Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 What Is Mobile Device Testing?
- 3 Types of Mobile Device Testing
- 4 How to Set up Mobile Device Testing Environment
- 5 Best Practices for Effective Mobile Device Testing
- 6 Common Challenges While Testing Mobile Devices
- 7 Can Mobile Device Testing be Automated?
- 8 Why Test on Real Devices vs Emulators?
- 9 How Can Testsigma Help with Mobile Device Testing
- 10 Conclusion
- 11 FAQs
Introduction
Stats state that mobile network subscriptions for smartphones came close to seven billion. This number is likely to cross 7.7 billion by 2028. Back in 2021, global smartphone revenue was about 481 billion U.S. dollars. By 2022, it seems to have fallen slightly to 463 billion. Sales may have dipped, but phones are getting more expensive. That price hike is helping the market stay stable. It shows how deeply smartphones are part of everyday life
Smartphones today are more than just calling devices. They wake you up. They show weather updates. They help you follow the news. You can send messages, check emails, and do video calls with loved ones. You can order groceries or get food delivered.
Mobile phones are now a regular part of your routine. So, it is important to make sure they work well. This is where mobile device testing matters.
Mobile device testing is a constantly evolving area. It involves different strategies to check mobile app performance, functionality, security, and user experience. In this article, you will get to know more about Mobile Device Testing, its setup, the challenges it brings, and how to deal with them.
What is Mobile Device Testing?
Mobile device testing checks how well a device works as a whole. This can be a smartphone, tablet, or wearable. It tests hardware like the camera, sensors, battery, and screen. It also tests software such as the operating system, user interface, and pre‑installed apps.
The goal is to make sure the device works reliably in different situations. Testing finds problems before users see them. These can include issues with speed, ease of use, network links, compatibility, security, or durability.
It includes testing things like:
- Touchscreen responsiveness
Does the screen react quickly when you touch it?
- Battery performance and charging
Does the battery last long? Does it charge properly?
- Camera and sensors
Is the camera clear? Do sensors like GPS or accelerometer work right?
- Signal and connectivity
How strong is the signal? Do Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and mobile data work smoothly?
- Audio quality
Are the speaker and mic clear? Can you hear and speak without issues?
- Screen display
Is the display bright? Are the colors and resolution good?
- Operating system behavior
Does the OS run well under normal and heavy use?
This testing helps companies like device makers, telecom brands, and OEMs. It helps them make sure the device works well before they sell it. Testing can be done by hand or using tools. Sometimes, the devices are also tested in harsh conditions.
In short, mobile device testing checks if the full device is ready, not just the apps inside it.
Types of Mobile Device Testing
Mobile device testing covers many types of checks. Each one looks at a different part of the device, how it works, how fast it is, how safe it is, and more. Below are the main types of mobile device testing:
- Functional Testing
This test checks if basic features like calls, messages, camera, and Wi Fi work properly. Makes sure the device handles everyday tasks without issues
- Performance Testing
Mobile performance testing looks at how the device handles pressure. You may run many apps at once or use it on a weak internet connection. It helps find out if the device slows down or crashes.
- Usability Testing
This checks if the device is easy to use. Testers give users simple tasks and watch how they use the device. It shows if people can use it without confusion.
- Compatibility Testing
Checks if the device works with different networks, SIM cards, systems, and accessories. Helps avoid problems after launch.
- Localization Testing
This checks if the device supports different languages and regions. It makes sure menus, text, and settings show up correctly in each language.
- Accessibility Testing
Mobile accessibility testing helps make sure people with disabilities can use the device. It tests features like screen readers and voice control tools.
- Battery Testing
This tests how long the battery lasts. It checks if apps drain power quickly and how well the device charges.
- Camera Testing
This checks how good the camera is. Testers take pictures and videos in different light settings to see how the camera performs.
- GPS Testing
This looks at how accurate the GPS is. Testers use the device for navigation to see if directions are correct.
- Security Testing
This checks if the device is safe to use. It tests how easy it is to hack or install harmful apps. The goal is to find weak spots and fix them.
- Certification Testing
This is done to meet official standards. A third-party team tests the device to make sure it follows rules. It is often needed before the device goes on sale.
How to Set up Mobile Device Testing Environment
Setting up a mobile phone testing environment means getting everything ready to test how a device performs as a whole. You are not just checking the software. You are also looking at the screen, battery, sensors, and how it connects to networks. A good setup helps you identify issues early and meet quality expectations before launch.
- Define the testing requirements and goals
Start by knowing what you want to test. This could include the network, camera, touch, GPS, speakers, or battery. You may be checking the full hardware-software setup or making sure the device meets international rules. You might also need to test how the device behaves in different situations, like heat or poor network areas.
- Prepare a controlled and well-equipped physical test lab
You need a proper physical lab space to begin the phone testing process. You have to keep the lighting and temperature in an unchanging state. It is always preferred to make use of anti static flooring and safe workbenches. It is very important to stock your lab with tools like screwdrivers, thermal cameras, and multimeters. Also include power supplies and USB ports that work well for multiple devices.
- Choose a wide range of real devices and accessories
When you begin the mobile phone test, it should be done on many real devices. For this, you need to include different models, screen sizes, and operating systems. If your testing includes accessories, you can add things like headphones, chargers, smartwatches, SIM cards, or other required things. You can test both single and dual SIM versions if needed.
- Install required operating systems, firmware, and diagnostic tools
Make sure each device has the right firmware. You also need tools to track logs, battery use, heat, and performance. Some tools can test the touch screen, gyroscope, or camera. You can also use special apps built just for internal testing.
- Set up network simulation and connectivity testing tools
It is important to test how the device connects to networks. You have to try it with multiple network types, including mobile data and Wi-Fi. You can use tools that create weak signals or switch networks to see how the device reacts. You can test roaming, signal drops, and recovery, too.
- Arrange environmental and durability testing setups
Mobile devices go through rough use. You need to test them in heat, cold, dust, or even underwater. Use machines to simulate drops, shakes, or moisture. Make sure this area is safe and does not damage your other tools.
- Configure logging, monitoring, and data capture systems
You should record how the device behaves while testing. You have to capture logs, battery stats, screen recordings, and temperature data. Use tools that collect this information live and store it securely. Keep clear records of the devices and test versions.
- Enable test automation where possible
Some testing can be automated. You can use tools to repeat taps, swipes, or volume changes. Most testing phones are still manual because of hardware, but automation helps with repeated tasks or stress tests.
- Ensure proper power and charging setup
Stable power is a must while performing mobile device testing. You have to use USB hubs, charging docks, and voltage checkers. This protects against overcharging or short circuits. You also need to test how fast the battery drains, how it charges, and whether it overheats.
- Maintain safety, security, and cleanliness in the lab
Keep the lab clean and safe. You have to organize wires and tools. Avoid placing test devices too close together. Use anti-static protection and keep safety gear like fire extinguishers ready. Train mobile testers to handle all tools carefully.
Best Practices for Effective Mobile Device Testing
Here are some useful tips for testing mobile devices:
- Know what you are testing
Start by understanding what you need to test. Focus on features your users care about. List the devices and systems your users are using. Once you know that, you can plan your testing steps clearly.
- Use real devices
Simulators and emulators can help. But they do not show real-world behavior. Always test on real devices to see how things truly work for you.
- Test across different devices and systems
Do not stick to new devices only. Try older phones too. Check different screen sizes and system versions. Many users may still use older devices, and you need to cover them.
- Check performance on various networks
Your app should work well on all networks. Test it on Wi-Fi and mobile data. Try both fast and slow networks. This helps you spot real issues.
- Test the user experience
It is not just about bugs. The app should be easy and smooth for users. Ask real users to try it and give you feedback. Their input helps you improve usability.
- Start testing early
Do not wait for the app to be finished. Start testing while you build it. Keep testing at every stage as this helps you find bugs early.
- Use automation where possible
Automation saves you time by handling repetitive tasks. Many mobile testing tools are available, like Testsigma. You can choose what works best for you.
- Keep testing after launch
Your work does not end at release. Keep checking the app regularly. This helps you fix new bugs before users face them.
Common Challenges While Testing Mobile Devices
Testing a mobile device is more than checking the screen or Wi-Fi. You are testing the full experience. This includes the hardware, battery, sensors, and performance in different situations. While doing this, you may face some common challenges.
- Wide range of devices and setups
There are thousands of phones out there. Each one has its own screen size, specs, and software version. Testing all of them is not possible. You need to pick the most used ones. Even then, covering every setup takes time and effort.
- Regular operating system updates
Android and iOS keep changing. A small update can break features. What worked before might fail now. You have to test again and keep up with OS changes.
- Limited access to real devices
Testing on real devices gives better results. But getting every phone is not easy. It costs money and time. Cloud testing helps, but it is slower. It can also not test some hardware parts.
- Battery and speed problems
You need to test how the phone works with low battery. Or when it is charging. Overheating is also a concern. These are hard to test the same way each time. Speed also changes with background apps or old hardware.
- Testing network and signal issues
Network testing is tricky. You have to check how the phone handles slow internet, weak signal, or no connection. You also need to test switching between mobile data and Wi-Fi. This needs special tools or setups.
- Testing sensors and hardware parts
Phones have many sensors like GPS, gyroscope, or proximity sensors. Testing them is not easy. You often need to move the phone or go outside. Repeating the same test each time is tough.
- Drop tests and extreme conditions
You may need to test the phone in heat, cold, dust, or water. Some tests require dropping the phone. These tests can damage the device. They are hard to repeat. You also need to stay safe while doing them.
- Tracking errors and getting logs
When the phone crashes, it can be hard to find out why. Not all devices give full logs. If you are testing buttons or physical parts, normal logging tools may not help.
- Manual testing takes time
Some tests must be done by hand. This includes touch, camera, or screen tests. Manual work is slow. It also increases the chance of missing bugs. Automation helps, but it cannot do everything.
- Security and privacy concerns
Tests may need personal data or login details. You must keep this data safe. Always clear test data after each run. Protect your test setups to avoid leaks or misuse.
Can Mobile Device Testing Be Automated?
Yes, you can automate mobile device testing. But it depends on what you want to test. If you are checking the software or system behavior, automation works well. But if you are testing hardware like buttons or sensors, you will need manual testing or tools.
Let us break it down.
Automation is good for tasks you repeat often. For example, you can use it to turn network on and off. You can check brightness or change settings. You can also run system checks. Tools and scripts help you do this without touching the device. This saves time, especially with many devices or updates.
But some mobile phone tests cannot be automated. You need to hold the device or use equipment. For example, testing the camera in low light. Or checking how it feels after a drop. You also cannot automate heat or sensor checks. These all need hands-on work.
So, automation helps with many tests. But it does not cover everything. The best way is to use both approaches for mobile device testing. You can use automation for tasks inside the software. This includes changing settings, moving through menus, or checking performance. These steps repeat often and do not need human thinking. Test scripts can do them quickly.
But testing the real device is different. You still need manual checks. For example, taking photos in low light. Or feeling how the phone fits in your hand. You also need to press buttons to see how they respond. These things need a human touch.
Why Test on Real Devices Vs Emulators?
When you test a mobile device, you have two main options. You can use real devices or emulators. Both are helpful, but for different reasons. Let us see why real devices give better results, and when emulators still work well.
Testing on Real Devices
Real devices show how things truly work. You are using the same hardware as your users. You can test touch, camera, screen, battery, and how the phone feels. You also see how it works in real-world cases. This includes weak signals, changing light, or fast app switching.
For example, if you want to check video quality, Bluetooth speed, or heat during use, only a real phone helps. Emulators cannot copy these things exactly.
Testing on Emulators
Emulators are the virtual devices that actually run on your computer. They function like phones but without real hardware. They are good in early testing. You can use them while building or fixing features. They help test layout, flows, and simple actions.
They are free and easy to use. That makes them great for quick checks or writing scripts. But they miss real-world behavior. You cannot test camera focus, GPS, or overheating issues on an emulator.
So, What’s the Difference?
Real devices give real results. You see what your users will see. However, emulators help with fast, early mobile device testing online but do not give you the full picture.
The Best Approach
Use emulators when you want to save time during development or test simple features. But before releasing anything to users, always test on real devices. That way, you catch real issues early and deliver a better experience.
How Can Testsigma Help with Mobile Device Testing
Cloud-based testing platforms let you test apps on many real devices. You do not need to buy or manage them yourself. This helps you test on different phones easily. But keep in mind, these platforms can be costly. So, it is smart to compare prices and features first.
One simple and low-cost option is using a mobile testing lab. Platforms like Testsigma offer this service. With Testsigma, you do not need to store or update many phones. You get access to over 3000 real Android and iOS devices in the cloud.
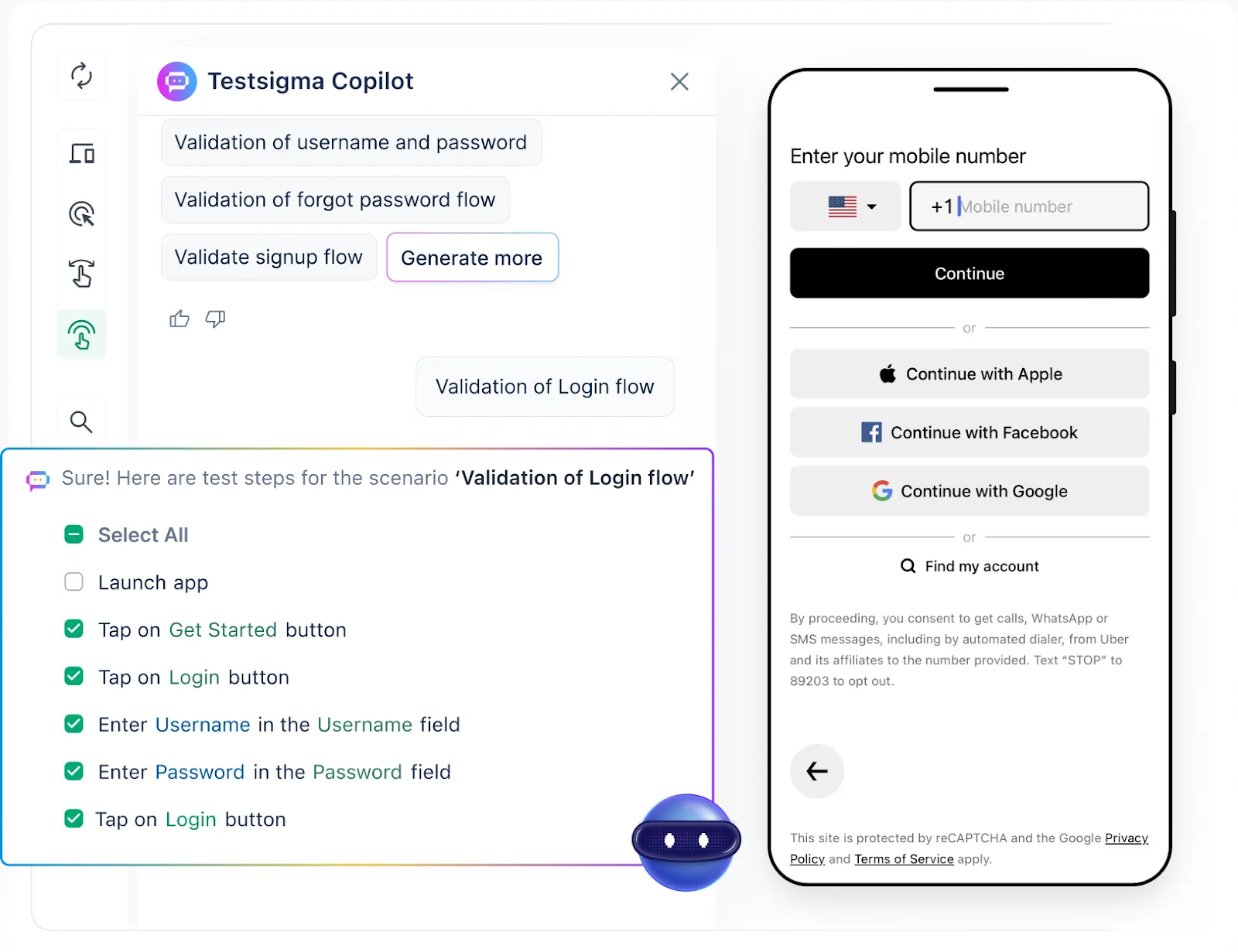
- Cross-Browser Testing
Check your app on all major browsers and versions. This helps your app work well everywhere.
- Parallel Test Execution
Run many tests at once on different devices. This helps you finish testing faster.
- AI-Driven Test Creation
Use AI to create test cases quickly. You save time on writing and updates.
- Test Suite Scheduling
Set up and run custom test groups. Test only what needs checking to save time.
- Unified Platform
Use one tool to test web, mobile, desktop, and API—all in one place.
- Easy Integrations
Connect with tools like JIRA, Jenkins, GitHub, and Azure DevOps. It fits into your current setup easily.
- Visual Testing
Catch layout and design issues fast with visual testing tools.
Create tests without writing code. It is simple for everyone to use.
- Inventory Management
Use both cloud and local devices in one test space. Manage them all in one place.
Testsigma enables mobile test automation without coding and supports real devices – Sign up for Free
Conclusion
Mobile device testing is essential to deliver reliable, secure, and seamless user experiences in a fragmented device ecosystem. While setup and execution come with challenges like device variety, security, and performance, the right strategy and tools can simplify the process. Mobile test automation platforms like Testsigma help teams overcome these hurdles with AI-driven, scalable, and unified testing solutions, making it easier to ensure quality at speed.
FAQs
Yes, but it can raise security, consistency, and coverage challenges.
Choose devices based on user statistics, such as, most used by your target users, across popular OS versions and screen sizes.
Data encryption, secure access, app sandboxing, and compliance with security standards.
They impact performance, compatibility, battery use, and user experience across devices.



