Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
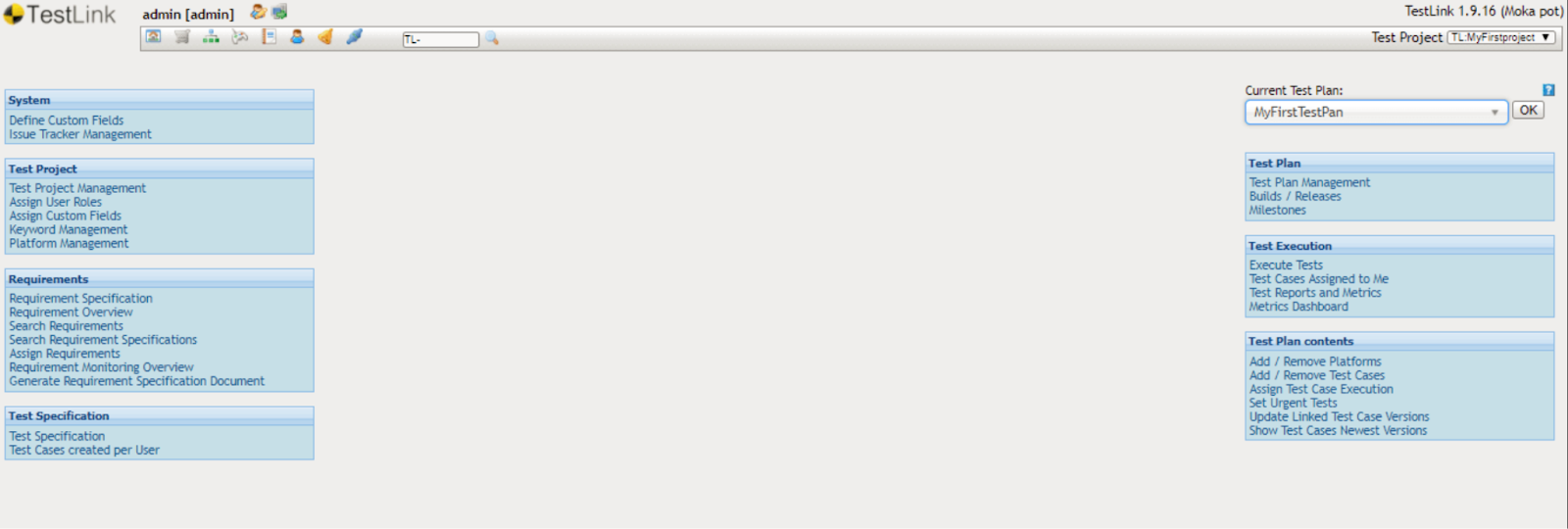
What is TestLink?
TestLink is an open-source test management tool used to document test cases, manage test plans, and execute tests manually. It allows QA teams to link requirements with test cases and track coverage throughout a release cycle. It also integrates with issue tracking tools like JIRA and Bugzilla, making it easier to connect failed tests with logged bugs. Built on PHP and MySQL, TestLink is often installed on a local or remote server and accessed via a browser.
Features of TestLink
TestLink provides several useful capabilities for managing tests efficiently. Below are its key features:
- Test Case Management
You can create detailed test cases with fields for preconditions, execution steps, and expected results. These cases are organized into test suites to help manage large volumes of tests.
- Test Plans and Test Suites
Test plans group test cases based on a specific release or cycle. Test suites offer a hierarchical structure for organizing and maintaining reusable test cases.
- Requirement Mapping
TestLink includes basic requirement management. You can link test cases to requirements, helping ensure that each functional requirement has corresponding tests.
- Integration with Bug Trackers
TestLink integrates with popular issue trackers like JIRA, Mantis, Bugzilla, and Redmine. When a test fails, you can file a bug directly to these tools from within TestLink.
- Test Reports and Metrics
It offers multiple built-in reports such as test execution results, test case coverage, and requirement-based test coverage. These are useful during project reviews.
- Role-Based Access
Different user roles can be created, such as testers, leads, and admins, with permissions for editing, executing, or managing projects. This controls access and improves collaboration in larger teams.
- XML-RPC API Integration
TestLink provides an API to push or pull data between automation frameworks or CI/CD pipelines. This is particularly useful for automated result logging.
- Web Interface
Being browser-based, TestLink allows teams in different locations to collaborate without needing any desktop installation.
Benefits of TestLink
TestLink remains in use for a reason. Below are the advantages that make the TestLink test management tool useful:
- Free and Open Source
One of the biggest pros is its open-source license. It offers all core test management features without any licensing fee.
- Centralized Test Repository
All test data is stored in a centralized repository, making it easier for teams to avoid redundancy and keep test cases up to date.
- Integration Support
The tool connects with popular issue tracking tools and can also be extended with automation results through the API.
- Traceability
With requirements-to-test-case mapping, teams can identify untested requirements and track test coverage more effectively.
- Platform Independence
TestLink runs on any platform that supports PHP and MySQL, offering flexibility across tech stacks.
Challenges of Using TestLink
Despite its strengths, the TestLink tool does have some limitations that teams need to consider before adopting it:
- Dated User Interface
The UI is functional but outdated. Navigation can be unintuitive for new users, and the lack of drag-and-drop or modern interactions can slow down workflows.
- No Native Automation Support
While the tool supports result submission via API, there is no built-in support for automation execution or self-healing test maintenance. This makes it harder to scale for automation-heavy teams.
- Complex Setup
Installing TestLink requires knowledge of PHP, MySQL, and web servers. There’s also manual effort involved in version upgrades and backups.
- Not Mobile-Friendly
TestLink’s interface is not optimized for mobile, which limits testing flexibility for users working across devices.
- Limited Collaboration Features
Modern test management tools offer real-time collaboration, comment threads, and versioning. These features are missing in TestLink, making teamwork harder.
How to Create Test Cases in TestLink?
Step 1: Log in and Select Project
Log in to TestLink and choose the project in which you want to create your test case.
Step 2: Navigate to Test Specification
Click on the Test Specification tab. This is where you manage test suites and test cases.
Step 3: Create a Test Suite (if Needed)
If there are no test suites yet, create one first:
- Click Create under Test Suite.
- Enter a Name and a Details/Summary describing the suite.
- Save it.
Step 4: Create a Test Case
- Select the desired Test Suite.
- Click Create Test Case.
- Fill in the following fields
- Test Case Title – Name of the test case.
- Summary – Purpose or intent of the test.
- Preconditions – Any setup required before execution.
- Steps – Sequential test execution steps.
- Expected Results – Outcome expected after each step.
Step 5: Save and Assign to Test Plan
- Click Create (or Save) to finalize the test case.
- To make the test case executable, link it to a Test Plan from the Test Plan Management module.
Step 6: Execute the Test
- Open the Test Execution tab.
- Select the Test Plan that contains the test case.
- Execute it and update the status as Passed, Failed, or Blocked based on the results.
Why Should Modern Alternatives to TestLink Be Considered?
TestLink has served its purpose for years, especially for teams looking for a free, no-frills test management tool. But testing has evolved, and so have the needs of QA teams. Modern test management platforms come with intuitive user interfaces, codeless workflows, and even AI-powered assistance. These features not only speed up the testing process but also make it accessible for non-technical team members like product managers, business analysts, and support teams who hold valuable product context.
Here’s why teams are increasingly shifting toward modern TestLink alternatives:
- Intuitive UI
Modern platforms are built with user experience in mind. They offer clean, responsive interfaces where anyone from testers to product owners can write and execute test cases without learning a new system or navigating outdated menus.
- AI-Powered Test Creation and Maintenance
Many modern TMS tools offer AI capabilities like natural language test creation, test case recommendations, and self-healing automation. This reduces the manual effort required in maintaining test suites and improves test coverage.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration
Contemporary tools support real-time collaboration with comments, mentions, shared dashboards, and version history. This bridges gaps between QA, development, and business teams.
- Seamless Integrations with DevOps Ecosystem
Modern solutions easily integrate with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and version control systems. This ensures test management stays aligned with agile and DevOps workflows.
- Advanced Reporting and Analytics
Modern TMS platforms provide in-depth analytics, visual dashboards, and KPIs to track quality trends, team performance, and release readiness in real time.
- Cloud-Based and Scalable
Unlike TestLink, which often needs local setup and manual upgrades, modern tools are cloud-hosted and auto-scaled. This allows distributed teams to access the platform from anywhere without infrastructure management.
- Enterprise-Grade Security and Compliance
Contemporary tools offer robust user permissions, audit logs, SSO, and compliance support for standards like SOC2, ISO, and GDPR, making them viable for enterprises.
- Built-in Support for Automation
A modern test management platform is also built to work hand-in-hand with an automation testing tool. Many offer native automation support or plug-and-play integrations for faster execution and reporting.
Test Management by Testsigma Vs TestLink
Test Management by Testsigma is a unified, codeless platform that enables teams to manage both manual and automated tests from a single interface. It helps QA teams scale their test management process without writing a single line of code. Whether you’re writing test cases, executing them, or reporting bugs, everything can be done seamlessly in one place.
AI Capabilities in Test Management by Testsigma
Unlike traditional tools like TestLink, Test Management by Testsigma is built around Agentic AI, a set of autonomous agents that simplify and speed up core testing tasks, while keeping human testers fully in control.
- Atto is an AI coworker that assists testers with routine test management tasks like writing test cases and tracking execution. It helps streamline collaboration and reduce manual effort without removing tester control.
- The Generator creates comprehensive test cases instantly from user stories, UI designs, walkthrough videos, and live applications. It converts business inputs into structured test cases without requiring manual input.
- The Runner executes test cases directly in the browser without additional setup and logs the results automatically. It simplifies test execution and ensures traceability of outcomes.
- The Sprint Planner detects new sprints from Jira, pulls in associated user stories, and generates test cases aligned with the sprint scope. This allows teams to begin testing as soon as development starts.
- The Bug Reporter generates detailed bug reports with reproduction steps, console logs, and screenshots. These can be sent to your issue tracker with a single click, reducing the time taken to report and resolve defects.
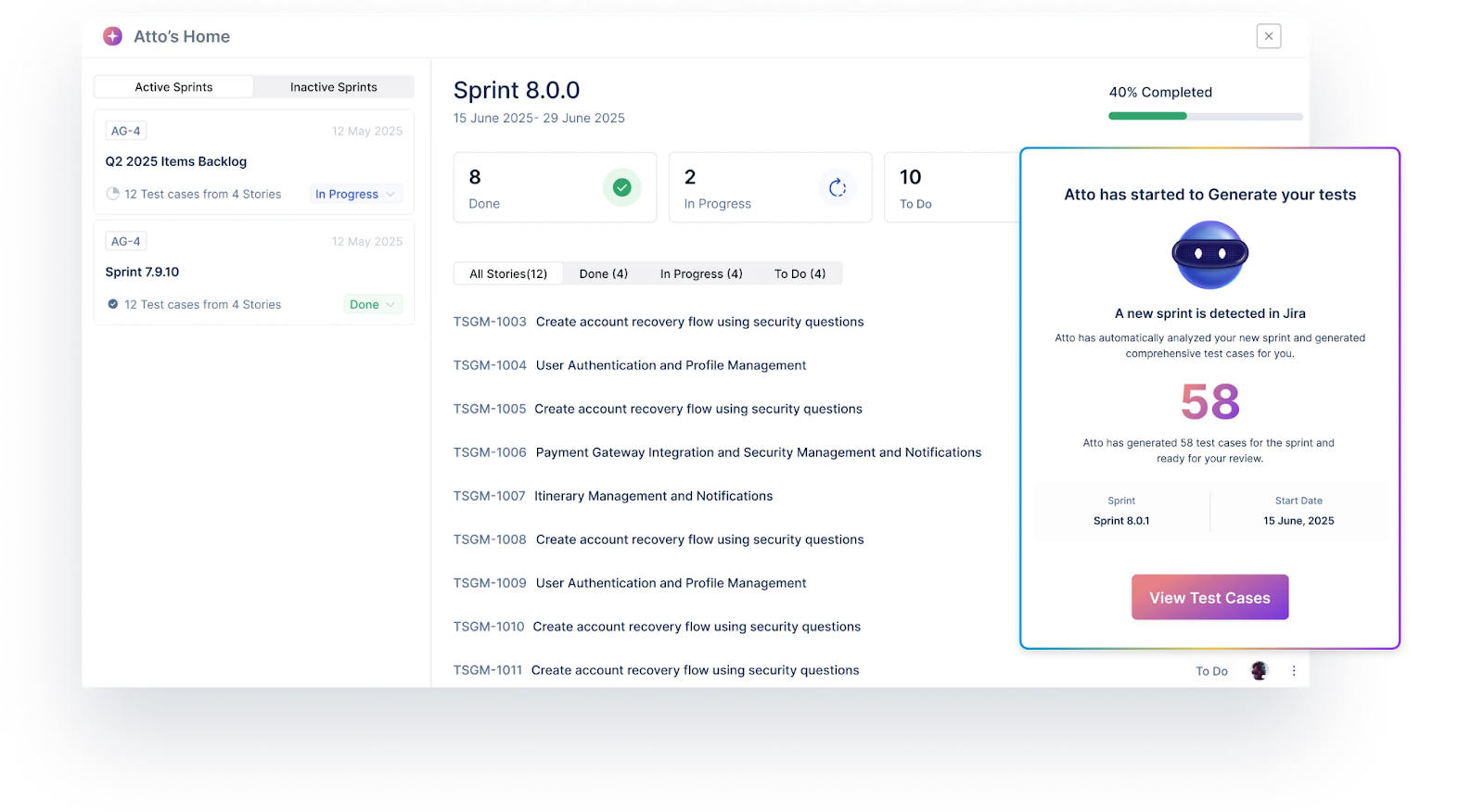
Features of Test Management by Testsigma
- Automatically generate test cases by detecting new sprints in Jira, pulling user stories, and creating test cases without manual input.
- Manage all test types in one place, including manual, automated, and exploratory tests, from a single interface to reduce context switching.
- Track test case changes with versioning to compare different versions side by side and maintain a history of edits.
- Monitor test run status in real time to keep track of progress and quickly respond to failures during execution.
- Collaborate with your team in real time using updates, comments, and status changes visible across the platform.
- Provides Native integration with Jira
Conclusion
TestLink continues to be a go-to option for many QA teams seeking a lightweight, open-source test management solution. While it lacks the features of newer tools, its no-cost model and basic functionality make it a useful option for teams with specific needs and technical comfort. If you’re looking for a more modern, scalable alternative that supports AI-powered test creation, real-time collaboration, and cross-platform automation, consider exploring Test Management by Testsigma.