Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Teams often choose PractiTest for its clarity, flexibility, and seamless integration with existing development workflows. In this blog, we’ll explore what PractiTest is, what you can do with it, what its features are, what advantages and limitations it has, and how you can manage tests using PractiTest in a detailed, practical way.
Table Of Contents
What is PractiTest?
PractiTest is a cloud-based end-to-end test management platform designed to support the full lifecycle of quality assurance and testing. It structures QA work into clear modules such as Requirements, Test Library, Test Sets & Runs, and Issues/Defects. It focuses on visibility, traceability, and seamless integrations by linking requirements to tests, tests to issues, and connecting with bug trackers, automation frameworks, and CI/CD tools. PractiTest also supports both manual and automated testing within the same platform, helping teams eliminate the need for separate tools and maintain a unified testing ecosystem.
Features of PractiTest
Here are the major features of the PractiTest test management tool:
- Centralised Test Management: Manage test cases, test runs, requirements, and defects all in one platform, eliminating fragmented data silos.
- Test Library with Reusability: You can create a repository of tests (with steps), reuse them across different test sets/runs, call nested tests and use parameters for data-driven testing.
- Requirements & Traceability: Link requirements (or user stories) to test cases, so you know what is covered (and what isn’t) and trace defects back to requirements.
- Test Sets & Runs Management: Create test sets (grouping of test instances) for release cycles, regression suites, sanity checks etc, run them, monitor status and reuse tests.
- Manual + Automated Test Integration: Manage manual and automated testing within the same environment. You can integrate automated test results via REST API or built-in tools like xBot/FireCracker.
- Customisable Dashboards & Reports: Create real-time dashboards, slice and dice data, export to Excel, embed in other reporting tools.
- Integration With Development & CI/CD Tools: Support for bug trackers (e.g., JIRA), automation frameworks, CI tools, third-party systems.
- Security & Compliance: Built with enterprise-grade security, certifications (e.g., ISO 27001), hosted on AWS with strong controls.
- Customisation & Workflow Flexibility: You can define custom fields, workflows, views, forms, layouts to match your team’s process rather than being locked into a rigid structure.
- Analysis & AI-Assisted Insights: Features like “Test Value Score” (AI-based) to prioritise tests according to value/impact.
Advantages of PractiTest
Here are five key benefits of using PractiTest:
- Improved Visibility of QA Activities: Because the platform centralises tests, runs, requirements, and defects, stakeholders can get real-time insight into testing progress, coverag,e and release risk.
- Better Traceability: Linking requirements → tests → test runs → issues means reduced gaps, fewer unknowns about what is covered or left untested.
- Integration with Existing Workflows: Since PractiTest supports integrations with bug trackers, CI/CD pipelines, and automation frameworks, it can fit into your existing toolchain rather than forcing a complete overhaul.
- Increased Efficiency & Reusability: Reusing tests across sets, using step parameters, and avoiding duplication of work helps save time, increase consistency, and reduce overhead.
- Scalability for Complex Environments: The tool is designed for enterprise-grade usage, supporting many users, projects, automation integrations, and high volumes of test artefacts, useful for teams growing or with heavy test workloads.
Limitations of PractiTest
Here are five things to watch when considering PractiTest:
- Cloud-Only Deployment: PractiTest is SaaS only; there is no on-premise/self-hosted option. Some organisations with strict regulatory or infrastructure requirements may find this limiting.
- Automation Engine Not Built-In: While you can integrate automation, PractiTest itself is not a test automation framework. You still need your automation tooling; PractiTest manages and reports results.
- Potential Complexity in Customisation: With flexibility comes configuration effort; for teams new to the tool, customising workflows, forms, and dashboards may require time and training.
- Cost Considerations for Large Teams: For organisations scaling with many users, many test artefacts, and heavy automation integration, the licensing/usage cost may grow.
- Learning Curve for Full-Feature Use: While basic usage may be straightforward, harnessing advanced features like AI-based scoring, complex integrations, and custom API workflows may require more expertise.
How to Manage Tests Using PractiTest?
Managing tests in PractiTest (i.e., the test-planning, execution, and analysis process) involves multiple phases. Below, we’ll walk through how you can create tests, execute them, and analyse test reports using PractiTest.
Create Tests
Navigate to the Test Library module. In PractiTest, you build your repository of tests here.
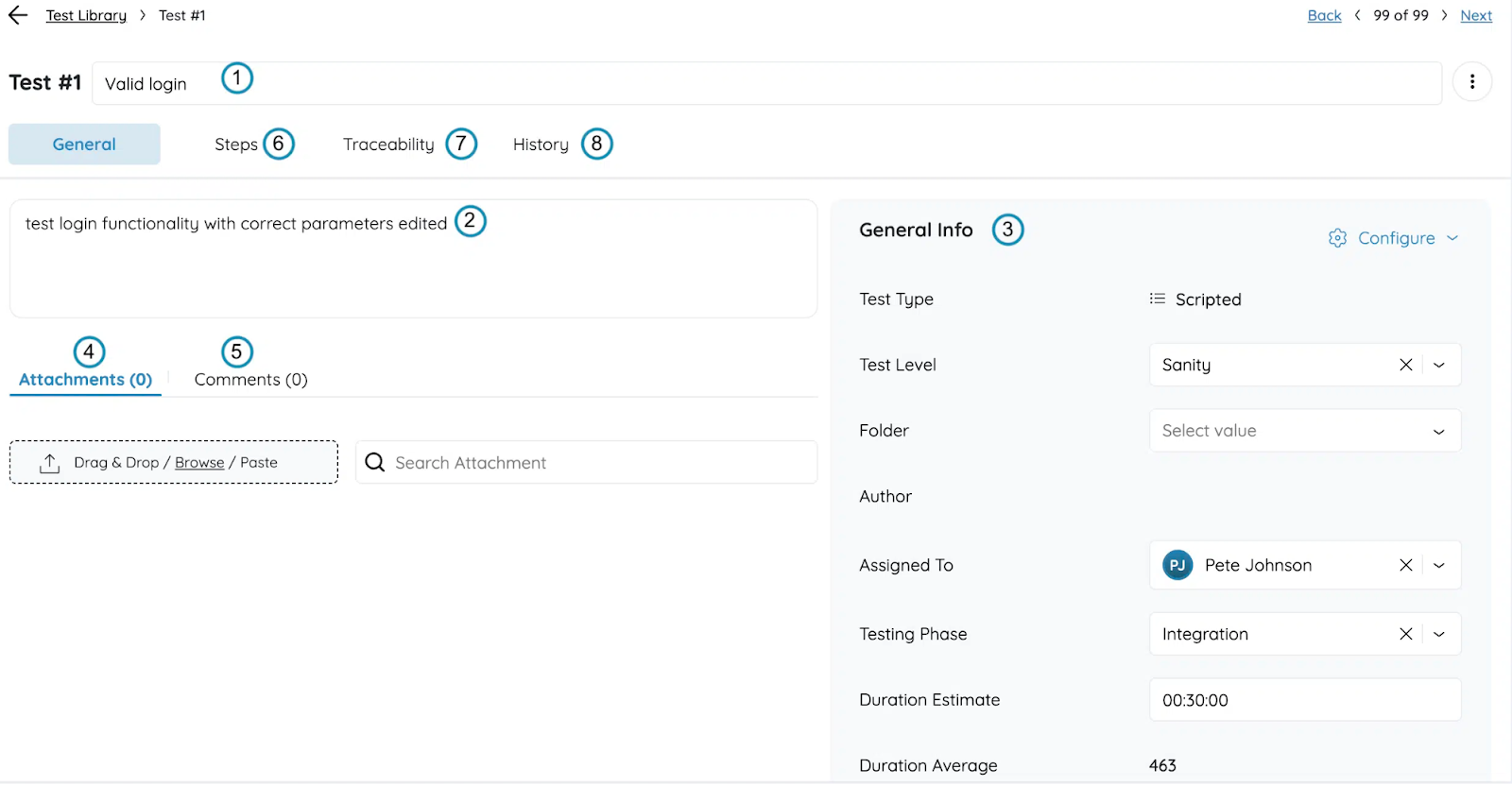
- Choose to create a new test case. Define the general fields: name, description, test type (e.g., scripted manual test or exploratory test).
- If it is a scripted test, go to the Steps tab and define the test steps: name, description, and expected result. You can attach files/links to each step.
- Use step parameters if needed to make the test reusable across different data sets or environments (e.g., multiple OS, browsers). You define placeholders using double brackets and then set possible values.
- Optionally, use the built-in AI assistant (SmartFox) to help generate test steps automatically from the test name/description, which can speed up test case creation.
- Link the test case to a requirement (in the Requirements module) for traceability. Because in PractiTest, you want to connect requirements → tests.
- Save the test case, organise in folders/tags as needed, so you can easily find and reuse in future test sets.
Execute Tests
- Move to the Test Sets & Runs module. This module handles the execution of tests you created.
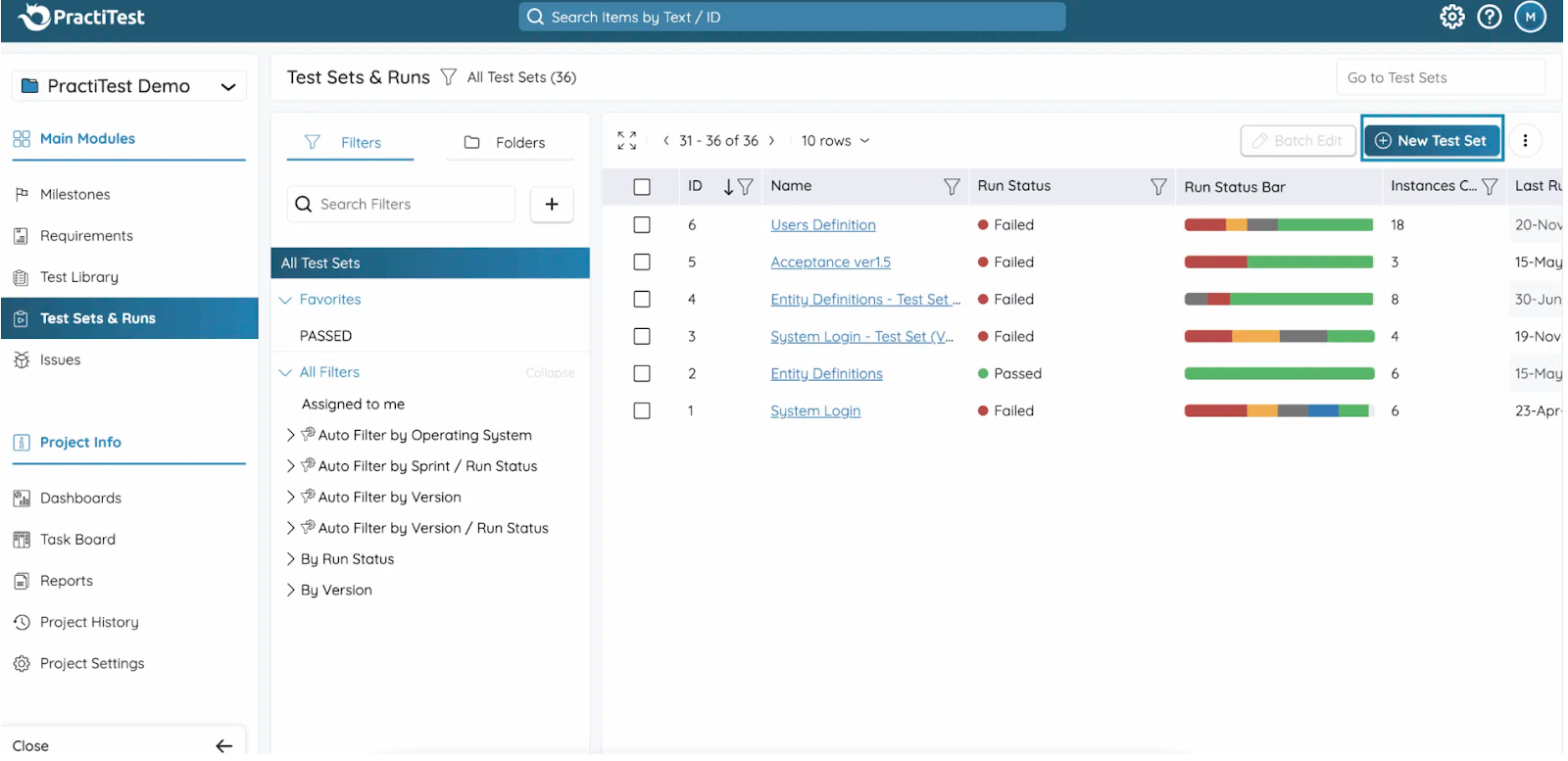
- Create a Test Set (which is a grouping of test instances) for a particular purpose , for example: a regression suite for version 1.2, or a smoke test for release.
- Add test instances into the test set: A test instance is a copy (or reference) of a test from the test library, allowing reuse of the test case in multiple contexts.
- Assign testers, set due dates, add metadata (custom fields) and start the run. During execution, testers mark each step or test as Passed/Failed/Blocked, attach files/screenshots/comments as needed.
- If you have automated tests integrated, PractiTest can receive automated test results via REST API or built-in integration (e.g., FireCracker or xBot). You can schedule runs and merge manual + automation results.
- As tests run, you’ll see status updates in the test set, e.g., how many test instances are complete, failed, or blocked. There are dashboards or mini-dashboards in each test set showing pass/fail over time.
Analysing Test Reports
- Use the built-in dashboards module in PractiTest to visualise your testing data: pass/fail rates, test durations, coverage, trends, and issues detected.
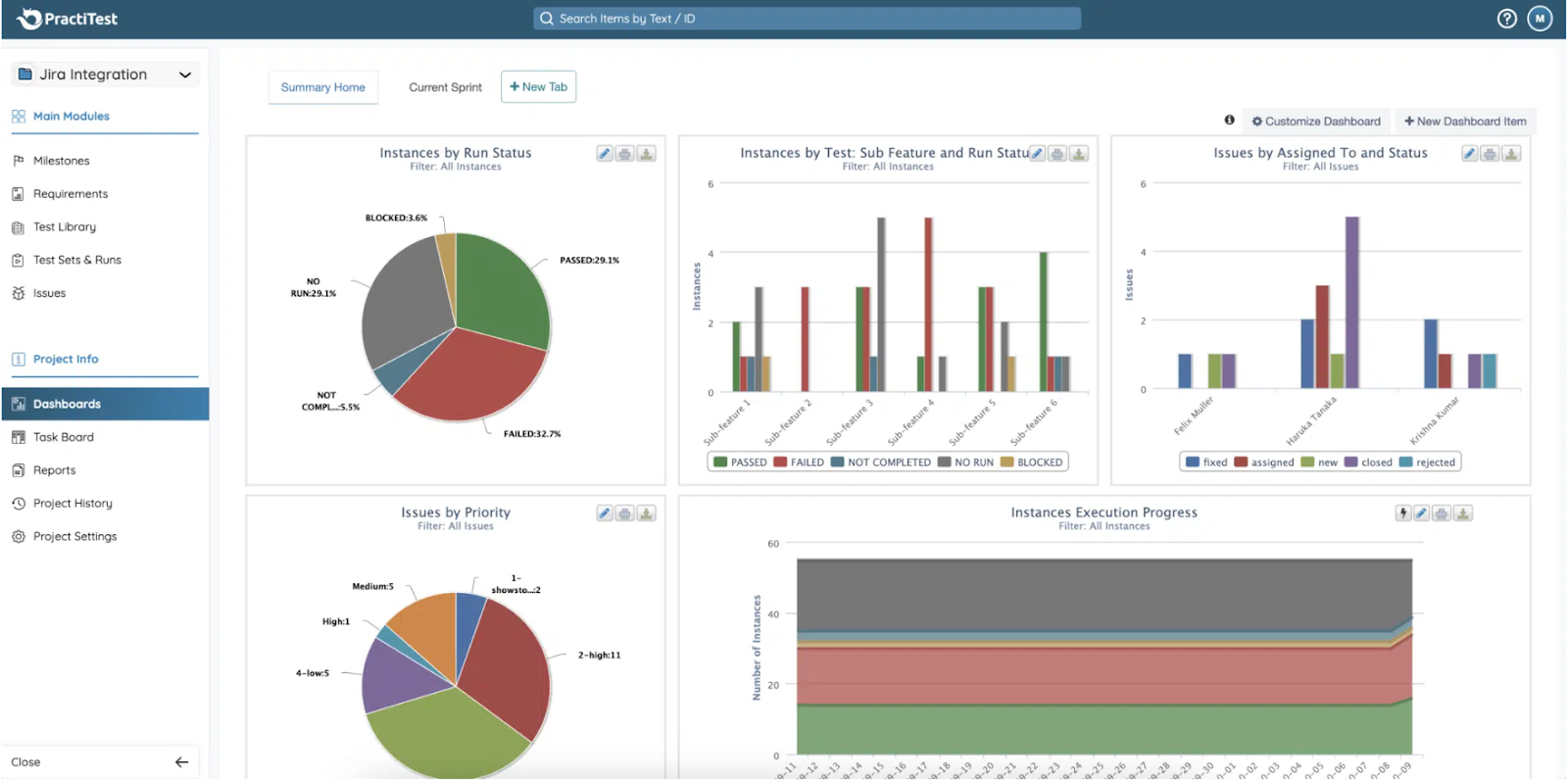
- Use filters and custom views to slice the data by project, tester, test set, requirement or any custom field. This helps you uncover bottlenecks or risk areas.
- Export reports (e.g., Excel, CSV) if you need to share with stakeholders outside the platform or embed into other reporting systems.
- Leverage traceability: for example, identify requirements that have no linked tests (i.e., risk of untested functionality), or identify tests that repeatedly fail and map them to defects to understand weak areas.
- Use advanced metrics: PractiTest’s AI-based features like “Test Value Score” can help you prioritise which tests to run next based on impact, thereby optimising your test cycle.
- Continuously refine your process: based on the data you see, you may restructure test sets, update test cases, remove redundant ones or automate tests for repeatedly failing manual cases. Over time, your QA process evolves within PractiTest.
What Test Management by Testsigma Offers That PractiTest Doesn’t
Test Management by Testsigma is an Agentic AI-powered solution that helps teams plan, execute, and track their testing process in one unified workspace. It goes beyond traditional test management by using intelligent agents to automate repetitive tasks like test creation, execution, and reporting. Designed for modern QA teams, it brings together manual, automated, and exploratory testing under a single platform that adapts to your workflow.
Features in Test Management by Testsigma that PractiTest does not have:
- AI Agents for End-to-End Testing Workflow
Test Management by Testsigma includes AI agents that handle the entire testing lifecycle from planning sprints and generating test cases to executing them and filing bug reports automatically. PractiTest includes AI-assisted suggestions but doesn’t offer this kind of autonomous, end-to-end AI workflow.
- Automated Test Case Generation
The Generator Agent can instantly create detailed test cases and steps from prompts, user stories, images, screenshots, PDFs, Figma design files, or walkthrough videos. PractiTest helps teams build and reuse manual test cases, but doesn’t generate complete tests directly from such varied sources.
- Automatic Bug Reporting with Complete Context
When a test fails, the Bug Reporter Agent automatically captures screenshots, logs, and environment details, then files a detailed bug report in integrated tools like Jira. PractiTest supports manual defect logging and linking, but doesn’t automate the bug reporting process through AI.
- Free Forever Plan and Lower Pricing
Testsigma offers a free-forever plan and affordable paid options, making it accessible for small teams. PractiTest doesn’t publicly list free plans or entry-level pricing.
- Unified Manual and Automated Testing in One Flow
In Test Management by Testsigma, manual, automated, and exploratory testing can all be managed and executed within the same unified workspace without switching tabs or juggling tools. PractiTest supports both manual and automated testing, but typically through distinct modules and integrations.
- AI-Driven Test Maintenance and Optimization
Testsigma includes AI agents that self-heal broken tests and optimize test suites to improve coverage and reduce redundancy. PractiTest offers reusability and parameterization but not AI-powered maintenance or optimization.
- Cross-Platform, Device, and API Automation
Testsigma supports automation across web, mobile, API, and ERP systems with built-in cross-browser and cross-device testing capabilities. PractiTest manages test automation integrations but doesn’t natively provide this multi-platform automation environment.
View detailed comparison: PractiTest vs Testsigma
Conclusion
PractiTest is a reliable cloud-based test management tool that helps teams organize tests, track defects, and maintain visibility across QA cycles. Many teams use it for its flexibility and structured approach, but it lacks agentic test management, where AI agents plan, create, execute, and report tests autonomously. As testing moves toward faster, AI-driven workflows, agentic test management becomes essential to save time and effort. Teams looking to experience this next step can try Test Management by Testsigma for free and see how intelligent AI agents transform the way testing is managed end-to-end.


