With over 3 billion active devices worldwide, Android dominates the mobile market. But this diversity comes at a cost; endless device models, screen sizes, and OS versions challenge app testing. Android testing ensures your app works flawlessly across this ecosystem, delivering seamless performance, security, and user experience.
Table Of Contents
- 1 Introduction to Android Testing
- 2 Overview
- 3 What is Android?
- 4 How Does Android Work?
- 5 What is Android Testing?
- 6 Why Android Apps Need Thorough Testing
- 7 Types of Android Testing
- 8 Popular Android Testing Tools and Frameworks
- 9 Strategies and Best Practices for Android Testing
- 10 Challenges of Android Testing and How to Overcome Them
- 11 How to Perform Android Testing (Step-by-Step Guide)
- 12 Why Choose Testsigma for Android Testing?
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Android Testing
Android testing validates an app’s performance across different devices, operating system versions, and real-world conditions. It helps ensure apps are fast, secure, and user-friendly, regardless of device or environment. Effective testing prevents crashes and bugs, improves app store ratings, strengthens user trust, and speeds up time to market.
Overview
What is Android Testing?
Android testing is the process of verifying that an Android app functions as intended across different devices, OS versions, and network conditions. It ensures that features work correctly, performance is smooth, and the app delivers a consistent user experience.
Why is Android Testing Important?
With Android powering billions of devices worldwide, your app must handle vast fragmentation in screen sizes, resolutions, hardware, and operating system versions. Testing helps identify bugs, UI glitches, and compatibility issues before they reach end users.
Common Types of Android Testing
- Functional Testing: Validates whether app features work as expected.
- UI/UX Testing: Ensures smooth navigation, responsive layouts, and consistent design.
- Performance Testing: Checks app speed, responsiveness, and stability underload.
- Compatibility Testing: Verifies app behavior across devices, OS versions, and configurations.
- Security Testing: Protects against vulnerabilities and data leaks.
What is Android?
Android is a powerful, open-source mobile operating system created by Google. First launched in 2008, it rapidly grew to dominate the global market due to its flexibility, scalability, and broad adoption by device manufacturers(OEMs). Today, Android goes far beyond smartphones; it powers tablets, smart TVs, wearables, automotive systems, and even IoT devices, making it the world’s most widely used operating system.
Also Read: Mobile Testing
How Does Android Work?
Android operates on a layered architecture that enables seamless interaction between hardware, system services, and applications:
- Linux Kernel – Handles low-level tasks like memory, process, and hardware management.
- Libraries & Android Runtime (ART) – Provide core APIs and manage how apps are executed.
- Application Framework – Offers developers access to system features such as UI, resource management, and notifications.
- Applications – The end-user apps that run on top of the framework.
A key challenge with Android is device and OS fragmentation. With hundreds of manufacturers, countless device models, and frequent OS version updates, ensuring consistent app performance requires thorough and continuous testing.
What is Android Testing?
Android testing verifies that a mobile application works as intended across different devices, screen sizes, and Android OS versions. It ensures the app is functional, reliable, secure, and delivers a smooth user experience under real-world conditions.
Why Android Apps Need Thorough Testing
Android powers billions of devices worldwide, but its openness also introduces complexity. With multiple manufacturers, custom ROMs, and frequent OS updates, no two Android devices are exactly alike. This fragmentation makes thorough Android testing essential.
Key reasons why Android app testing is critical include:
- Device Diversity – Android apps must work seamlessly across thousands of devices with different screen sizes, resolutions, chipsets, and hardware capabilities.
- OS Version Updates – Multiple Android versions remain active simultaneously, requiring backward compatibility and regular regression testing.
- Performance & Stability – Users expect apps to load quickly, consume minimal resources, and run without crashes, even under poor network or low-battery conditions.
- Security & Privacy – Open-source flexibility also means higher risk. Rigorous testing ensures data protection, secure authentication, and compliance with privacy standards.
- User Experience & Retention – A poorly tested app often leads to negative reviews, uninstallations, and lost revenue. Apps that are stable and user-friendly consistently achieve higher ratings and customer loyalty.
In short, comprehensive Android testing is not optional; it’s a competitive necessity for ensuring quality, protecting users, and succeeding in the crowded Google Play Store.
Types of Android Testing
Unit Testing
Unit testing focuses on validating individual components or modules of an Android app, such as functions, classes, or methods. It ensures that each code unit performs as expected, often using frameworks like JUnit or Mockito.
Integration Testing
Integration testing checks how different app modules or services work together. It validates data flow, API calls, and module interactions, helping detect issues when combining independently tested units.
End-to-end Testing
End-to-end (E2E) testing simulates real-world user journeys from login to checkout or profile updates, ensuring the app behaves correctly from start to finish across devices and environments.
UI Testing
UI testing verifies that an app’s user interface elements, such as buttons, menus, forms, and layouts, function correctly and look consistent across different screen sizes and resolutions. Tools like Espresso and UI Automator are widely used.
Performance Testing
Performance testing measures an app’s performance under stress, evaluating speed, responsiveness, memory usage, battery consumption, and scalability under different network conditions or heavy loads.
Security Testing
Security testing ensures an Android app is protected against data leaks, insecure authentication, or unauthorized access. It safeguards sensitive user data and helps meet compliance standards.
Usability Testing
Usability testing evaluates how intuitive and user-friendly the app is. Collecting feedback from real users ensures the design, navigation, and workflows provide a smooth user experience.
Regression Testing
Regression testing confirms that new features, updates, or bug fixes do not break existing functionality. It is critical in continuous delivery pipelines to maintain stability with every release.
Popular Android Testing Tools and Frameworks
Here are some of the most popular Android testing tools and frameworks to help deliver high-quality Android apps.
- Testsigma – An Agentic, codeless test automation platform that supports Android, iOS, web, and API testing on a scalable real-device cloud.
- Espresso – A native Android test framework by Google that offers fast, reliable UI testing with easy integration into Android Studio.
- Appium – An open-source, cross-platform tool that allows automation of Android and iOS apps using WebDriver APIs.
- Robotium – Known as “Selenium for Android,” it’s excellent for black-box UI testing of native and hybrid Android applications.
- UI Automator – A Google framework that enables UI testing across multiple apps and system interactions on Android devices.
- JUnit – A widely used Java-based unit testing framework, often the foundation for Android’s unit and integration testing.
- Selendroid – A test automation framework for Android apps, handy for older Android and hybrid apps.
Strategies and Best Practices for Android Testing
To deliver high-quality Android apps, QA teams must adopt a brilliant mix of automation, real-device validation, and continuous improvement. Some proven best practices include:
- Adopt Shift-Left Testing – Start testing early in the SDLC to catch defects before they become costly.
- Automate Repetitive Tests – Use tools like Testsigma for regression and functional testing to save time.
- Test on Real Devices – Online Android Emulators are helpful, but real devices reveal hardware, battery, and network issues.
- Leverage Cloud Device Farms – Use platforms that help scale testing across thousands of device-OS combinations.
- Integrate Testing with CI/CD – Continuous testing ensures faster releases and reduces deployment risks.
- Prioritize Security Testing – Protect sensitive user data with robust authentication and encryption checks.
- Focus on User Experience (UX) – Validate usability, accessibility, and navigation to ensure intuitive and user-friendly apps.
- Monitor Post-Release Performance – Use analytics and crash reports to improve future updates continuously.
Read more about automated mobile app testing
Also Read: automated mobile app testing
Challenges of Android Testing and How to Overcome Them
- Device fragmentation – Use cloud-based device farms to test across thousands of devices and OS combinations without maintaining physical labs.
- OS version updates – Maintain backward compatibility test suites and run regression tests after every new Android release.
- Performance variability – Validate app behavior under different conditions, such as low battery, weak networks, and heavy load.
- Security risks – Run penetration tests, vulnerability scans, and encryption checks to safeguard sensitive data.
- Test maintenance overhead – Reduce flaky scripts with AI-powered automation tools that offer self-healing capabilities.
How to Perform Android Testing (step-by-step Guide)
Requirement Gathering
Define the app’s objectives, features, and expected user behavior. Precise requirements help QA teams choose the right testing strategy and tools.
Environment Setup
Configure the test environment with real devices, emulators, Linux Android emulators, or cloud device farms. Set up necessary SDKs, APIs, and automation frameworks to replicate real-world conditions.
Writing & Executing Tests
Create test cases covering functionality, UI, performance, and security. Use frameworks to automate repetitive scenarios and execute them across devices.
Analyzing Results & Reporting Bugs
Collect test results, identify defects, and log them with detailed reports. Use analytics and dashboards to track trends, improve quality, and ensure faster bug resolution.
Why Choose Testsigma for Android Testing?
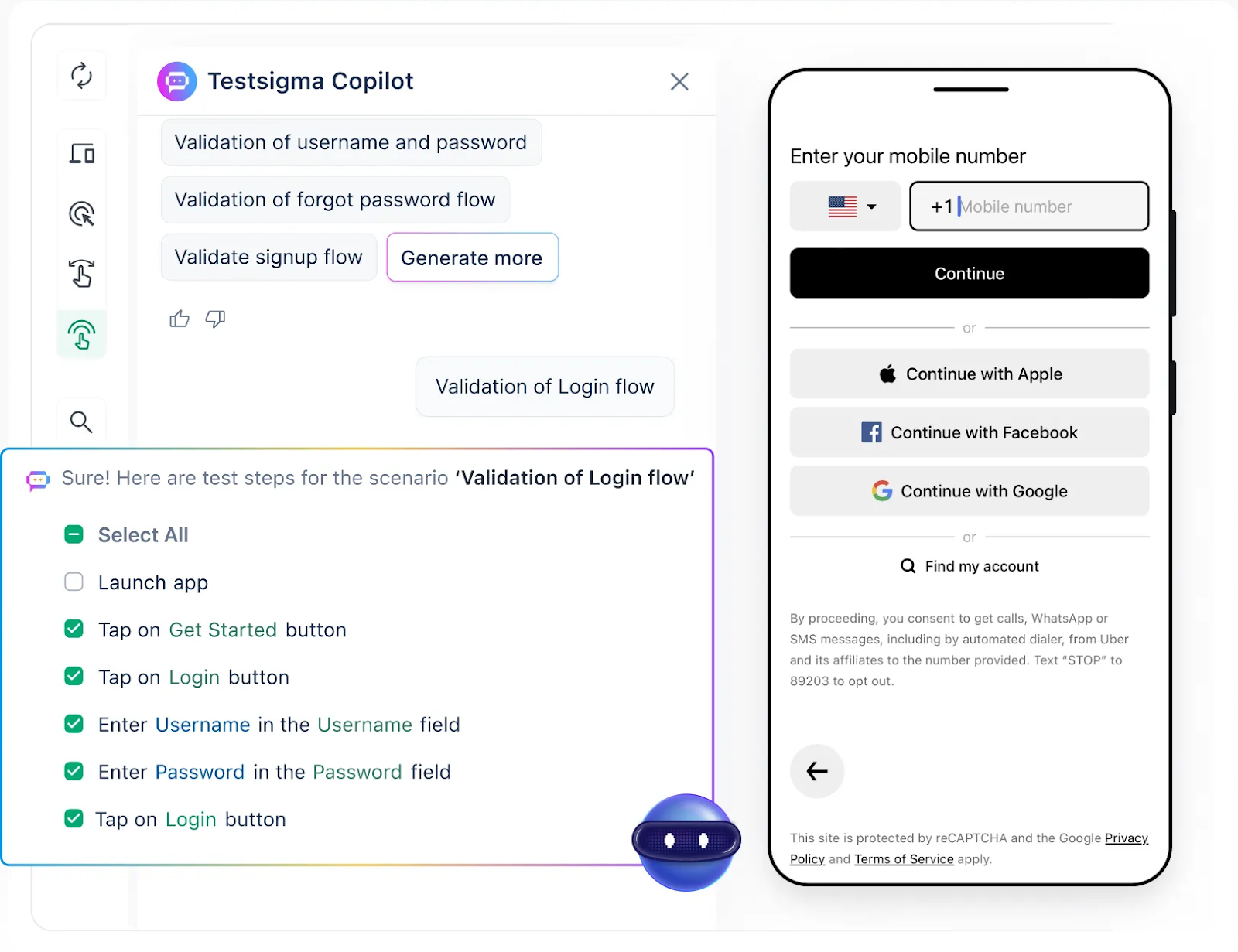
Manual testing or fragmented tools can slow down Android app releases. Testsigma simplifies and accelerates Android app automation with an AI-driven, codeless automation platform designed for scale. Whether you’re building consumer apps, enterprise solutions, or mobile-first products, Testsigma ensures faster delivery with fewer bugs.
Key Benefits of Using Testsigma for Android Testing:
- Codeless Test Automation – Write tests in plain English using NLP, making automation accessible to testers and non-technical team members.
- Real-Device Cloud – Test across thousands of Android devices, OS versions, and screen sizes without maintaining an in-house lab.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing – Reduce flaky tests with self-healing capabilities that automatically adapt to app UI changes.
- Cross-Platform Support – Test Android, iOS, web, and APIs in a unified platform.
- CI/CD Integration – Seamlessly integrate with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab, and other DevOps tools for continuous testing.
- Comprehensive Reporting – Get detailed test insights, logs, and defect reports to speed up debugging and release readiness.
With Testsigma, QA teams can move faster, reduce testing costs, and deliver bug-free Android apps at scale.
Frequently Asked Questions
Android app testing verifies an application’s functionality, performance, usability, and security on different Android devices and OS versions. It ensures the app works consistently across smartphones, tablets, and other Android-powered devices.
You can test your mobile app using a mix of manual and automated testing. Manual testing helps validate usability and real-world scenarios, while automated tools like Testsigma streamline regression, UI, and performance testing across multiple devices.
Internal testing allows you to distribute your app to a limited group, such as your QA team, before a public release. Using the Google Play Console’s internal testing track, you can share your APK or app bundle with testers, collect feedback, and fix issues early.
To test an Android APK, install it on real devices or use emulators to validate functionality, UI, and performance. For scalable testing, use cloud-based platforms like Testsigma’s real-device cloud, which lets you run the same APK on hundreds of device-OS combinations.


