Your product runs perfectly in the lab but falls apart the moment real customers touch it. That’s the pain every QA leader knows, and it’s usually a sign that in-house checks just can’t keep up.
Crowdsourced testing fills that gap by bringing real users, real devices, and fast, global feedback. We’ll unpack the benefits of crowdsourced testing, how to pick a crowd testing service for your needs, and how to apply crowdsourced testing best practices.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is crowdsource testing?
- 2 Key benefits of crowdsourced testing
- 3 How the crowdsourced testing model works
- 4 4 use-cases of crowdsourced testing
- 5 Pros and cons of crowdsource testing
- 6 Choosing the right crowdsourced testing service or platform
- 7 Challenges and how to mitigate them
- 8 Crowdsourced testing best practices
- 9 Crowdsourced testing as a competitive advantage for QA teams
- 10 FAQs on crowdsourced testing
What is Crowdsource Testing?
Crowdsourced testing is a QA approach where real users worldwide test your product in real-world conditions. For instance, a company like Airbnb will release a new mobile feature to a global pool of external testers before rolling it out live.
Those testers use their own devices, languages, and network conditions, often uncovering UX gaps, localization issues, and device-specific bugs that Airbnb’s internal QA might never encounter.
With a managed, crowd-sourced QA model, teams can tap into thousands of real-world environments on demand. This leads to faster bug discovery, broader device coverage, and more stable releases.
The crowdtesting market is projected to reach approximately USD 451,158.05 million by 2031, underscoring the growing importance of real-world testing in modern software development. When teams start scaling QA with crowdtesting and apply best practices, it acts as a powerful extension of their in-house QA, delivering a better UX and higher customer trust.
Curious about bug testing? Read our guide on the complete bug life cycle
Key Benefits of Crowdsourced Testing
While crowdsourced testing is great for catching early bugs, its advantages go much deeper. It enhances product quality by simulating real-world environments, engaging diverse users, and utilizing agile test cycles that in-house teams often struggle to match.
Here are the standout benefits:
- Broader device and environment coverage: Thousands of real devices, networks, and OS versions get involved, revealing issues that controlled labs simply don’t surface.
- Faster bug discovery at scale: Large tester pools work in parallel, helping teams identify critical defects within hours and accelerate release timelines.
- Fresh, unbiased user insights: External testers interact with your product like new customers, highlighting UX gaps and friction points internal teams may overlook.
- Stronger localization and regional accuracy: Native testers validate language, culture-specific flows, currencies, and compliance nuances across different markets.
- Flexible, on-demand resourcing: Crowdtesting ramps up instantly during high-pressure sprints and scales down just as quickly when cycles slow.
- Better regression and edge-case coverage: Distributed users encounter rare scenarios and inconsistent behaviours, thereby strengthening overall stability and reducing unexpected failures.
- Reduced QA overhead and infrastructure cost: Teams achieve wider coverage without hiring additional QA staff or maintaining costly device labs.
When these strengths come together, teams move faster, catch more issues, and ship products that feel ready for real users from day one.
How the Crowdsourced Testing Model Works
A structured crowdsourced testing model runs in a clear sequence from tester selection to final integration. Below are the steps most QA teams follow when working with crowd testing services or managed crowd-sourced QA partners.
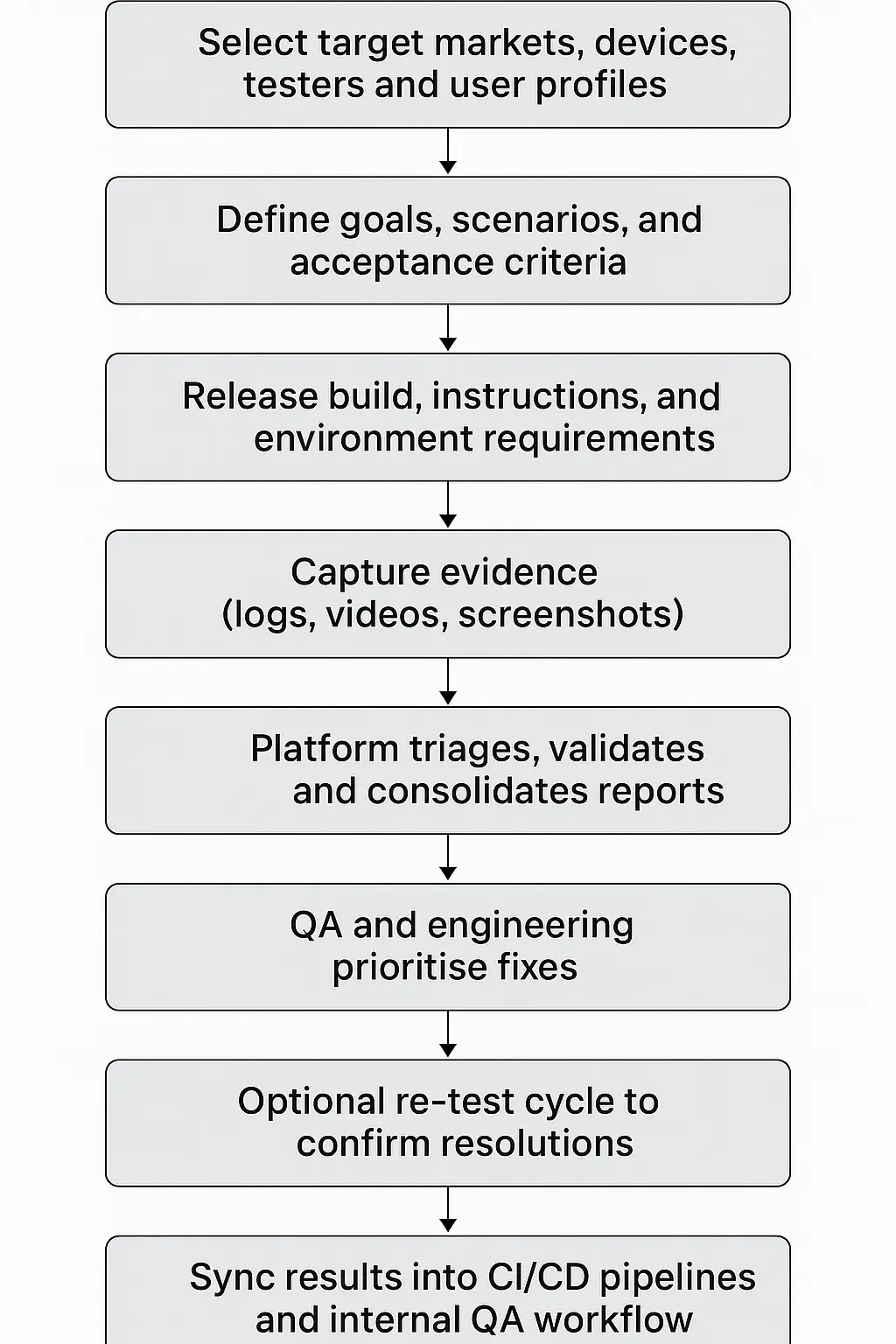
Here’s how the full workflow typically unfolds.
Vetting and Managing a Global Tester Pool
Platforms maintain large communities of pre-qualified testers across regions, devices, OS versions, and domains. Managers filter this pool based on skills, languages, accessibility needs, or market relevance. Strong tester curation ensures reliable reports and consistent testing quality for every cycle.
Defining Test Objectives, Device/user Profiles, and Environment Setup
Before the cycle begins, teams clarify what the test must achieve, such as functional checks, UX validation, localization accuracy, or insights into real-user behavior.
Requirements include device types, bandwidth conditions, OS versions, or geo-specific testers. Clear objectives improve the precision of real-user crowd testing and reduce noisy, irrelevant feedback.
Test Execution, Reporting, Feedback Loop, and Turnaround Time
Crowdsourced cycles move quickly once the build goes live, and the steps below show how a typical crowdsourced testing run unfolds.
- Crowd participants receive build notes, scenarios, and environment requirements from the crowd testing service.
- Testers run core flows, attempt edge cases, and capture evidence through screenshots, logs, or recordings.
- All findings move into a structured reporting layer used in managed crowd-sourced QA cycles.
- Project managers validate reproducibility, filter duplicates, and prepare a clean, developer-ready issue list.
- Turnaround times remain fast, with a few hours for light checks and 24–48 hours for more comprehensive testing rounds.
Blending Results into CI/CD, QA Workflows, and Internal Processes
Crowdsourced findings integrate with Jira, Azure DevOps, GitHub Issues, or whatever tracking system the team uses. Results feed directly into sprint cycles, regression suites, and automation plans. Internal QA remains in control of prioritization, while crowdtesting acts as an extension that broadens coverage and fills blind spots.
4 Use-Cases of Crowdsourced Testing
Crowdsourced testing has evolved into a flexible QA layer used across product, engineering, and CX teams. It adapts to different stages of the lifecycle, different markets, and different testing goals. Below are the most valuable ways companies use crowdtesting today.
1. Scaling Windows Releases with Global Device Insights (Microsoft)
Crowd participants help Microsoft uncover unpredictable behaviour across rare hardware combinations, older chipsets, and unusual driver stacks. Engineers receive findings from real devices they would never include in internal labs. Crowdsourced testing becomes a source of “hidden environment” coverage that improves system stability at scale.
2. Validating Country-Specific Booking Journeys at a Global Scale (Airbnb)
Airbnb taps regional testers to walk through real payment steps, local copy, and cultural UX norms. Testers highlight issues tied to language, currency formats, and location logic before a major rollout. Crowd testing services provide the product team with clarity on how launches are perceived in each market.
3. Uber – Real-World Network and Device Variability
Uber depends on real-user crowd testing to simulate unpredictable city conditions. Testers use mid-range Android phones, unstable networks, and crowded urban routes to reveal GPS drift, OTP delays, and lag in the driver app. The findings guide engineering teams toward fixes that directly impact on-time rides.
4. Spotify – Behaviour across Headphones, Bluetooth Devices & Car Systems
Spotify runs crowdsourced testing for software to understand how playback works across Bluetooth speakers, car infotainment systems, wired headphones, and OS updates. Testers report desyncs, pairing failures, and volume inconsistencies. This helps Spotify maintain smooth listening experiences across thousands of device ecosystems.
Pros and Cons of Crowdsource Testing
While crowdsourced testing offers wide coverage, real-user insights, and rapid cycles, it also presents a few drawbacks that teams should be aware of.
Below are the pros and cons so you can decide whether crowdtesting services and crowd-sourced QA fit your product and release workflow.
| Pros of crowdsourced testing | Cons of crowdsourced testing |
| Massive real-user coverage across devices, OS versions, networks, and regions – ideal for crowdsourced testing for software targeting global markets. | Limited control over test environments, since testers use personal devices and real-world setups. |
| Rapid execution through parallel testers, helping teams speed up cycles and scale QA quickly with crowdtesting. | Varying skill levels across testers may introduce noise unless the platform has strong vetting. |
| Unbiased UX insights from fresh users who spot friction points internal teams miss. | Security considerations for sensitive builds unless NDAs, private groups, or restricted access workflows are used. |
| Accurate localization and cultural validation from native testers is essential for multi-country launches. | Higher noise in reports if test objectives or acceptance criteria are unclear. |
| Flexible, on-demand scaling without hiring full-time QA staff or investing in device farms. | Less ideal for deep system-level or hardware-integrated testing, where controlled labs are necessary. |
| Cost-effective expansion of test coverage through managed crowd-sourced QA instead of internal scaling. | Limited diagnostic visibility compared to structured lab logging tools. |
Products that rely on a global reach, stable UX, or varied device environments benefit significantly from crowdsourced testing. If your priorities lean toward speed, accuracy, and real-world scale, crowdtesting aligns perfectly with a modern QA workflow.
Choosing the Right Crowdsourced Testing Service OR Platform
Picking a crowdsourced testing partner becomes much easier when you know exactly what to evaluate.
Below are the core criteria QA managers rely on when assessing crowd testing services:
- Tester pool size and diversity: Look for verified testers across regions, devices, OS versions, languages, and accessibility profiles.
- Device and platform coverage: Ensure support for mobile, web, IoT, smart TVs, wearables, gaming consoles, or any niche environments you require.
- Geographic reach: Regional testers are crucial for ensuring localization accuracy, seamless payment flows, compliance, and culturally sensitive UX.
- Reporting quality: Prioritize platforms with clear steps to reproduce, severity tagging, device metadata, screenshots, logs, and triage validation.
- Integration support: The service should seamlessly integrate with Jira, Azure DevOps, GitHub Issues, and your CI/CD pipelines.
- Cost model flexibility: Options usually include per-bug, per-hour, per-cycle, subscription, or enterprise fixed-fee, so choose based on release volume.
- Triage and re-test quality: Strong filtering and re-validation ensure engineers work only with actionable reports.
- Turnaround speed: Fast cycles (hours, not days) matter for agile teams pushing frequent releases.
If you’re still unsure whether in-house QA, outsourced testing, or crowdsourced testing fits your needs, the comparison table below will help you see the trade-offs at a glance.
| Model | Strengths | Limitations | Best for |
| In-house QA | Full ownership, deep product context, tight collaboration | Limited device diversity, slower scale, and high staffing cost | Complex systems, heavy regression, long-term maintenance |
| Outsourced QA (Traditional vendors) | Predictable capacity, structured process | Less real-user diversity, slow iteration, and high long-term expense | Enterprise setups needing long-running QA support |
| Crowdsourced testing | Global coverage, fast execution, real-user environments, scalable, and cost-efficient | Lower environment control requires precise scoping | Multi-country apps, mobile-first products, UX-heavy flows, rapid releases |
Want to automate all this? Testsigma’s crowd testing automation handles it end-to-end
Challenges and How to Mitigate Them
Even though crowdsourced testing unlocks massive coverage and real-user insight, it also introduces challenges teams should prepare for. Here are the most common issues QA leaders face when working with crowd testing services, along with practical ways to mitigate them.
1. Variable Tester Quality and Inconsistent Reporting
Crowd pools often include testers with different skill levels, which can create noise in reports or incomplete findings during crowd-sourced QA cycles.
Mitigation: Choose platforms with strict vetting, certification programs, skill-based routing, and multi-level reviewer checks. Provide detailed scenarios, expectations, and evidence requirements to ensure consistent, high-quality reports.
2. Confidentiality and DATA Security Concerns
Sharing builds outside your organization introduces risk, especially for sensitive apps, financial testing flows, or early-stage features tested through crowdsourced testing for software.
Mitigation: Work with platforms that enforce NDAs, device verification, IP tracking, and encrypted build distribution. Utilize masked data, sandbox environments, and region-specific access controls for enhanced protection.
3. Overwhelming Volume of Feedback
Large tester groups can generate hundreds of reports, making it hard to sift through the noise to find truly actionable bugs. This is common during exploratory real-user crowd testing.
Mitigation: Use structured triage workflows, assign severity tags, merge duplicates, and rely on platform-driven validation layers. Define roles such as QA handles triage and engineering handles prioritization to keep feedback organized.
4. Difficulty Integrating Results into Existing QA Workflows
Crowdsourced cycles move fast, but internal teams may struggle to map results into Jira, CI/CD pipelines, or sprint plans.
Mitigation: Pick crowd testing services that support native integrations with Jira, GitHub, Azure DevOps, and automation tools. Align cycles with sprint cadence, define ownership for each issue type, and use re-test loops before promoting builds.
Handled well, these strategies transform challenges into predictable, manageable steps, enabling your crowdsourced testing model to operate smoothly and enhance your overall QA system.
Crowdsourced Testing Best Practices
To get reliable outcomes from crowdsourced testing, teams need structure, clarity, and the right partner. Below are practical guidelines that keep crowd-sourced QA efficient and consistent.
- Set clear goals and scope: Define devices, regions, user profiles, and coverage needs before launching a cycle.
- Use a hybrid model: Combine in-house QA depth with crowd testing services for real-user diversity.
- Select the right engagement style: Open crowd, managed platform, or hybrid, depending on release speed and risk.
- Standardize triage and reporting: Create formats, severity rules, and feedback loops to avoid noise.
- Enforce strong security: NDAs, masked data, sandbox builds, and governance checks for safe external testing.
- Work with vetted testers: Pick platforms with device verification, skill assessments, and domain expertise.
A setup built on these principles keeps your crowdsourced testing model predictable, scalable, and aligned with long-term QA goals.
Crowdsourced Testing As a Competitive Advantage for QA Teams
Crowdsourced testing provides QA teams with broader coverage and faster feedback by engaging real users across various devices, regions, and networks.
The model enhances software quality by identifying issues that internal teams may overlook, particularly in UX, localization, and diverse real-world conditions. Pairing in-house QA with trusted crowd testing services creates a balanced, scalable approach that supports rapid releases.
Many parts of crowd-sourced QA can also be automated, reducing manual work and cutting operational costs. To do this, use a no-code testing platform that centralizes workflows and accelerates every cycle. This combination delivers stronger releases with far less effort.
FAQs on Crowdsourced Testing
Outsourced testing relies on a fixed vendor team, while crowdsourced testing uses a global, on-demand tester pool for broader devices, regions, and real-user environments.
Crowd-sourced QA isn’t ideal for highly confidential builds, hardware-dependent systems, or deep system-level testing that requires controlled lab conditions.
Most crowd testing services deliver initial results within a few hours, with full cycles typically completed in 24–48 hours.
Quality depends on platform vetting and triage workflows; strong crowdsourced testing models deliver both high-quality insights and scale, not just volume.
Use NDAs, sandbox builds, encrypted distribution, and vetted testers through secure crowdsourced testing for software platforms.
