Prompt Templates for Pro-level test cases
Get prompt-engineered templates that turn requirements into structured test cases, edge cases, and negatives fast every time.
Did you know that, according to a recent report, 35% of digital enterprises consider manual testing the most time-consuming activity within a test cycle? In this guide, we’ll explore what QA automation is, how it works, when to use it, and the top tools and best practices that make it successful.
Table Of Contents
Overview
What is QA Automation?
QA automation is the process of using tools and scripts to automatically execute test cases, compare results, and report defects without manual effort. It enables faster, consistent, and repeatable software validation throughout the development lifecycle.
When to Use QA Automation in Testing
- Regression testing to ensure new changes don’t affect existing functionality.
- Performance and load testing to simulate heavy user traffic.
- Cross-browser and cross-device validation for broader user coverage.
- Data-driven testing when the same tests run with multiple datasets.
- Continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines for every code commit.
- Repetitive or high-risk scenarios to reduce human error and manual effort.
Benefits of Automated QA
- Enables faster release cycles with quick and repeatable test execution.
- Expands test coverage across browsers, devices, and environments.
- Improves accuracy and reliability by reducing manual intervention.
- Saves time and cost over multiple releases.
- Supports agile and DevOps workflows with continuous testing.
- Provides detailed reports and traceability for better defect tracking.
What is QA Automation?
QA automation is the process of using software tools to automatically execute test cases, compare actual outcomes with expected results, and report issues without manual intervention. It’s a way to speed up repetitive or time-consuming testing tasks, such as regression, performance, or cross-browser testing, while ensuring consistency and reliability.
Unlike manual testing, where QA testers execute each test by hand, automated QA testing relies on scripts or no-code platforms to simulate user actions, validate functionality, and detect defects early in the development cycle. This enables continuous testing in agile and DevOps workflows, reducing human error and increasing test coverage.
When to Use QA Automation in Testing
1. Regression Testing
When frequent code changes occur, automating regression tests ensures that new updates don’t break existing features. It saves time and gives teams quick feedback about product stability after every build.
2. Performance and Load Testing
Automation is essential when you need to simulate thousands of concurrent users. Automated load tests help identify system bottlenecks and ensure your application performs well under stress.
3. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Testing
Automated QA testing allows you to validate your web or mobile app across multiple browsers, operating systems, and devices quickly , something that would take days if done manually.
4. Data-Driven Testing
When the same test needs to be executed with different datasets, automation helps in managing and validating multiple inputs efficiently, improving coverage and reducing manual data handling.
5. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
In agile pipelines, automation ensures that tests are triggered automatically after every code commit. This keeps the product stable while maintaining the pace of rapid releases.
6. High-Risk or Repetitive Test Scenarios
Scenarios that involve repetitive actions or are prone to human error, such as form submissions or login flows, are ideal candidates for automation.
Also Read: AI in software testing?
How Does QA Automation Work?
1. Test Planning and Tool Selection
The QA automation engineer defines test objectives and scope, and identifies which test cases to automate. The right automation tool (like Testsigma or Selenium) is chosen based on application type, tech stack, and budget.
2. Test Case Design and Script Creation
In this phase, test cases are written either through scripting (like in Selenium) or using a no-code approach (like in Testsigma). Each test defines expected inputs, actions, and results.
3. Test Environment Setup
A stable test environment, with the right browsers, devices, and network configurations, is prepared to ensure accurate results. This often includes integration with CI/CD tools.
4. Test Execution
Automated tests are executed on local machines, virtual environments, or cloud-based platforms. The execution can be triggered manually or automatically as part of a CI/CD pipeline.
5. Reporting and Analysis
After execution, test results are automatically recorded and analyzed. Defects are logged, reports are generated, and insights help QA teams make quick go/no-go decisions.
6. Maintenance and Updates
As the application evolves, automation scripts are updated to reflect new changes in UI or functionality to keep the test suite reliable and relevant.
Manual Testing Vs Automated Quality Assurance Testing
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automated Quality Assurance Testing |
| Execution Speed | Slow and time-consuming | Fast and repeatable |
| Accuracy | Prone to human error | Highly consistent and reliable |
| Test Coverage | Limited by tester time and effort | Broad, covering multiple environments |
| Reusability | Test cases need to be re-executed manually | Scripts can be reused across builds |
| Cost Over Time | Lower initial cost but higher long-term cost | Higher initial setup cost but saves long-term |
| Ideal For | Exploratory and usability testing | Regression, performance, and functional testing |
| Scalability | Hard to scale for large apps | Easily scalable with cloud or CI/CD setups |
Benefits of Automated QA
1. Faster Release Cycles
Automated QA testing helps teams run thousands of test cases within minutes. This speeds up release cycles, enabling faster feedback and continuous delivery.
2. Better Test Coverage
Automation allows tests to run across multiple platforms, browsers, and configurations, increasing overall coverage and reducing missed bugs.
3. Improved Accuracy and Reliability
Once created, automated tests execute consistently, reducing the chances of human oversight and ensuring that every run produces comparable results.
4. Cost-Effective in the Long Run
Although the initial setup takes effort, automation saves significant time and cost over multiple releases by reducing manual labor and repetitive work.
5. Supports Agile and DevOps Pipelines
Automated quality assurance integrates seamlessly with CI/CD tools, ensuring that every build is tested automatically before deployment.
6. Enhanced Reporting and Traceability
Modern QA automation tools generate detailed logs, screenshots, and defect reports, helping teams quickly identify root causes and track fixes efficiently.
Top 5 QA Automation Tools
1. Testsigma
Testsigma is a cloud-based, agentic AI-powered test automation platform designed for agile teams to automate web, mobile, desktop, API, SAP, and Salesforce testing, all in simple English, without coding. It enables QA teams to accelerate releases with minimal maintenance and integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines.
Features
1. No-Code Test Creation
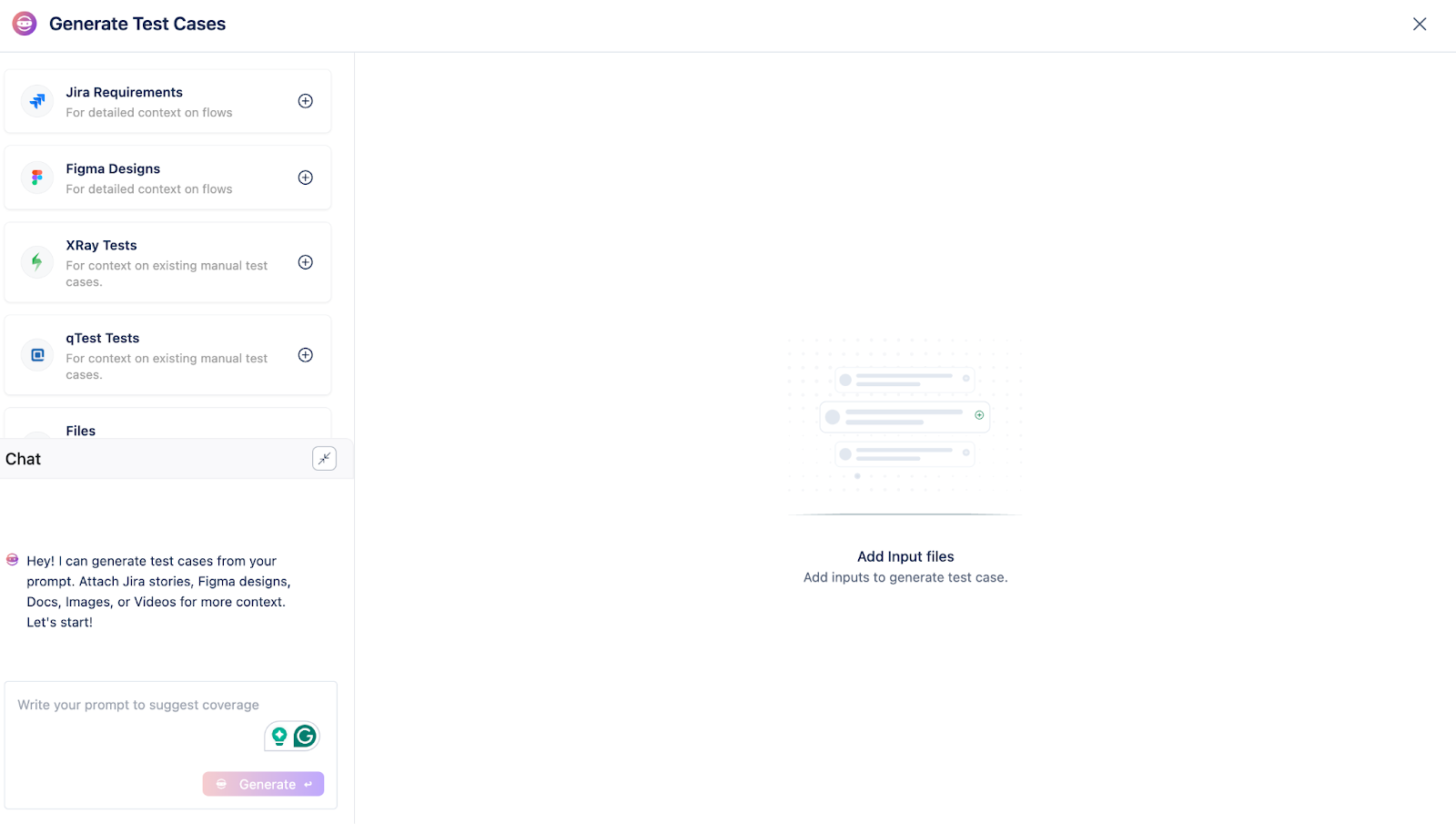
Testsigma lets users create automated test cases in plain English using NLP (Natural Language Processing). This means that anyone, even those without programming knowledge, can design and maintain tests efficiently. In addition, testers can use the Generator agent to automatically generate test cases directly from prompts, Jira, Figma designs, PDFs, docs, images, screenshots, and videos.
2. Cross-Platform Testing
It supports testing across web, mobile (Android and iOS), desktop, APIs, and ERPs like Salesforce and SAP from a single unified platform. This helps teams manage all types of automation under one workflow.
3. Cloud-Based Test Execution
Testsigma provides access to 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations in the cloud. QA teams can test across multiple environments without setting up local infrastructure.
4. Parallel and Cross-Browser Execution
You can run hundreds of tests simultaneously across browsers like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Safari. This parallel execution dramatically reduces total test time.
5. Data-Driven Testing
Testsigma allows dynamic test execution using external data sources such as Excel, CSV, or databases. It helps simulate real-world scenarios with multiple data inputs.
6. AI-Powered Test Maintenance
Its AI engine detects UI or object changes automatically and suggests quick updates to broken test steps, minimizing test flakiness and reducing maintenance effort. The Healer agent works exclusively for self-healing and autonomously maintains your test scripts.
7. Continuous Integration (CI/CD) Support
Testsigma integrates with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, Azure DevOps, and GitLab to support continuous testing within pipelines.
8. Reusable Custom Functions
Teams can build reusable logic blocks or custom functions, which can be reused across multiple test cases to improve efficiency and maintain consistency.
9. Test Reporting and Analytics
Comprehensive dashboards provide visual insights into test runs, pass/fail rates, defect density, and performance trends. This supports faster debugging and decision-making.
10. Integrations with Dev Tools
It integrates seamlessly with tools like Jira, Slack, TestRail, and Trello, allowing instant defect reporting and collaboration between QA and dev teams.
11. REST API Testing
Users can automate REST API validation, assertions, and data verification with easy-to-create test cases, no coding required.
12. Version Control and Collaboration
Testsigma allows multiple testers to collaborate on the same project while tracking version history, changes, and ownership in real-time.
13. On-Premise Deployment Option
For teams with data compliance needs, Testsigma offers an on-premise setup for complete control over data and environment configurations.
2. Selenium
Selenium is an open-source web automation framework that allows developers and QA engineers to automate browser actions using programming languages like Java, Python, C#, and Ruby. It’s best known for flexibility and community support.
Features
1. Selenium WebDriver
This is the core component that directly interacts with browsers to automate actions such as clicks, navigation, or data entry. It’s the foundation for cross-browser automation.
2. Cross-Browser Compatibility
Selenium supports Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Opera. QA engineers can ensure consistent web behavior across all browsers.
3. Multi-Language Support
Developers can write test scripts in multiple programming languages, allowing flexibility depending on the team’s skill set.
4. Selenium Grid
This feature enables parallel execution across different browser/OS combinations. It’s ideal for running large test suites faster.
5. Selenium IDE
A Chrome and Firefox plugin that allows record-and-playback testing, perfect for beginners or quick script generation.
6. Integration with CI/CD Tools
Selenium integrates seamlessly with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and Bamboo for automated test runs in pipelines.
7. Extensive Framework Support
It can be combined with frameworks like TestNG, JUnit, and NUnit for better reporting, test organization, and assertions.
8. Community and Ecosystem
Selenium’s massive community ensures regular updates, plugins, and troubleshooting support across different use cases.
9. Open-Source Flexibility
Completely free to use and customizable, Selenium allows teams to tailor automation frameworks to their requirements.
3. Appium
Appium is an open-source mobile automation framework for testing native, hybrid, and mobile web apps on Android and iOS platforms. It uses the WebDriver protocol, making it compatible with Selenium-based frameworks.
Features
1. Cross-Platform Testing
Appium allows a single test script to be reused across Android and iOS apps, saving time and reducing redundancy.
2. Multi-Language Support
Supports multiple languages like Java, Python, Ruby, PHP, and JavaScript, allowing flexibility for development teams.
3. Real Device and Emulator Testing
Tests can be executed on real mobile devices, simulators, or emulators, ideal for debugging and performance validation.
4. No App Recompilation Needed
Appium doesn’t require modifying or recompiling the app under test, ensuring compatibility with production builds.
5. Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
Appium integrates with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, Bamboo, and TeamCity for automated mobile testing in continuous delivery workflows.
6. Parallel Execution and Cloud Support
It supports parallel execution on cloud device farms like BrowserStack and Sauce Labs, improving scalability.
7. Gesture and Sensor Simulation
Appium can simulate touch gestures, location data, and device orientation to validate complex user interactions.
8. Extensive Community and Plugin Ecosystem
Being open-source, Appium has a strong community offering libraries, plugins, and integrations for extended functionality.
9. Automation for Native, Hybrid, and Web Apps
It supports apps built with native SDKs, web views, and hybrid frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Cordova.
4. Cypress
Cypress is a JavaScript-based end-to-end testing framework built for modern web applications. Unlike Selenium, it runs directly inside the browser, providing faster and more reliable test execution.
Features
1. Real-Time Reloading
Cypress automatically reloads and re-executes tests whenever code changes, giving instant feedback to developers.
2. Time Travel Debugging
You can visually see how each command was executed during a test, making debugging faster and more intuitive.
3. Automatic Waiting
Cypress automatically waits for DOM elements, animations, and network calls to resolve before moving to the next step, reducing flaky test failures.
4. Fast In-Browser Execution
It runs directly within the browser, providing near-instant results without the need for remote WebDriver connections.
5. Interactive Dashboard
The dashboard service records test results, screenshots, and videos, helping teams monitor executions in real time.
6. Built-in Assertions
Cypress includes a complete set of assertions to validate DOM elements, API responses, and application states.
7. Network Traffic Control
You can stub, mock, or intercept network requests, which makes testing APIs and front-end behavior easier.
8. Parallel and CI Integration
Cypress integrates with Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions, supporting parallel test execution for faster CI runs.
9. Screenshots and Video Recording
It automatically captures screenshots on failure and records videos of test runs for better reporting.
10. Rich Documentation and Plugin Library
Cypress offers excellent documentation and plugins that extend functionality, such as visual testing or accessibility validation.
5. SoapUI
SoapUI is a leading API testing tool for validating SOAP, REST, and GraphQL web services. It helps teams automate functional, performance, and security testing of APIs with minimal scripting.
Features
1. SOAP and REST API Testing
SoapUI supports comprehensive testing for both SOAP and REST protocols, allowing QA engineers to automate end-to-end API validation.
2. Functional and Regression Testing
You can automate repetitive API tests to ensure consistent behavior across builds, supporting both single and batch executions.
3. Data-Driven Testing
It allows using external data sources (Excel, XML, databases) for dynamic test execution with varying inputs and outputs.
4. Security and Penetration Testing
SoapUI includes built-in tools for testing vulnerabilities such as SQL injection and XML bombs, ensuring API robustness.
5. Load and Performance Testing
QA teams can simulate concurrent users to test API scalability and performance under load.
6. Test Assertions
Built-in assertions validate response status, time, schema, and content to ensure data integrity and correctness.
7. Comprehensive Reporting
SoapUI generates detailed execution reports, logs, and charts for tracking performance and debugging.
8. CI/CD Integration
It integrates with Jenkins, Azure DevOps, and Bamboo to enable automated API testing during deployment cycles.
9. Extensibility via Groovy Scripting
For complex scenarios, Groovy scripting can be used to customize workflows, validations, and automation logic.
10. GraphQL Testing Support
SoapUI supports GraphQL endpoints, allowing schema validation and query/mutation testing.
11. Open Source and Pro Versions
While the open-source version offers core functionality, the Pro version (ReadyAPI) adds advanced reporting, environment management, and data-driven testing capabilities.
QA Automation Best Practices
- Choose the right automation tool that aligns with your application type and team skills.
- Start with high-value test cases like regression or smoke tests before expanding coverage.
- Maintain modular, reusable test scripts to simplify updates.
- Regularly review and refactor automation scripts to keep them efficient and relevant.
- Integrate your automated QA tests into CI/CD pipelines for continuous feedback and faster releases.
How Can Testsigma Help with QA Automation?
Testsigma is a codeless test automation platform with agentic AI capabilities. So, what does that mean for agile QA teams? Simply put, with Testsigma, teams can create tests in simple English and use AI agents to autonomously handle various testing activities such as test case generation, execution, and maintenance.
But Testsigma doesn’t just automate your tests; it goes a step further. Its AI agents analyze the root cause of test failures, identify edge case scenarios, and continuously improve the efficiency of your testing process while freeing testers from repetitive work. Designed for modern agile teams, Testsigma helps save hours of time, effort, and resources, enabling QA engineers to focus on innovation and quality instead of grunt work.
Meet the AI Agents in Testsigma:
- The Generator
This agent can take prompts, Jira, user stories, Figma design files, images, screenshots, or even videos and turn them into automated test cases without any scripting. It helps teams skip the manual test creation process and quickly achieve wider test coverage.
- The Optimizer
The Optimizer Agent increases test coverage by identifying edge case scenarios that might be missed in regular testing. It also helps clean up redundant or low-value tests, ensuring your suite remains effective and focused on real risks.
- The Analyzer
When a test fails, the Analyzer Agent digs into the details to uncover the root cause. It highlights recurring failure patterns and helps you understand why something broke, enabling faster debugging.
- The Healer
As your application evolves, this agent automatically updates test scripts, locators, and flows to match new changes. It ensures your automation remains accurate and reduces the time spent on manual maintenance.
- The Runner
The Runner Agent is responsible for executing test suites across environments, devices, or browsers according to the plan. It manages scheduling, parallel execution, and environment selection so tests run reliably and at scale.
Benefits of Using Testsigma for QA Automation
Faster Test Creation
With Testsigma, you can create automated tests 10x faster using simple English. Whether you use the NLP editor, the Generator Agent, or the built-in Recorder, Testsigma eliminates scripting hassles and lets teams move from idea to execution in minutes.
Autonomous Testing
Testsigma’s agentic AI takes automation to the next level. Different agents handle everything, from test generation, execution, and analysis to optimizing coverage, maintaining scripts, and reporting bugs. Your testing practically runs on autopilot.
No Tool Switching
Run all your tests across web, mobile, desktop, API, Salesforce, and SAP on a single unified platform. You no longer need to juggle multiple tools for different testing needs.
No Physical Device Lab Needed
Access 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations directly from the cloud. Teams can test anytime, anywhere, without setting up or maintaining an in-house device lab.
No Need to Change Your Current Tech Stack
With 30+ native integrations, Testsigma fits seamlessly into your existing workflows. It connects effortlessly with your CI/CD, issue tracking, and communication tools, keeping everything in sync.
Power of Legacy Tools, Built for Modern Teams
Testsigma brings the reliability and depth of traditional testing tools but with the simplicity and flexibility today’s agile teams need. It’s everything QA teams expect from enterprise-grade automation, without the complexity.
Conclusion
QA automation helps teams test faster, reduce errors, and maintain product quality across frequent releases. It removes repetitive manual effort and brings more consistency to every build. With tools like Testsigma, teams can automate end-to-end testing across web, mobile, API, and desktop applications in one place. As testing becomes more intelligent with AI and automation, QA engineers can focus on delivering better user experiences instead of repetitive checks.
FAQ
You can automate tests that are repetitive, predictable, and time-consuming. Common examples include regression tests, smoke tests, data-driven tests, API tests, and performance tests. UI and functional tests can also be automated if the workflows are stable and well-defined.
Automated QA testing works well for web, mobile, desktop, and API-based applications. It’s especially effective for large or frequently updated apps that require regular regression checks, multi-platform testing, or complex user flows.
A QA Automation Engineer designs, builds, and maintains automated test scripts to validate software quality. They choose the right tools, create reusable test frameworks, integrate automation into CI/CD pipelines, and analyze test results to identify defects early in the development cycle.


