Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What Is Usability Testing?
- 3 Why Usability Testing Is Critical For Software Success
- 4 Types of Usability Testing Methods
- 5 When And How Often To Conduct Usability Testing
- 6 Step-by-Step Guide To Conducting Usability Testing
- 7 Common Usability Testing Challenges And Solutions
- 8 Measuring Success: Key Usability Testing Metrics
- 9 Top 8 Benefits of Website Usability Testing
- 10 Testsigma for Automating Your Usability Tests
- 11 Summary
- 12 Frequently Asked Questions
Overview
What is usability testing?
Usability testing is a user-focused method where real people interact with a product to uncover design, functionality, and overall experience issues. It’s iterative, behavior-driven, and ensures products are intuitive, efficient, and user-friendly.
Types of usability testing
- Explorative Testing – Identify early design issues and gather user insights.
- Comparative Testing – Compare two products or versions to see which performs better.
- Assessment Testing – Measure task success, time, and error rates.
- Validation Testing – Confirm usability before product launch.
Challenges in usability testing
- High Time and Cost Investment – Usability testing can be resource-intensive, especially with larger user groups.
- Recruitment Challenges – Finding representative users is difficult but essential to avoid biased insights.
- Defining the Right Scope – Testing everything isn’t feasible, so identifying the most critical features and user flows is key.
- Data Reliability Issues – User bias, rushed feedback, or altered behavior (Hawthorne Effect) can impact the accuracy of results.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability testing is a user-centered evaluation method where real people interact with a product to reveal design, functionality, and overall experience issues. Unlike automated tests, it requires human input to understand how easily users can achieve their goals, though parts like data tracking and analysis may be automated. It’s not a one-time task but an iterative process that helps refine products throughout development.
Usability testing isn’t about opinions, popularity, or replacing user research; it’s about observing real behavior to improve usability. While it doesn’t guarantee perfection, it reduces flaws, boosts user satisfaction, and ensures products align with audience needs. It is applicable to websites, web automation, apps, services, and even physical products, and it ensures that technology is functional and truly user-friendly.
Also Read: mobile usability testing
Why Usability Testing is Critical for Software Success
Usability testing is necessary to ensure that a product, website, or application is intuitive, efficient, and aligned with user expectations. Its primary purpose is to evaluate how easy it is for the target audience to complete tasks and interact with the product. With website testing and observing real users, teams gain valuable insights into pain points, frustrations, and needs, allowing them to refine design, navigation, and functionality.
The benefits of usability testing go beyond fixing issues; it directly impacts business success:
- Improved User Experience: Creates seamless, user-friendly interactions that enhance satisfaction and engagement.
- Reduced Development Costs: Detects and fixes issues early, avoiding expensive redesigns post-launch.
- Increased Conversion Rates: Streamlines calls-to-action and purchase flows, boosting customer acquisition.
- Better Brand Perception: Positive experiences foster loyalty and retention.
- Competitive Advantage: Identifies gaps competitors may overlook, differentiating your product.
- Enhanced SEO Results: User-friendly sites perform better in search rankings.
- Efficient Navigation: Helps users quickly find what they need with minimal effort.
- Increased Revenue: Smooth user journeys drive conversions and long-term growth.
In short, usability testing bridges the gap between design intentions and real-world user behavior, making it a cornerstone of software and business success.
Types of Usability Testing Methods
Usability testing can take many forms, depending on the goals, stage of development, and depth of insights required. Below are the most common types:
- Explorative Testing
Done in the early design phase, this type helps uncover how users understand features, navigate prototypes, and where they face challenges. It provides valuable direction before heavy development work begins. - Comparative Testing
Users complete tasks across two or more products or versions of the same product to evaluate which delivers a better user experience. This helps benchmark usability and guide design decisions. - Assessment Testing
Focused on measuring task performance, this type tracks success rates, errors, and time on task. It provides objective data on usability strengths and weaknesses, enabling teams to refine workflows. - Validation Testing
Conducted at the end of development, validation testing ensures the final product meets usability goals, is intuitive, and is ready for release. - Moderated Testing
A facilitator observes and guides users as they complete tasks, either in a lab or remotely. This is ideal for collecting detailed feedback and exploring user thought processes. - Unmoderated Testing
Users complete tasks independently, which are often recorded for later analysis. It’s scalable, cost-effective, and suitable for quick insights. - Card Sorting & Tree Testing
These methods reveal how users group, label, and navigate information, helping optimize site or app architecture. - Clickstream Analysis
By tracking user interactions, this type identifies browsing patterns, navigation issues, and hidden friction points. - Eye-Tracking & Heatmaps
Measures where users look, click, and focus attention are proper for optimizing layouts and calls to action. - A/B Testing
Compares two design versions to determine which performs better regarding usability and conversions. - Guerrilla Testing
Quick, informal testing with readily available participants like colleagues or people in public spaces to gather immediate feedback on early prototypes.
When and How Often to Conduct Usability Testing
Usability testing should be done early and often throughout the development process. Running tests in the early stages helps identify problems before they become costly to fix, while testing before launch ensures a smooth user experience from day one. Post-launch, it’s equally important to conduct usability testing after significant updates to confirm that new features are intuitive and do not compromise existing functionality.
While usability testing relies heavily on human observation and feedback, certain aspects can be automated. Data collection, user behavior tracking, and repeatable test cases identified during usability sessions can be automated to save time and ensure consistency. These automated checks are especially valuable in regression testing, helping teams maintain usability standards as the product evolves.
Step-by-step Guide to Conducting Usability Testing
Conducting usability testing involves careful planning, execution, and follow-up. The process can be broken down into phases with practical steps to ensure meaningful results.
1. Planning
- Define objectives: Set clear goals for what you want to learn, such as navigation ease and task completion rates.
- Identify the target audience: Recruit participants who represent your real users.
- Design tasks and scenarios: Create realistic goals for participants to complete.
- Choose the testing style and method: Moderated, unmoderated, remote, or in-person testing.
- Prepare tools and environment: Select the right testing platform, set up recording tools, and outline your usability testing plan.
2. Conducting
- Introduce the test: Brief participants about the purpose without influencing their behavior.
- Run the sessions: Observe participants as they complete tasks, noting where they succeed or struggle.
- Encourage open feedback: Ask questions to capture thoughts, frustrations, and expectations.
- Record sessions: Video, audio, or screen recordings help with detailed analysis later.
3. Analyzing
- Review results: Review notes, recordings, and metrics such as task success rates, time on task, and error counts.
- Identify patterns: Spot recurring issues or behaviors that highlight usability problems.
- Prioritize findings: Focus first on issues that most impact user success and satisfaction.
4. Reporting & Action
- Share results with stakeholders: Present findings in a clear, non-technical format.
- Propose solutions: Suggest design improvements or workflow changes.
- Develop a usability report: Include objectives, participants, tasks, metrics, key findings, and actionable recommendations.
- Plan future iterations: Address anomalies, track progress, and schedule follow-up usability tests to validate fixes.
Common Usability Testing Challenges and Solutions
Usability testing is one of the most effective ways to validate user experience, but like any process, it has strengths and weaknesses.
Pros
- Early issue detection: Identifies usability problems before launch, saving time and reducing costly rework.
- Better user experience: Leads to higher satisfaction, increased adoption, and improved conversion rates.
- Lower support costs: Clearer interfaces reduce the need for extensive customer support.
Cons & Challenges
- Time and cost investment: Usability testing can be resource-intensive, especially with larger user groups.
- Finding the right participants: Recruiting representative users is complex but critical to avoid biased results.
- Selecting the right focus areas: Testing everything is impractical; identifying the most impactful features and flows is a challenge.
- Unreliable feedback: Users may rush through tests or provide feedback influenced by personal bias or rewards, making it hard to filter genuine insights.
- Hawthorne Effect: Users may alter their behavior when they know they are being observed, leading to inaccurate data.
- Incomplete coverage: Usability tests may miss edge cases or complex scenarios that real-world usage can expose.
- Data management issues: Feedback is often unstructured and filled with outliers, requiring careful filtering and analysis to extract meaningful insights.
Overcoming the Challenges
To maximize the value of usability testing, teams should:
- Recruit a diverse and representative sample of users.
- Focus testing efforts on high-impact areas of the product.
- Use multiple testing sessions and triangulate results to reduce bias.
- Combine qualitative feedback with quantitative data (task completion, error rates, etc.) for balanced insights.
- Apply iterative testing cycles to refine findings and continuously improve the product.
Measuring Success: Key Usability Testing Metrics
The effectiveness of usability testing is measured not just by identifying issues but by quantifying how well users can accomplish tasks. Success depends on both the metrics you track and the scenarios you test.
Key Metrics for Usability Testing
- Clear Objectives & Target Audience: Success starts with well-defined goals and testing participants who accurately represent end users.
- Appropriate Methods & Tools: Using the proper testing techniques and platforms ensures reliable and actionable results.
- Task Completion: Percentage of users who complete assigned tasks without assistance.
- Time on Task: How quickly users complete tasks, reflecting efficiency and ease of use.
- Error Rate: Number and type of errors users encounter while performing tasks.
- User Satisfaction: Qualitative feedback and standardized measures like SUS (System Usability Scale) or CSAT (Customer Satisfaction).
- Comprehensive Reporting: Findings documented in a structured, stakeholder-friendly format that drives design improvements.
- Iteration & Retesting: Continuous improvement cycle where fixes are implemented, validated, and refined over multiple rounds.
Top 8 Benefits of Website Usability Testing
Website usability testing is integral for businesses to maintain a user-friendly interface and enhance customer satisfaction. It provides significant benefits to a website, including:
- Improved User Experience – Usability Testing allows the identification of any issues that may make it difficult for users to navigate through your site.
- Increased Conversion Rates – Testing identifies issues with call-to-action buttons or purchase processes, improving conversion rates.
- Cost Savings – Early detection of problems ensures minimal expenditure on fixing them after launching the website.
- Competitive Advantage – Identifying user concerns that competitors are not addressing can provide a competitive edge.
- Enhanced SEO Results – Good usability directly translates into better Google rankings, which leads to more traffic from search engines.
- Efficient Navigation– A well-designed website promotes intuitive navigation, allowing users to find what they need quickly and hassle-free.
- Better User Engagement – Users with a satisfying platform experience can return or recommend it to others.
- Increased Revenue Generation– A user-friendly website leads customers further down the conversion funnel, thus resulting in higher revenue generation potential for online businesses.
Testsigma for Automating Your Usability Tests
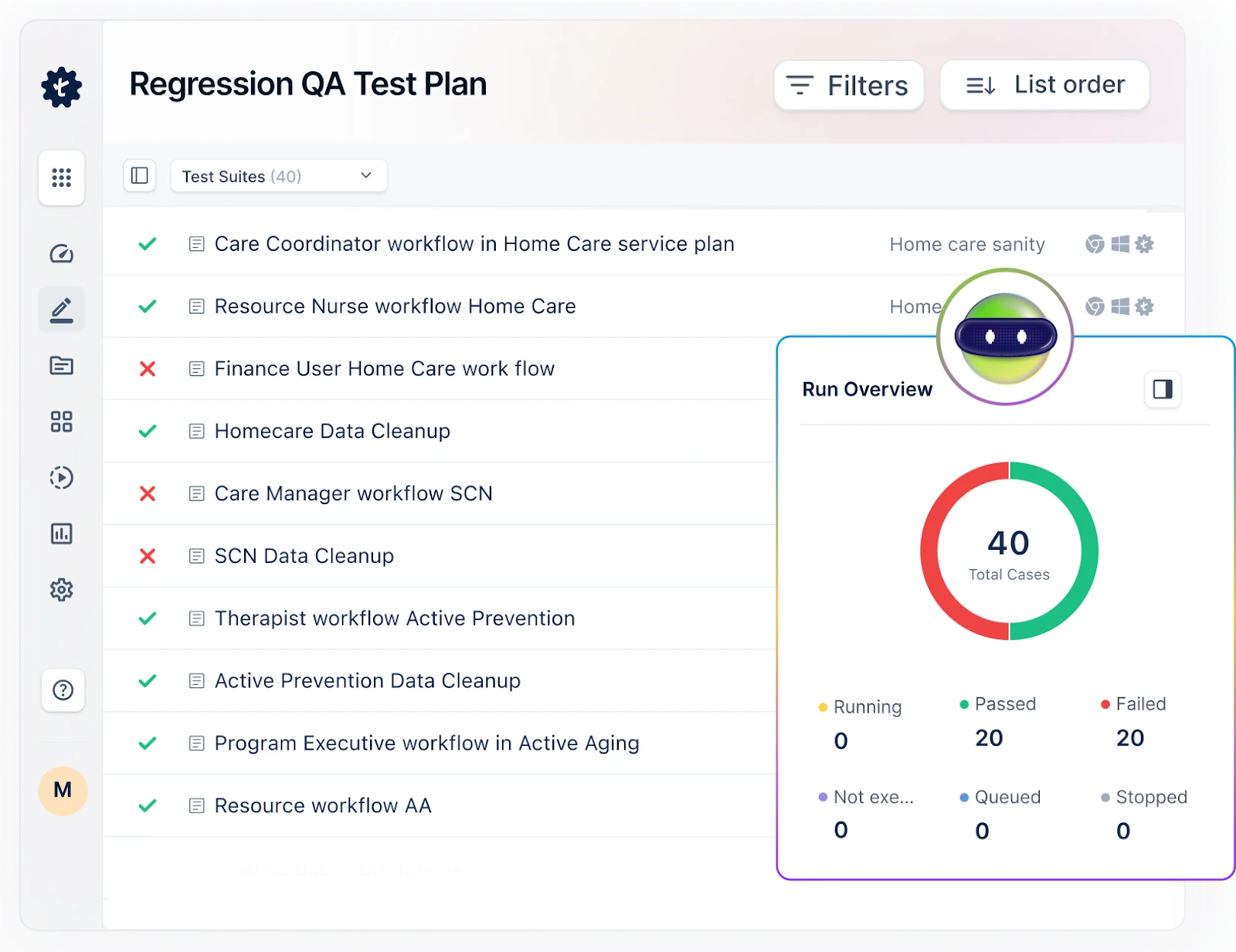
Testsigma is a complete test automation tool that makes usability testing easier. It helps teams automate and simplify test scenarios. The platform has a simple interface that lets us create reusable test cases. These test cases can be run on different platforms and devices, so we can check the user experience consistently. By adding usability tests to the CI/CD pipeline, Testsigma improves teamwork and speeds up feedback, helping teams deliver software that is easy to use and of high quality.
How Testsigma Helps in Automating Usability Testing?
- No Code, Low Code: Testsigma is a no-code test automation tool that makes test case creation and maintenance as easy as writing simple English sentences.
- Centralized Test Management: We can create, manage, and run usability test cases in one place. This helps make sure tests are the same across different environments.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Testsigma lets us test on different devices and browsers. This simulates many user experiences, giving us accurate results. Testsigma lets you automate tests for web, mobile, desktop, and APIs from the same place.
- Real-Time Feedback: It connects to CI/CD pipelines, so usability tests run automatically. Feedback comes right away.
- Collaboration and Reporting: The tool gives detailed reports and metrics. This helps teams spot usability issues and work together to fix them.
- Reusable Test Cases: We can create test cases that we can reuse. This saves time and effort when doing the same usability tests over and over.
- User-Centric Test Execution: Testsigma focuses on real user actions, making the tests more relevant and effective in checking usability.
Summary
In summary, Usability Testing assesses a product’s ease of use, efficiency, and satisfaction by observing users engaging in specific tasks.
The goal is to uncover any usability issues preventing users from achieving their desired objectives efficiently. Through this blog, you can now understand Usability Tests provides valuable insights into how users interact with a product, identifying pain points and areas for improvement. By conducting this testing, companies can ensure that their products meet user needs and are optimized for usability.
Frequently Asked Questions
The number of users we need for usability testing can change depending on the test’s scope and goals. But, usually, 5 to 7 users are enough to find most usability problems. This is because after about five users, the number of new issues found goes down a lot. But for bigger systems or different user groups, we may need more users. It is important to balance the need for different feedback with our available resources. This way, we can get the best results from the test.
The main function of usability testing is to evaluate the effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction of a product or service for its users. It identifies and addresses usability issues early in the design process to improve overall user experience.
The five major components are learnability, efficiency, memorability, errors, and satisfaction.
Usability test results can be analyzed by first collecting, cleaning, and sorting the data in a specific format. Then, the team can collect issues that are commonly reported as separate sections and their own findings in another section. All these findings, along with the methods used, audience targeted, selection criteria, etc. can be added to the usability test report.
An effective usability test script should be able to accomplish the tasks required by the testers and not get into any technical details since users are not technical. An effective usability testing script is organized into various explicit steps that a user needs to perform. For instance, navigational steps, instructions to keep speaking about what they are doing, and providing regular feedback through comments or voice channels.

