validating a mobile application’s functionality, usability, and responsiveness by executing test scenarios directly on Android or iOS devices without automation tools.
How to Perform Manual Mobile App Testing?
Performing manual mobile app testing effectively involves:
- Understanding requirements to cover functional, UI, and performance expectations.
- Creating test cases for core features, edge cases, and user interactions.
- Setting up environments using real devices, emulators, or a real device cloud.
- Executing tests manually and documenting results with screenshots or logs.
- Logging defects with detailed reproduction steps and environment details.
- Retesting fixes and verifying regression areas to ensure stability.
Testing mobile apps manually remains a critical part of the quality assurance process, even in a world dominated by automation. It helps validate real user experience across different devices, screen sizes, and environments before scaling up automation efforts. This blog explores how to test mobile applications manually, its challenges, best practices, and more.
What is Manual Mobile App Testing?
Manual mobile application testing is the process of testing mobile apps manually without using automation tools. Testers perform actions on Android or iOS devices to validate the functionality, usability, and responsiveness of the applications.
Key Characteristics of Manual Mobile App Testing?
- Device-Based Execution: Manual mobile testing is performed directly on real devices or emulators without automation scripts.
- User-Centric Approach: It focuses on assessing the app from a real user’s perspective, capturing experience-based issues.
- Exploratory Testing: Testers often explore beyond defined test cases to catch hidden bugs.
- Flexible Testing: It allows real-time adaptation to test scenarios based on app behavior.
- Low Initial Setup: Manual mobile app testing requires minimal infrastructure compared to automated testing.
Explore the best mobile testing tools for automating mobile app testing!
How to Perform Manual Mobile Testing Effectively?
To test mobile applications manually, you need a well-structured process that adapts to different devices, platforms, and use cases.
Methods for Manual Mobile Testing
- Testing on Emulators or Simulators
Simulators (for iOS) and emulators (for Android) replicate device behavior on desktops, offering a convenient and cost-effective way to validate apps during early development.
- Testing on a Real Device Cloud
Real device cloud platforms allow testers to perform Android manual testing and iOS manual testing on hundreds of real devices remotely, enabling broader device coverage.
Process for Manual Mobile Testing
- Understand the Requirements: Start by gathering all functional, UI, and performance expectations for the mobile app.
- Create Test Cases: Define test scenarios covering core functions, edge cases, and UI interactions.
- Set Up the Environment: Choose between physical devices, emulators, or real device clouds for testing.
- Execute Tests: Perform each test case manually, documenting all steps, inputs, and outcomes.
- Log Defects: Record bugs with screenshots, steps to reproduce, and device/environment details.
- Retest and Verify Fixes: Re-execute failed cases after fixes and validate regression points.
Different Environments for Manual Mobile Testing
- Development Environment: Ideal for early-stage bug detection using emulators or simulators.
- QA/Staging Environment: Suitable for structured mobile manual testing before release.
- Production Environment: Used for smoke testing after deployment, usually on real devices.
Checklist for Manual Mobile App Testing
Before signing off on a build, use this checklist to ensure key areas are covered in your mobile application manual testing.
- App Installation and Launch: Confirm the app installs correctly, launches without crashing, and loads within an acceptable time.
- UI and UX Validation: Check for proper alignment, font size, button placements, and intuitive navigation.
- Device Compatibility: Test on different OS versions, screen sizes, and resolutions to ensure consistent behavior.
- Network Conditions: Evaluate app response under different network types, speeds, and offline mode.
- Battery and Resource Usage: Assess whether the app drains battery, uses excess CPU, or affects other apps.
- Permissions and Notifications: Verify that the app asks for required permissions and handles notifications as expected.
- Error Handling: Ensure meaningful messages are displayed for failures like login errors or failed transactions.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them in Manual Mobile Testing
- Device Fragmentation
Different devices with varying screen sizes, OS versions, and hardware configurations make mobile app manual testing complex.
Solution: Use a real device cloud or device lab to cover a wide range of devices efficiently.
- Time-Intensive Execution
Manual tests are slower to execute, especially when validating multiple scenarios repeatedly.
Solution: Prioritize high-risk and exploratory testing manually, while planning automation for repetitive cases.
- Limited Reproducibility
Bugs might not reproduce consistently across devices or sessions.
Solution: Document all steps, environment settings, and logs meticulously to aid debugging.
- OS Updates and App Crashes
Frequent OS updates can cause unforeseen crashes or UI issues in existing apps.
Solution: Include testing for latest OS versions in your Android app manual testing and iOS manual testing process.
- Human Error
Manual testing is prone to oversight due to fatigue or inconsistent execution.
Solution: Use structured test cases and checklists to ensure thorough and repeatable testing.
Automate Android app testing using the right Android testing tools?
Best Practices for Testing Mobile Apps
- Test on both emulators and real devices for balanced coverage.
- Prioritize manual mobile testing on critical user journeys and device configurations.
- Maintain a clear and updated test case repository to track coverage.
- Test app performance under varying network and battery conditions.
- Regularly update test scenarios as features evolve.
- Include regression testing in every cycle to catch unintended side effects.
- Collaborate closely with developers to understand technical constraints and expected behaviors.
When Should You Choose Manual Mobile Testing for Mobile Apps over Automation?
| Scenario | Manual Mobile Testing | Automation Testing |
| New Feature Validation | Recommended | Not ideal initially |
| Exploratory or Ad Hoc Testing | Best suited | Not applicable |
| Short-Term or One-Time Projects | Cost-effective | High setup cost |
| UX and UI Validation | Human-centric evaluation | Limited visual insight |
| Frequent UI Changes | Flexible and adaptive | Needs frequent script updates |
| Regression and Repetitive Scenarios | Time-consuming | Highly efficient |
| Mobile App Performance Testing | Not suitable | Best suited |
Confused about what to automate and what not to automate in testing?
Why Use Testsigma for Mobile Testing?
Testsigma is an AI-powered test automation platform that also supports mobile app testing for both Android and iOS. Testsigma makes test automation accessible to manual testers by allowing them to create test scripts in plain English using NLP-Engine and AI agents.
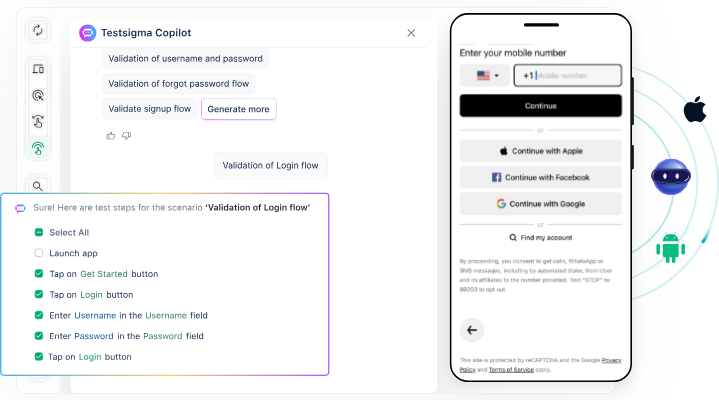
Key Features of Testsigma
- Unified Testing: Automate hybrid, native, and cross-platform mobile apps in one platform.
- Easy Transition to Automation: Manual testers can write automated test scripts without writing code.
- 3000+ Real Devices on the Cloud: Instantly test on a wide range of real Android and iOS devices, browsers, and OS versions.
- Parallel Testing Support: Run manual tests simultaneously on multiple devices to save time and improve coverage.
- Mobile Accessibility Testing: Ensure your app is accessible to users with diverse needs using accessibility test checks.
- Mobile Compatibility Testing: Validate your app’s behavior across different screen sizes, OS versions, and device configurations.
- Detailed Reports and Analytics: Get actionable insights with execution logs, screenshots, and test metrics to speed up debugging.
Conclusion
Manual mobile testing plays a crucial role in ensuring mobile apps deliver seamless and bug-free experiences across devices. While automation accelerates regression cycles, manual efforts bring essential human insight, especially during exploratory, UI, or first-time testing phases. A well-balanced testing strategy that includes manual testing is essential for mobile app success.


