Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is a Remote Test Lab?
- 2 Different Devices Supported by a Remote Test Lab
- 3 Why Use a Mobile Device Lab in a Remote Test Lab?
- 4 Remote Testing Lab vs Local Test Environments
- 5 Why Use a Mobile Device Lab in a Remote Test Lab?
- 6 Remote Testing Lab vs Local Test Environments
- 7 Remote Test Lab in Testsigma
- 7.1 Features of Our Remote Mobile Test Lab:
- 7.1.1 1. Real Devices in the Cloud
- 7.1.2 2. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
- 7.1.3 3. No-Code Test Automation
- 7.1.4 4. Agentic AI-Powered Testing
- 7.1.5 5. Parallel Test Execution
- 7.1.6 6. Self-Healing Tests
- 7.1.7 8. Network Testing
- 7.1.8 9. Visual Testing
- 7.1.9 10. Accessibility Testing
- 7.1.10 11. Smart Reporting and Debugging
- 7.1.11 12. Built for Collaboration
- 7.1.12 13. CI/CD Integrations
- 7.2 Why Testsigma for Remote Test Labs?
- 7.1 Features of Our Remote Mobile Test Lab:
- 8 FAQs
What is a Remote Test Lab?
A remote test lab is a cloud-based platform that offers access to a wide range of real devices and testing environments over the Internet. It allows testers and developers to conduct manual or automated tests on actual devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or IoT devices, without physically owning or maintaining each one.
Whether you’re doing mobile app testing or web testing, a remote test lab lets you run manual and automated tests on real Android and iOS devices, desktops, and browsers, anytime, from anywhere. Maintaining a checklist for mobile app testing is also a good practice to ensure a strategic and comprehensive testing approach. You can also access emulators and simulators if needed.
Different Devices Supported by a Remote Test Lab
| Mobile Devices (Most Common Category) | |
| Smartphones | Android: Samsung, Google Pixel, OnePlus, etc. OS versions: Android 8 to Android 16, iPhone: iPhone SE, 11–16 series, including Pro, Mini, Pro Max variants |
| Tablets | Android: Samsung Galaxy Tab, Google Pixel Tablet, etc. iPads: iPad Air, Pro, Mini, and standard models with various iPadOS versions |
| Web Devices (Desktop / Laptop Environments) | |
| Operating Systems | Windows 10 and 11; macOS (various versions); and Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Fedora, etc.) |
| Browsers | Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, Internet Explorer (legacy testing), across multiple versions |
| Web Testing Setup | Devices simulated through real/virtual environments for cross-browser and cross-platform testing |
| IoT Devices | |
| Smart Home Devices | Smart speakers (Amazon Echo, Google Nest), smart plugs, lights, locks, thermostats, doorbells, cameras |
| Wearables | Smartwatches (Apple Watch, Samsung Galaxy Watch), fitness trackers (Fitbit, Garmin, etc.) |
| Smart TVs & Streaming Devices | Samsung Smart TVs (Tizen OS), Android TVs, Roku, Apple TV, Fire TV |
| Industrial IoT Devices | Sensors, actuators, and controllers used in industries like manufacturing, agriculture, and healthcare (often in private lab setups) |
| Automotive Devices | |
| Infotainment Systems | Head units using Android Automotive OS, QNX, or proprietary systems from auto brands |
| Electronic Control Units (ECUs) | Controls for engine, airbags, brakes, etc. |
| ADAS Hardware | Testing of sensors and processors related to ADAS: radar, lidar, cameras |
| Communication Modules | 4G/5G in-car connectivity modules |
| Specialized Devices | |
| Gaming Consoles | PlayStation, Xbox, Nintendo Switch: limited availability, usually in internal QA labs |
| Point-of-Sale Systems | Used for retail software testing; includes barcode scanners, touch-enabled POS machines |
| Medical Devices | Specialized remote labs for health-tech testing (compliant with strict regulatory standards) |
| Robotics | Labs used for testing robotic hardware/software integrations (e.g., warehouse automation bots) |
| Networking Hardware | Routers, switches, and firewalls used for network-level testing |
Why Use a Mobile Device Lab in a Remote Test Lab?
A remote test lab provides instant access to thousands of real devices and browsers hosted in the cloud, eliminating the hassle of in-house maintenance. Within this setup, the mobile device lab is a dedicated space for testing mobile applications across a wide range of Android and iOS devices.
Here’s why QA teams rely on mobile device labs:
1. Tackle Device Fragmentation
New devices enter the market every other day, with different screen sizes, resolutions, OS versions, and hardware. A mobile testing lab gives you access to the latest and most popular Android and iOS devices so that you can ensure app compatibility across the board.
2. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Coverage
Users might access your app via Chrome on Android, Safari on iOS, or even Firefox on a tablet. With a remote test lab, you can run tests across different browser-device-OS combinations to catch layout breaks, functional bugs, and inconsistent behavior early.
Explore the full range of platforms, browsers, and mobile devices available for testing with Testsigma.
3. Real Hardware Testing for Mobile Features
Virtual devices can’t fully replicate mobile hardware. To test features like GPS, camera, fingerprint sensors, or Bluetooth, mobile device labs give you access to real devices, making your tests more accurate and reliable.
4. Simulate Real Network Conditions
Test how your app performs in real-world scenarios like slow 3G, fluctuating networks, or high-latency environments. A remote test lab lets you simulate these conditions to ensure your app is stable and responsive under all circumstances.
5. Reproduce and Debug Real-User Issues
If a user reports a crash or layout bug on a specific device, you can quickly access that exact model in your mobile device lab. Reproduce the issue, inspect the UI, and debug faster with visual and performance insights.
6. Performance Monitoring on Real Devices
Measure how your app impacts battery life, CPU and memory usage, and load times on different devices. A mobile device testing lab ensures your performance testing reflects real user experiences.
Remote Testing Lab Vs Local Test Environments
You might already know what a test environment is, and there are two main types: remote testing labs and local test environments.
What is a local test environment? A local test environment means you set up and manage all the testing tools and devices yourself. This involves setting up and maintaining physical devices, emulators/simulators, and browser configurations directly on your premises or individual tester/developer machines.
On the other hand, we have already seen that a remote test lab is often cloud-based and lets you access a wide range of real devices and browsers over the Internet instead of owning or maintaining them.
Here’s a table comparing remote test labs and local test environments in detail:
| Aspect | Remote Test Lab | Local Test Environment |
| Device Availability | Wide range of real devices, browsers, and OS combinations available on demand | Limited to what’s physically owned or accessible in-house |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; add more devices or users instantly via cloud | Not easily scalable; adding devices requires purchase and setup |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based; no upfront hardware cost | High initial investment in devices and maintenance |
| Maintenance & Updates | Managed by provider; no manual updates needed | Requires manual maintenance, OS/browser updates, and troubleshooting |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere, anytime over the internet | Tied to physical location; limited remote access |
| Cross-Device/Browser Testing | Easily test across multiple devices and browser versions simultaneously | Limited combinations; parallel testing is restricted |
| Real-World Conditions | Simulate real networks, locations, device conditions (battery, sensors, etc.) | Difficult to replicate diverse real-world conditions |
| Test Coverage | High test coverage with a broad device/browser matrix | Limited coverage; may miss edge cases |
| Setup Time | Minimal; ready-to-use instantly | Time-consuming; needs manual configuration |
| Collaboration | Teams across geographies can test on the same environment | Harder for distributed teams to access shared local setups |
| Hardware-Dependent Testing | Supports camera, GPS, biometrics, Bluetooth, etc. on real devices | Limited or not possible, especially on desktops or with emulators |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time metrics like CPU, memory, and battery usage on real devices | Often needs additional tools or is not available |
| Security & Compliance | Cloud providers offer secure environments with access controls | More control over data, but needs its own security protocols |
Why Use a Mobile Device Lab in a Remote Test Lab?
A remote test lab provides instant access to thousands of real devices and browsers hosted in the cloud, eliminating the hassle of in-house maintenance. Within this setup, the mobile device lab is a dedicated space for testing mobile applications across a wide range of Android and iOS devices.
Here’s why QA teams rely on mobile device labs:
1. Tackle Device Fragmentation
New devices enter the market every other day, with different screen sizes, resolutions, OS versions, and hardware. A mobile testing lab gives you access to the latest and most popular Android and iOS devices so that you can ensure app compatibility across the board.
2. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Coverage
Users might access your app via Chrome on Android, Safari on iOS, or even Firefox on a tablet. With a remote test lab, you can run tests across different browser-device-OS combinations to catch layout breaks, functional bugs, and inconsistent behavior early.
Explore the full range of platforms, browsers, and mobile devices available for testing with Testsigma.
3. Real Hardware Testing for Mobile Features
Virtual devices can’t fully replicate mobile hardware. To test features like GPS, camera, fingerprint sensors, or Bluetooth, mobile device labs give you access to real devices, making your tests more accurate and reliable.
4. Simulate Real Network Conditions
Test how your app performs in real-world scenarios like slow 3G, fluctuating networks, or high-latency environments. A remote test lab lets you simulate these conditions to ensure your app is stable and responsive under all circumstances.
5. Reproduce and Debug Real-User Issues
If a user reports a crash or layout bug on a specific device, you can quickly access that exact model in your mobile device lab. Reproduce the issue, inspect the UI, and debug faster with visual and performance insights.
6. Performance Monitoring on Real Devices
Measure how your app impacts battery life, CPU and memory usage, and load times on different devices. A mobile device testing lab ensures your performance testing reflects real user experiences.
Remote Testing Lab Vs Local Test Environments
You might already know what a test environment is, and there are two main types: remote testing labs and local test environments.
What is a local test environment? A local test environment means you set up and manage all the testing tools and devices yourself. This involves setting up and maintaining physical devices, emulators/simulators, and browser configurations directly on your premises or individual tester/developer machines.
On the other hand, we have already seen that a remote test lab is often cloud-based and lets you access a wide range of real devices and browsers over the Internet instead of owning or maintaining them.
Here’s a table comparing remote test labs and local test environments in detail:
| Aspect | Remote Test Lab | Local Test Environment |
| Device Availability | Wide range of real devices, browsers, and OS combinations available on demand | Limited to what’s physically owned or accessible in-house |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; add more devices or users instantly via cloud | Not easily scalable; adding devices requires purchase and setup |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go or subscription-based; no upfront hardware cost | High initial investment in devices and maintenance |
| Maintenance & Updates | Managed by provider; no manual updates needed | Requires manual maintenance, OS/browser updates, and troubleshooting |
| Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere, anytime over the internet | Tied to physical location; limited remote access |
| Cross-Device/Browser Testing | Easily test across multiple devices and browser versions simultaneously | Limited combinations; parallel testing is restricted |
| Real-World Conditions | Simulate real networks, locations, device conditions (battery, sensors, etc.) | Difficult to replicate diverse real-world conditions |
| Test Coverage | High test coverage with a broad device/browser matrix | Limited coverage; may miss edge cases |
| Setup Time | Minimal; ready-to-use instantly | Time-consuming; needs manual configuration |
| Collaboration | Teams across geographies can test on the same environment | Harder for distributed teams to access shared local setups |
| Hardware-Dependent Testing | Supports camera, GPS, biometrics, Bluetooth, etc. on real devices | Limited or not possible, especially on desktops or with emulators |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time metrics like CPU, memory, and battery usage on real devices | Often needs additional tools or is not available |
| Security & Compliance | Cloud providers offer secure environments with access controls | More control over data, but needs its own security protocols |
Remote Test Labs Vs. Local Test Environments: Which to Choose?
Remote test labs are generally preferred by modern development teams for their scalability, cost-effectiveness, broad device coverage, and easy integration with CI/CD pipelines. They are particularly effective for testing mobile and web applications. However, they aren’t without limitations.
Explore the major app testing challenges and how to solve them to ensure your strategy is foolproof.
Local test environments suit smaller teams with niche requirements, handling data of extremely sensitive nature, or for deep, low-level hardware debugging that requires direct physical access. However, they have certain limitations and overheads when it comes to coverage and scalability.
Remote Test Lab in Testsigma
Testsigma provides a complete mobile and web application testing solution for QA professionals looking for a remote test lab that offers scalability, ease of use, and AI-powered automation. As a no-code automation platform, Testsigma gives you instant access to a powerful cloud-based remote test lab.
You can run both manual and automated tests across more than 3000 real devices and virtual environments, covering a wide range of browsers, operating systems, and Android and iOS devices, without the need to maintain any physical lab infrastructure. With the support of its Agentic AI coworker, Atto, Testsigma helps you create, execute, and maintain tests quickly and intelligently.
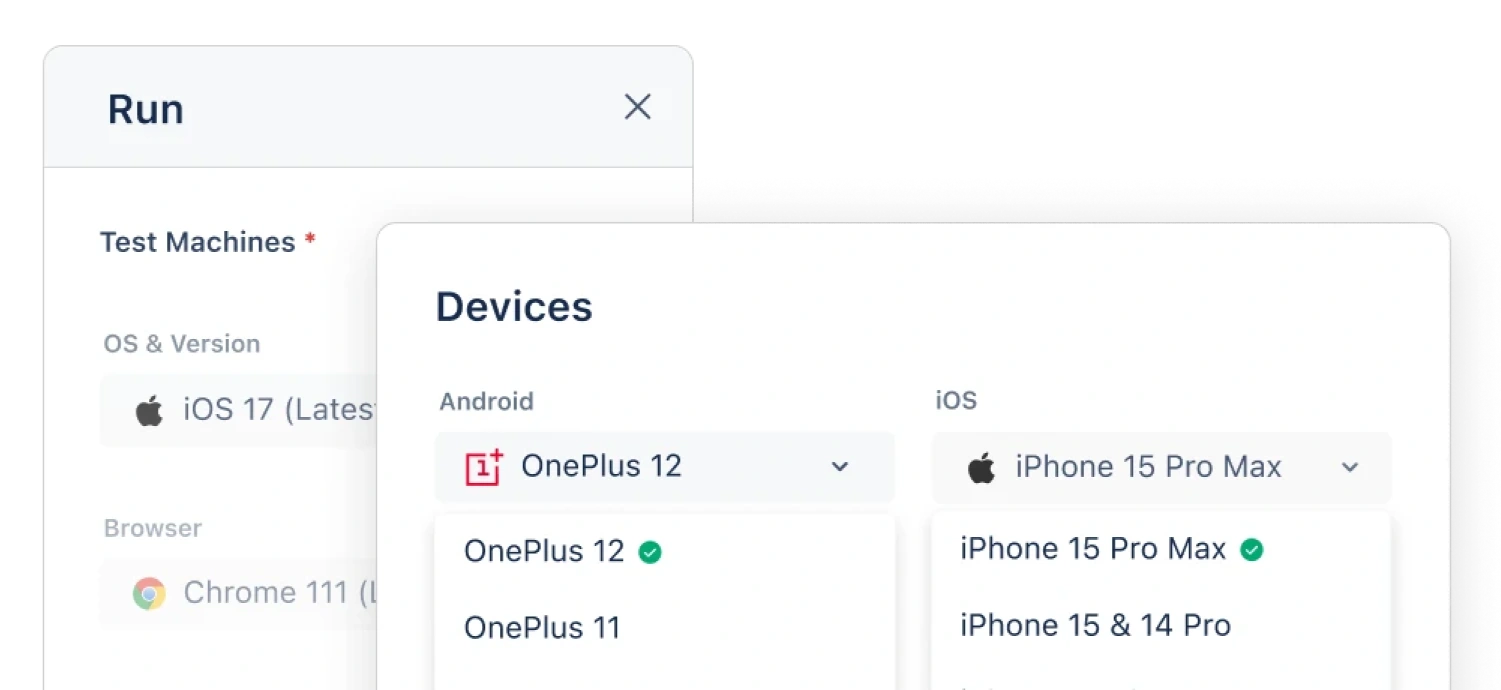
Features of Our Remote Mobile Test Lab:
1. Real Devices in the Cloud
Access over 3000 real Android and iOS devices in our mobile device lab, hosted within a scalable remote test lab environment. Test across the latest models, OS versions, and screen sizes without managing any hardware.
2. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
Run tests across all major browsers, including Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Edge on Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. Ensure consistent app performance across different device-browser-OS combinations.
3. No-Code Test Automation
Create test cases in plain English using Testsigma’s no-code platform without writing code.
4. Agentic AI-Powered Testing
Testsigma’s Agentic AI capabilities include Atto, your AI coworker, and a suite of intelligent agents that support every testing stage from creation to maintenance, making your QA process faster and more autonomous.
5. Parallel Test Execution
Run multiple tests simultaneously across devices in the remote test lab. Reduce execution time and accelerate delivery with parallel testing.
6. Self-Healing Tests
When your app UI changes, Testsigma automatically updates affected test cases. This reduces test failures and helps maintain a stable test suite.
8. Network Testing
Simulate network conditions like low bandwidth or 3G to test in real-world scenarios.
9. Visual Testing
Identify layout issues, visual regressions, and inconsistencies across devices and screen sizes. Validate UI appearance and responsiveness with every test run.
10. Accessibility Testing
Ensure your app meets WCAG and ADA compliance standards. Detect accessibility issues early with built-in integrations like Axe-Core.
11. Smart Reporting and Debugging
View logs, screenshots, and video recordings for every mobile test. Easily identify and fix issues with these insights.
12. Built for Collaboration
Share test results, leave comments, and tag team members directly in the platform. Align QA, development, and product teams in one workspace.
13. CI/CD Integrations
Connect with Jenkins, GitHub, Azure DevOps, Jira, Slack, and more. Seamlessly integrate automated testing into your continuous delivery pipelines.
Why Testsigma for Remote Test Labs?
- No need to buy or maintain physical devices.
- Get instant access to any device or browser your users rely on.
- Build and maintain tests faster with a no-code, AI-driven approach.
- Speed up testing with parallel execution and intelligent automation.
- Collaborate and scale effortlessly across distributed teams.
FAQs
Log in to a cloud-based testing platform like Testsigma.
Select a real Android or iOS device from the lab.
Launch and interact with your app directly from your web browser.
Run manual or automated tests without any physical setup.
Eliminate the need for physical devices and infrastructure.
Provide instant access to thousands of real devices and browsers.
Support both manual and automated testing.
Enable cross-browser and cross-device testing from anywhere.
Scale easily for distributed teams and CI/CD workflows.
You need to test across various devices, browsers, and OS versions.
Managing a physical lab is costly or impractical.
Teams are distributed across locations.
You want to run parallel or CI/CD-integrated tests.
You need quick access to rare or user-reported device environments.
Provide access to the latest Android and iOS devices.
Support both manual and automated mobile testing.
Help validate app performance across screen sizes and OS versions.
Allow debugging on real hardware for better issue resolution.
Eliminate delays in setting up and maintaining test environments.
Growing device fragmentation in the mobile market.
Demand for faster, high-quality releases.
Cost savings on infrastructure and maintenance.
24/7 access to real devices from anywhere.
Support for automated, parallel, and cross-platform testing.


