Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Table Of Contents
- 1 What is Enterprise Application Testing?
- 2 Why is Enterprise Application Testing Important?
- 3 Types of Enterprise Application Testing
- 4 Best Practices for Effective Enterprise Application Testing
- 5 Challenges in Enterprise Application Testing
- 6 Top Tools for Enterprise Application Testing
- 7 Role of Test Automation in Enterprise Application Testing
- 8 FAQs
What is Enterprise Application Testing?
Enterprise application testing is the process of validating the performance, reliability, security, and scalability of software systems that support core business operations in large organizations. Whether it’s ERP, CRM, HRM, or custom-built platforms, testing enterprise applications helps ensure seamless functionality across environments and devices. A well-defined enterprise testing strategy reduces risks, prevents system downtime, and supports regulatory compliance.
Simply put, if you’re wondering what enterprise testing is, it’s a safeguard for business continuity and customer trust, ensuring every software update, integration, or deployment keeps your enterprise running without disruption.
Why is Enterprise Application Testing Important?
Enterprise application testing plays a critical role in maintaining performance, stability, and business continuity across complex digital ecosystems. Here’s why it’s indispensable for modern organizations:
- Ensures System Reliability
Enterprise applications power critical business functions. Testing helps prevent disruptions by ensuring systems run smoothly and consistently, even as demands grow.
- Supports Scalability
As businesses expand, so do the demands on their applications. Enterprise testing ensures that systems can scale effectively to accommodate increased users, data, and transactions without performance degradation. - Maintains Business Continuity
Downtime in enterprise systems can impact operations, revenue, and customer trust. Rigorous testing safeguards critical workflows such as CRM, finance, and logistics. - Enables Effective Risk Mitigation
By identifying bugs, bottlenecks, and security vulnerabilities early, enterprise testing minimizes the risk of major failures post-deployment. - Facilitates Smooth Integrations
Enterprise software often integrates with multiple systems and third-party tools. Testing ensures new modules or updates don’t break existing workflows. - Strengthens Regulatory Compliance
In regulated industries, testing ensures enterprise systems meet compliance standards by validating accuracy, security, and data integrity. - Accelerates Digital Transformation
Testing supports transformation efforts by validating whether enterprise applications can handle evolving workloads, user behaviors, and integration demands. - Improves Operational Agility
A solid enterprise testing strategy enables faster deployments and updates without sacrificing quality, helping businesses adapt quickly to market needs.
Types of Enterprise Application Testing
Enterprise applications are complex systems comprising interconnected components. Various types of testing are essential to ensure their smooth functioning. Let’s explore the different testing methods used for enterprise application testing:
Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures that your enterprise application meets all its functional requirements.
Smoke and Sanity Testing
After each software release, smoke testing confirms the system’s stability and identifies any anomalies. Sanity testing, conducted after smoke testing, verifies that major application functionalities work perfectly independently and when combined.
Regression Testing
When changes are made to the software, regression testing ensures the application continues to function smoothly without breaking existing features.
User Acceptance Testing
In the final phase, clients perform user acceptance testing to ensure the application meets all requirements before its release to the market or production environment.
API and Compatibility Testing:
API testing validates the functionality, reliability, performance, and security of APIs used in the enterprise application. Compatibility testing ensures the application runs on various hardware, operating systems, browsers, networks, and mobile devices.
Database and Security Testing
Database testing analyzes tables, schema, triggers, and data consistency to assess the database’s responsiveness. Security testing identifies system threats, vulnerabilities, and potential risks and addresses them through coding.
Performance and Visual Testing
Performance testing evaluates the application’s stability, speed, scalability, and responsiveness under different workloads. Visual testing helps identify UI changes when accessed from various devices and browsers.
Deployment and Recovery Testing
Deployment testing simulates the user environment and tests the application on different platforms. Recovery testing ensures the application returns to a stable state after a failover.
Enterprise test automation ensures all tests run correctly, keeping your platform smooth and free from disruptions.
Best Practices for Effective Enterprise Application Testing
The following are some of the enterprise application testing best practices that can help you:
1. Develop a Test Plan
- A test plan serves as a roadmap for the testing process.
- It should define objectives, scope, test scenarios, and other key factors.
- Consider business requirements, user expectations, and regulatory compliance.
2. Utilize Automation Tools
- Automation speeds up testing and improves accuracy.
- Supports various testing types like regression, functional, and performance testing.
- Automates repetitive tasks, increasing test coverage and efficiency.
- Reduces manual effort and human errors.
3. Leverage Risk-Based Testing
- Identify high-risk areas using risk assessment.
- Prioritize testing of critical functions to catch errors early.
- Allocate testing resources effectively for better results.
4. Integrate Security Testing
- Detects vulnerabilities and mitigates security risks.
- Ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations.
5. Deploy Shift-Left Approach
- Start testing early in the development phase.
- Reduces costs and effort needed for bug fixes.
- Improves test coverage, speed, and overall software quality.
6. Optimize Test Data Management
- Use high-quality, relevant test data to replicate real-world scenarios.
- Ensures efficient and accurate testing outcomes.
Challenges in Enterprise Application Testing
1. Complex System Integrations
Enterprise environments involve tightly integrated systems such as ERPs, CRMs, databases, cloud services, and legacy applications. Testing across these diverse platforms requires deep knowledge of each system and a coordinated approach to validate end-to-end workflows.
2. High DATA Volumes and Test Coverage
Enterprise applications handle large-scale transactional data. Ensuring comprehensive test coverage without impacting performance or data integrity is a major challenge. Testers must create realistic data sets and simulate various usage scenarios without overwhelming the system.
3. Frequent Updates and Continuous Change
With agile development and frequent software updates, maintaining up-to-date test scripts and regression suites is time-consuming. Test automation helps, but requires ongoing maintenance to stay aligned with evolving business requirements.
4. Scalability and Performance Validation
Testing for scalability is critical, especially as enterprises expand operations or enter new markets. Simulating thousands of concurrent users and validating system behavior under load demands advanced performance testing tools and infrastructure.
5. Security and Compliance Risks
Enterprise systems often process sensitive data subject to strict compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOX). Testing must go beyond functionality to include security assessments, vulnerability scanning, and compliance validation, without exposing confidential data.
6. Tool and Environment Constraints
Many enterprises face limitations with outdated tools, legacy systems, or fragmented testing environments. This makes test execution and reporting inconsistent, especially when teams are distributed across multiple locations.
7. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Ensuring a consistent user experience across different devices, browsers, and operating systems adds another layer of complexity, particularly when applications are accessed by global teams and external users.
Enterprise applications are specifically geared to handle the challenges of managing processes across distributed environments, a capability often praised in Nextiva reviews for its reliability and performance.
Top Tools for Enterprise Application Testing
As enterprise systems grow in complexity and scale, choosing the right testing platform becomes critical to ensure quality, performance, and business continuity. The best enterprise testing tools are designed to handle large-scale test automation, support cross-platform coverage, and integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines. Below are some of the leading tools tailored for enterprise-grade testing needs:
1. Testsigma
Testsigma is a powerful cloud-based codeless AI-driven test automation platform built for modern enterprises. It enables QA teams to create and manage tests in plain English, making it accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
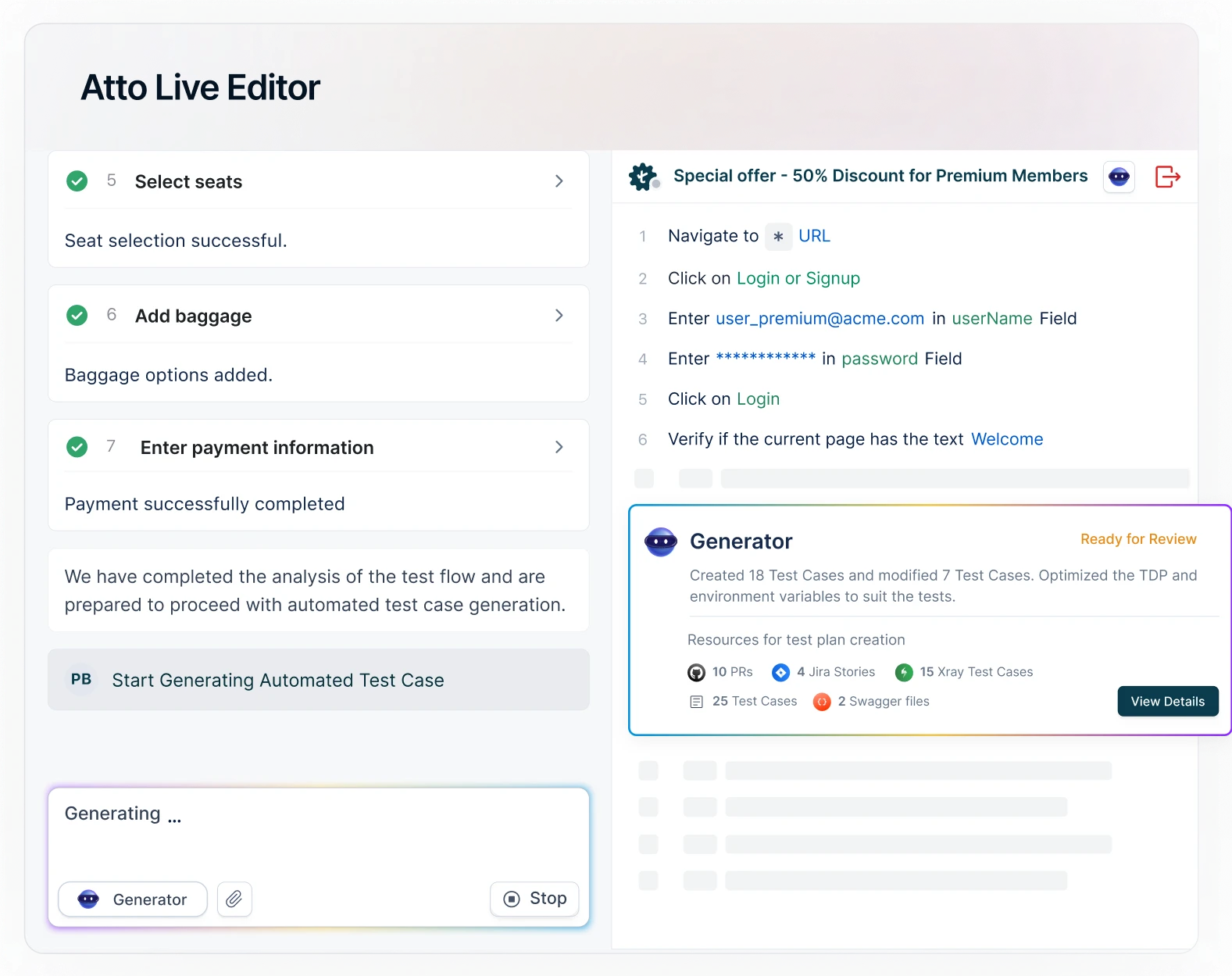
Key Highlights:
- AI agents – Copilot and Atto for AI-powered test automation
- No-code test creation using NLP (Natural Language Processing)
- Unified support for web, mobile, API, and desktop application testing
- Auto-healing of tests to reduce 90% maintenance efforts
- Real-time test execution on cloud or local devices
- Built-in integrations with Jira, Jenkins, Slack, and CI/CD tools
Best For:
Testsigma combines the flexibility of AI-driven automation with enterprise-grade scalability. It’s ideal for teams seeking faster test cycles without compromising reliability or security.
2. Micro Focus UFT One
Micro Focus UFT One is a long-established enterprise testing tool that supports functional and regression testing across a wide range of enterprise applications.
Key Highlights:
- Advanced AI-based object recognition
- Broad technology coverage (SAP, Oracle, Salesforce, etc.)
- Data-driven, keyword-driven, and hybrid testing support
- Strong integration with ALM and CI/CD systems
- Parallel test execution for faster cycle times
Best For:
Large enterprises with legacy applications and strict compliance needs that require deep technology support and test coverage.
3. Ranorex Studio
Ranorex Studio is a GUI-focused test automation platform suitable for large desktop and enterprise apps.
Key Highlights:
- Drag-and-drop test creation with codeless automation
- Support for desktop, web, and mobile applications
- Reusable test modules and data-driven testing
- In-depth object recognition with RanoreXPath
- Built-in reporting and CI/CD integration
Best For:
It’s especially effective in enterprises with heavy desktop app usage and strict GUI validation requirements.
4. QA Wolf
QA Wolf is a cloud-native test automation platform offering a fully managed testing service for web applications.
Key Highlights:
- Real-time test execution in the cloud
- Built-in alerting and bug reporting
- Minimal setup, zero maintenance required
- 100% test coverage guarantee for supported apps
Best For:
Startups and mid-size enterprises looking for hands-off automation with enterprise-level support and fast turnaround.
5. Testmonitor
TestMonitor is a dedicated enterprise-grade test management tool that combines manual testing with structured workflows and team collaboration.
Key Highlights:
- Requirements traceability and risk-based testing
- Comprehensive issue tracking and test planning
- Custom workflows and access control
- Detailed analytics and reporting for stakeholders
- Integration with Azure DevOps, Jira, Slack, and more
Best For:
Organizations that require structured manual testing with full traceability and collaborative features across large QA teams.
Role of Test Automation in Enterprise Application Testing
Test automation plays a critical role in ensuring software quality, accelerating release cycles, and maintaining system stability at scale. Manual testing alone cannot keep up with the speed and complexity of modern enterprise applications, especially when dealing with continuous updates, integrations, and compliance requirements.
Test automation enables QA teams to run repetitive, high-volume tests quickly and accurately, freeing up time for exploratory and strategic testing. It ensures that business-critical workflows remain unaffected during deployments and allows enterprises to scale testing across web, mobile, API, and desktop platforms.
Enterprises need testing solutions that scale with complex systems while reducing time-to-release. Testsigma delivers this with AI-powered automation, including self-healing tests, intelligent test prioritization, and natural language authoring, which reduces maintenance overhead and accelerates QA cycles.
By seamlessly integrating into enterprise CI/CD pipelines, Testsigma empowers QA leaders to achieve continuous, reliable, and faster releases, making it a strategic enabler for digital transformation.
Boost test coverage across complex enterprise systems- Try Testsigma!
FAQs
Enterprise application testing is the process of validating the performance, reliability, security, and scalability of software systems that support core business operations in large organizations.
Testing enterprise applications provides various benefits, including improved software quality, minimized risks, and increased efficiency. It ensures that applications fulfill business requirements, maintain reliability and security, and integrate smoothly. Additionally, testing contributes to cost reductions, quicker delivery times, and a better user experience.
To address the testing challenges faced in B2B enterprise applications, it is essential to adopt a risk-based testing approach, prioritize key functionalities, utilize automation, and foster robust collaboration among development, testing, and business teams. Additionally, implementing continuous testing practices and integrating feedback from previous releases will enhance the testing process over time.
Testing an enterprise application involves understanding the application’s requirements, creating a robust test plan, automating tests whenever possible, managing test data effectively, and employing defect tracking systems.



