System UI is the backbone of the Android user experience, encompassing everything visible on the device that isn’t part of any individual app, like the status bar, navigation bar, and lock screen. This guide clarifies what system UI is, highlights its key components, explores types and the special case of system UI Android, and details the purpose and use of the System UI Tuner for testers and developers alike.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Overview
- 2 What Is System UI?
- 3 Key Components of a System UI
- 4 Types of System UI
- 5 How Does System UI in Android Work?
- 6 Why Customize The System UI In A Software Testing Scenario
- 7 How To Use System UI?
- 8 What Is System UI Tuner?
- 9 Functions Of The System UI Tuner
- 10 Advantages Of Implementing System UI Tuner
- 11 How To Enable The System UI Tuner
- 12 How To Disable The System UI Tuner
- 13 How Testsigma Supports UI Testing
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 FAQs
Overview
What is System UI
System UI is the collection of all interface elements on an Android device that are separate from individual apps.
Types of System UI
There are various types of System UI depending on the Android version and manufacturer customizations. These include stock Android UI (pure Google version), OEM skins such as Samsung One UI, Xiaomi MIUI, and custom ROMs, each offering different features and visual styles.
How Does System UI in Android Work?
System UI runs as a system-level application whenever the device boots up, managing all non-app user interface elements. It interacts closely with Android’s system services to handle notifications, navigation, quick settings, and other core device visuals, ensuring seamless user interaction across apps and system features.
What is System UI?
System UI refers to all the visual and interactive elements built into an operating system that enable users to navigate and interact, except those in third-party apps. In simple terms, system UI covers everything users see on Android beyond apps, including the notification area, status and navigation bars, lock screen, and more.
Key Components of a System UI
System UI typically consists of:
- Status Bar: Displays notifications, battery, signal, and time.
- Navigation Bar: Home, back, and recent apps buttons.
- Lock Screen: The security or welcome screen when the device is powered on.
- Notification Panel: Pull-down tray for notifications and quick settings.
- Quick Settings: Toggles for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, flashlight, and more.
- Volume and Power Controls: On-screen overlays for adjusting sound and powering down.
- Split Screen and Picture-in-Picture: Multitasking interface elements on YouTube
- Screenshot and UI overlays: System-initiated popups, overlays, and more.
Types of System UI
The term system UI covers several layers and customizations in Android, each delivering unique experiences:
1. Stock Android (aosp System UI)
- The clean, minimal interface was originally designed by Google (Android Open Source Project). It features standardized navigation, a notification shade, and limited pre-installed apps.
- Best for smooth updates, minimal bloat, stability, and a “vanilla” feel.
2. Google Pixel UI
- Google’s proprietary skin for Pixel devices closely resembles stock Android with exclusive features like advanced AI, Call Screen, and Pixel-only design tweaks.
- Best for users wanting fast updates and extra Google-driven functionality, testers seeking a reference device.
3. Oem Skins
- Samsung One UI: Adds more customization and features (like theming, split-screen enhancements, device-specific widgets), but also extra pre-installed apps. Power users appreciate deep control, testers must note diverse behaviors.
- OPPO Color OS, OnePlus Oxygen OS: Feature-heavy, distinctive visuals, and robust customization, but sometimes introduce unique interaction flows.
- Xiaomi MIUI: Changes system gestures and interfaces to mimic iOS, with features like Game Turbo and separate notification handling.
- ASUS Zen UI & ROG UI: Zen UI is close to stock; ROG UI caters to gamers with overlays and performance controls.
- Sony Xperia UI: Simple, stock-aligned, with discreet Sony-only add-ons.
4. Custom Roms and Third-Party Launchers
- Community-driven firmware like LineageOS, or third-party launchers modifying look/behavior without root.
- Best for deep personalization, open-source testing, and experiment-centric automation.
5. Layout-Based Variants
- LinearLayout: Components align vertically or horizontally.
- RelativeLayout/ConstraintLayout: Sophisticated placement relative to other elements, essential for adaptive testing.
- FrameLayout, TableLayout, ListView, GridView: Populate overlays, tabbed panels, or scrolling content, altering UI event flows during tests.
Testers must be aware that each skin or layout can change gesture responses, notification handling, or overlay behavior, which is critical for exhaustive UI automation and compatibility.
How Does System UI in Android Work?
System UI in Android is an internal service responsible for all user interface elements that are not part of an app, ensuring consistency and a unified experience across the system, which is essential knowledge for efficient testing.
How System UI Works:
- System Process: Runs as a system-level application, initiated during device boot. It coexists outside user apps, handling core device visuals and user interactions.
- Handles Non-App UI: Manages notification bar, navigation bar, lock screen, quick settings, power menus, and system dialogs, relaying information and shortcuts irrespective of the foreground app.
- UI Thread Management: Integrates with Android’s UI thread to queue and process gestures, animations, and transitions, ensuring smooth device-wide operations.
- Notification Management: Listens for system and app events, posting notifications and quick actions in real time.
- Customization via Skins/Tuner: Accepts OEM or user customizations through system settings, third-party launchers, or the System UI Tuner, altering default behaviors for diverse device experiences.
- Stability & Security: Monitors app overlays, permissions, and restricts critical UI areas to thwart malicious manipulation, vital for automated UI testing reliability.
- Lifecycle Hooks: Responds to system changes (orientation, input source, display state), invoking onCreate, onStart, and other lifecycle methods to manage state persistence.
Why Customize the System UI in a Software Testing Scenario
Customizing the System UI is crucial for testers who need to:
- Simulate different user experiences: For example, hiding navigation controls for immersive testing.
- Adapt to various device states: Some devices have unique system UI behaviors due to OEM overlays, which automated tests must recognize.
- Verify notification and quick settings interactions: Ensures that app notifications or toggles work as intended when the device UI is customized.
- Accessibility testing: Testers can adjust UI elements to simulate various accessibility modes for comprehensive coverage.
How to Use System UI?
Using System UI usually means interacting with device-level forks or menus:
- For daily users: Adjust elements in Settings or the System UI Tuner if available.
- For testers and automation: Simulate UI changes using user interface testing tools that support easy automation to mimic real user behavior on different device skins.
- Manual steps: Pull down the notification tray, access quick settings, modify the status bar, etc.
What is System UI Tuner?
The System UI Tuner is a hidden settings menu, introduced in Android 6.0 (Marshmallow), enabling users and testers to customize parts of the system interface not exposed in standard settings. Think of it as an “advanced options” toolkit for status and navigation bar tweaks.
Functions of the System UI Tuner
With the System UI Tuner, users can:
- Enable or disable icons in the status bar (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.).
- Personalize navigation and status bars for cleaner or more informative layouts.
- Adjust the Quick Settings panel, rearranging tiles for convenience.
- Toggle dark or night mode.
- Manage Do Not Disturb preferences at a granular level.
Advantages of Implementing System UI Tuner
The System UI Tuner provides advanced controls for customizing the device interface. Its benefits go beyond just visual tweaks and are significant for both manual and automated testers:
- Custom Status Bar Icons
Hide or show specific notification and status icons, reducing clutter during smoke or regression testing and isolating specific system states for precise validation.
- Enhanced Accessibility Testing
Adjust system visuals (like contrast, layouts, quick toggles), simulating conditions for accessibility compliance or user groups with special needs, important for inclusive app QA.
- Streamlined Notification Management
- Immersive Mode Simulation
- Customizable Quick Settings
Rearranging tiles or adding/removing toggles allows simulation of real user setups, helping verify app behavior alongside different system states, from airplane mode tests to location permission scenarios.
- Rapid Troubleshooting and Debugging
Toggle UI elements and states during bug investigations, reproducing edge-case environments for faster resolution and repeatability in both manual and CI-driven automated pipelines.
- Consistency Across Devices and OS Versions
The Tuner helps normalize the test environment by reducing visual inconsistencies across different OEM skins or Android versions, resulting in less flaky automated tests.
By mastering the System UI Tuner, testers can create and validate real-world device scenarios, ensure greater coverage, and remove ambiguity in automation results, directly impacting product quality and user experience.
How to Enable the System UI Tuner
Steps to enable System UI Tuner (on Android 6.0/7.0, availability on later versions varies):
- Slide down the notification tray to open Quick Settings.
- Press and hold the gear icon at the top-right for a few seconds.
- Receive a message confirming the addition to Settings.
- Find System UI Tuner at the bottom of Settings.
This unlocks advanced customization options for both every user and test engineer.
How to Disable the System UI Tuner
To remove the System UI Tuner:
- Go to Settings > System UI Tuner.
- Tap the three-dot menu at the top right.
- Select “Remove from Settings” and confirm.
Disabling restores the default system UI, useful when tests or troubleshooting are finished.
How Testsigma Supports UI Testing
Testsigma is an AI-driven, codeless test automation platform that streamlines your entire testing workflow with intelligent AI Agents, eliminating the need for any coding. It offers a unified solution for testing mobile, web, desktop, APIs, SAP, and Salesforce apps, so you can avoid juggling multiple tools.
UI testing is vital as it ensures visual and functional consistency, which is critical to user satisfaction and business success. Testsigma’s AI Agents autonomously automate tests, reducing manual effort and enhancing reliability.
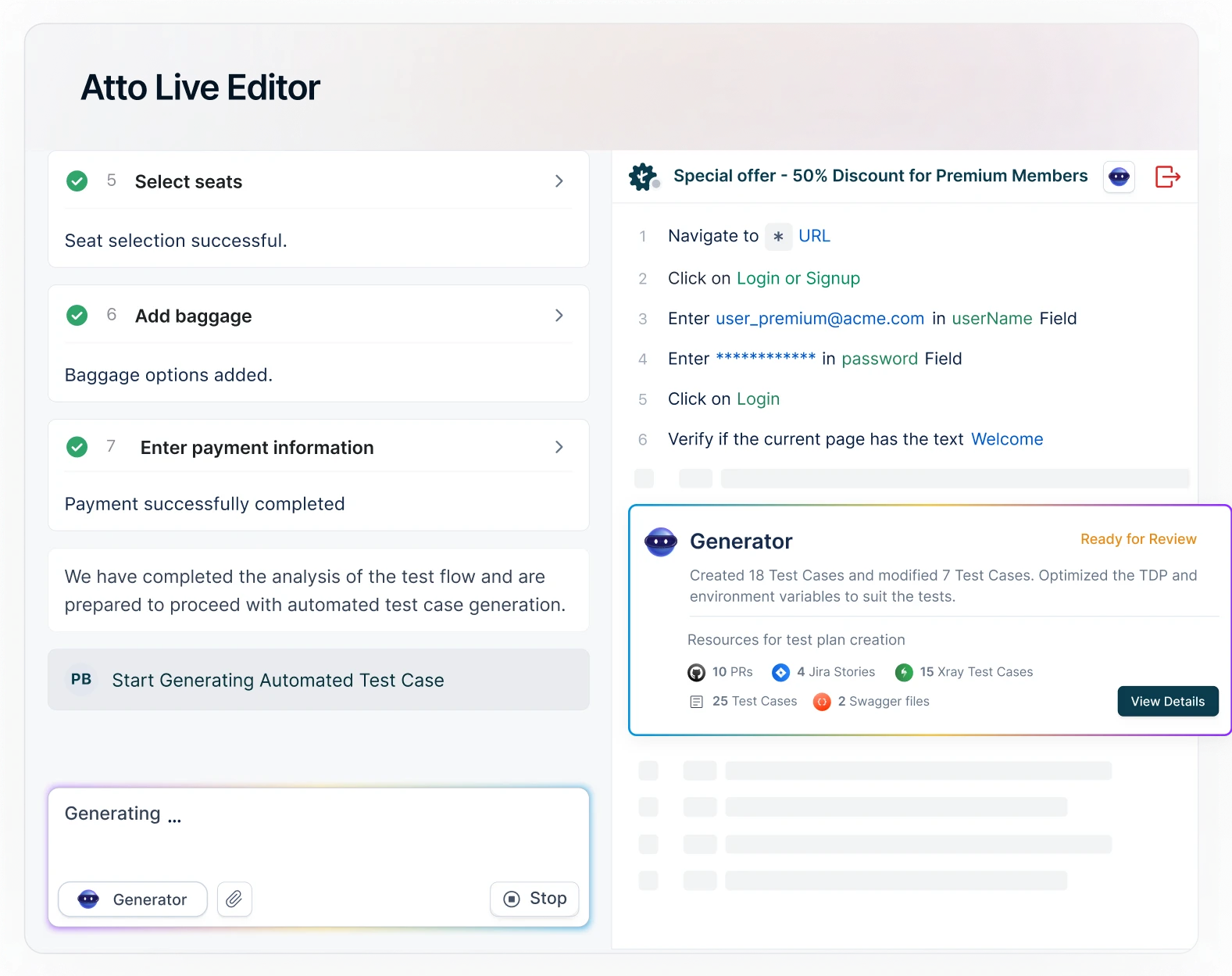
How Testsigma Enhances UI Testing Efficiency
- Autonomous Testing: AI Agents run tests independently, handling dynamic UI elements and minimizing manual input.
- Simple Test Creation: Create tests in plain English via NLP or auto-generate them with the Generator Agent, enabling easy access for technical and non-technical users.
- Unified Platform: Test mobile, web, desktop, APIs, SAP, and Salesforce on one platform.
- Cross-Browser & Device Testing: Access 3,000+ real browser and device combinations on the cloud without costly labs.
- Parallel Execution: Run multiple tests simultaneously to speed up feedback and meet tight deadlines.
- Self-Healing Tests: AI-powered script updates reduce failures caused by UI changes automatically.
- 30+ Integrations: Easily connect with tools like JIRA, Jenkins, GitHub, ensuring smooth DevOps pipelines.
- Scalability: Cloud-based platform scales effortlessly from small teams to enterprises, maintaining performance and reliability.
Conclusion
System UI is more than just a backdrop to Android apps, it shapes the entire device experience, from status bars to quick settings. For manual and automated testers, understanding what is system UI and its customization tools empowers more effective, comprehensive test coverage across devices and Android versions.
FAQs
System UI is a built-in Android service that manages core interface elements like the status bar, navigation controls, and notifications. It runs in the background to keep the device’s visual experience consistent and responsive. Apps and users interact with it constantly, but cannot remove it.
System UI affects how users receive app notifications and interact with device controls, impacting overall user experience. Testing ensures apps work correctly with different UI customizations and device skins. It helps catch issues with overlays, notifications, or navigation before release.
Yes, many modern Android System UIs include AI-based features like adaptive brightness, smart replies, and contextual suggestions. These enhance usability and personalize the user experience. Testers need to check how these AI elements interact with apps.
Users can customize the System UI by changing icon visibility, quick settings, themes, or using the System UI Tuner on supported devices. Device manufacturers often provide extra customization layers. Options vary based on Android version and OEM skin.


